Geofoam is a multi-functional construction material that has all different types of applications. It is expanded polystyrene (EPS) or extruded polystyrene (XPS) manufactured into large lightweight blocks. It is a go-to material for building different structures, foundations and buildings because of its unique physical properties, flexibility and the great value it brings. The blocks vary in size but are often 2 m × 0.75 m × 0.75 m (6.6 ft × 2.5 ft × 2.5 ft).
Geofoam is manufactured to be an ultra-lightweight fill material that is resistant to damage caused by compression. The primary function of geofoam is to provide a lightweight void fill below a highway, bridge approach, embankment or parking lot. From roadways, landscaping and thermal insulation to stadiums and movie theaters, the possibilities are endless when it comes to geofoam. It is also used in much broader applications, including lightweight fill, green roof fill, compressible inclusions, thermal insulation, and drainage. It is flexible to work with and is considerably lighter than other fill alternatives.
Geofoam shares principles with geocombs which has been defined as “any manufactured material created by an extrusion process that results in a final product that consists of numerous open-ended tubes that are glued, bonded, fused or otherwise bundled together.” It is extremely light weight and can withstand harsh conditions. The cross-sectional geometry of an individual tube typically has a simple geometric shape (circle, ellipse, hexagon, octagon, etc.) and is on the order of 25 mm (0.98 in) across. It has proven to be the material of choice to use in landfills, stabilizing slopes, bridge embankments, etc.
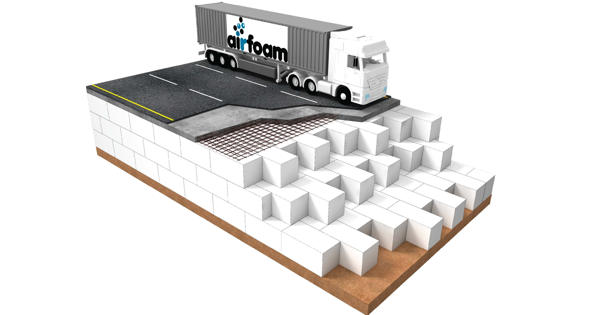
Advantages of using geofoam include:
- Low density/high strength: Geofoam is 1% to 2% the density of soil with equal strength.
- Predictable behavior: Geofoam allows engineers to be much more specific in the design criteria.
- Inert: Geofoam will not break down, so it will not spread into surrounding soils. This means that geofoam will not pollute the surrounding soil.
- Limited labor required for construction: Geofoam can be installed by hand using simple hand tools.
- Decreases construction time: Geofoam is quick to install and can be installed during any type of weather, day or night, resulting in faster installation time.
Disadvantages of using geofoam include:
- Fire hazards: Untreated geofoam is a fire hazard.
- Vulnerable to petroleum solvents: If geofoam comes in contact with a petroleum solvent, it will immediately turn into a glue-type substance, making it unable to support any load.
- Buoyancy: Forces developed because of buoyancy can result in a dangerous uplift force.
- Susceptible to insect damage: Geofoam can be treated to resist insect infestation. When geofoam is used for insulating buildings where wood is present damage to the geofoam can be limited by use of insect treatment.
Information Source: