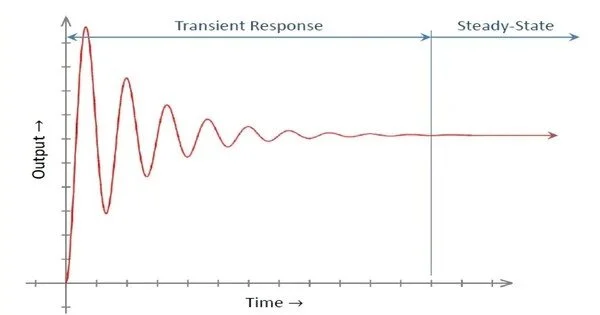
A transient response is the response of a system to a change from an equilibrium or steady state in electrical and mechanical engineering. It refers to the temporary and often oscillatory behavior that occurs before the system reaches a new steady state. The transient response is not always associated with abrupt events, but rather with any event that disrupts the system’s equilibrium. The impulse response and step response are transient responses to a specific input (an impulse and a step, respectively).
In electrical engineering, the transient response is the circuit’s temporary response that will fade over time. It is followed by the steady state response, which is the behavior of the circuit after an external excitation has been applied for a long time.
- Electrical Engineering:
Transient response is frequently associated with electrical circuits and systems in electrical engineering. When there is a sudden change in a system’s input, such as a step change in voltage or current, the system’s components and energy storage elements (such as capacitors and inductors) respond to this change. The transient response describes the system’s behavior during the time it takes to reach a new equilibrium.
- Mechanical Engineering
Transient response is used in mechanical engineering to describe mechanical systems that contain springs, dampers, and masses. For example, when a force is suddenly applied to a mechanical system or when the system’s initial conditions change abruptly, the resulting motion and deformations exhibit a transient response.
Characteristics of Transient Response
- Oscillations: Before the system settles down, transient response frequently includes oscillations. These oscillations can be damped (decreased gradually) or undamped (continued).
- Settling Time: The settling time is the amount of time it takes for the system to stabilize. Engineers are frequently concerned with how quickly a system can recover from a disturbance.
- Rise Time: Rise time in electrical systems is the time it takes for a signal to transition from a specified low value to a specified high value. It quantifies how quickly the system reacts to a step input.
- Damping Ratio: The damping ratio is a parameter that describes the amount of damping in a system. Overdamped systems respond slowly, whereas underdamped systems can produce oscillatory responses.