General Banking of EXIM Bank.
Introduction:
Bangladesh is the less LDC country. The people want to saving their money smoothing transaction for business person and ensure security of the processing wealth of the climate.
So the people try to saving their wealth on the activities of commercial banks. So the Exim bank is to provide the general banking service.
Deposit:
The Exim proved two kinds deposit system.
- Demand Deposit
- Time Deposit
Demand Deposit: This deposit an withdrawn without notice. The Exim bank accepts demand deposit through the opening of-
Current account: Current account is another the account holder can make numerous transaction within a working day. There is no restriction the number and the amount of withdrawn from the current account within the an liability touch. Generally current account is opened for business persons and for easy transaction there are no interest is paid which account.
Saving Account: Saving bank account is mean for the people of the lower middle classes who wish to save part of their incomes. There is restriction on withdrawn is a month. There interest on 8% – 12% based on loss and profit. But the Exim bank personal deposit profit on 12% it is highest profit rate on banking sector in Bangladesh.
2. Time Deposit :
Time deposit are-
¨ FDR – Fixed Deposit Receipt.
¨ STD – Short Time Deposit.
¨ BCD – Bearer Certification Deposit etc.
Also the Exim bank conducted-
¨ Cash transaction
¨ Demand Draft (DD)
¨ Telegraphic Transaction (TT)
¨ Payment Order (PO)
Conversion into Islamic Banking
General Meeting held on December 28, 2003 and obtaining confirmation from the honorable High Court Division of Bangladesh Supreme Court. The Exim Bank had been converted into a full fledged Islami bank based on Shariah from traditional interest based banking. They started functioning as an Islami bank with effect from 1st July 2004 with the approval of Bangladesh Bank. Before conversion they put option to all of their valued customers through news media in addition to personal contact with them to accept the decision taken by there.
General Products and Services of EXIM Bank
The Bank has introduced a number of financial products and services since its banking operation. Among them Mudaraba Monthly Incom Scheme, Mudaraba Monthly Saving Scheme, Mudaraba Multiplus Savings Scheme, Mudaraba Super Savings Scheme, Mudaraba hajj Scheme, have widely been accepted among the people.
Mudaraba Monthly Income Scheme
It is a monthly income scheme that really makes good sense as well as a sure investment of steady return. Under this scheme, customer has to deposit a fixed amount of money for five years and in return he will receive benefits on monthly basis. Benefits starts right from the first month of opening an account under the Scheme and will continue up to five years when the depositor will get refund of his deposit. This scheme is a sure investment for a steady return.
Mudaraba Monthly Saving Scheme
The prime objective of this scheme is to encourage people to build up a habit of saving. In this scheme one can save a fixed amount of money every month and receive substantial lump sum of money after five, eight, ten or twelve years.
Mudraba Multiplus Savings Scheme
Under this scheme, depositor’s money will be almost tripled in 13 (thirteen) year period. Any individual, Company, Educational Institution, Government Organization, NGO, Trust, Society etc. may invest their savings under this scheme.
Mudraba Super Savings Scheme
It helps to build up capital. Super saving Scheme offers a small depositor to invest his/her fund (minimum 1,00,000/-) and the fund will be almost double in 8 (eight) years period. This scheme will secure the future of the investment with ease.
Mudraba Hajj Scheme
In order to smooth arrangement of fund for performing Hajj, the bank has introduced this scheme for 5, 8, 10, 15 & 20 year’s period.
Foreign Exchange
Both multinational enterprise and small import and export companies must understand exchange rates. Also bank and international Bank must understand exchange rates. The exchange rate can influence where a wholesaler or retailer buys and sells products. Foreign exchange also can influence where manufacture acquires ran materials or components and produces products.
Foreign exchange includes currencies and others instruments of payment denominated in currencies, it is important to understand exchange rates and how foreign currencies are Traded before looking at how companies use foreign exchange and protect themselves against potential foreign exchange risk.
Term and definition of foreign exchange
An exchange rate is the number of units of one currency needed to acquire one unit of another currency.
Spot rate:
The spot rate is the rate quoted for current foreign currency transaction that require eight immediate delivery or delivery within two business days.
Inter bank transaction:
Inter bank transaction are exchange between commercial bank that collectively make up the inter bank market. The spot rate also applies to over the counter (OTC) Transaction which usually involve non-bank customers and require some day settlement.
Forward rate:
Forward rate is a contractual rate between a foreign exchange Trader and the traders client for delivery of foreign currency some time in the future after at least two business day but usually after at least one month.
The spot market:
The spread in t he spot market is the difference between lthe bid (buy) and offer (sell) rate quoted buy the foreign exchange trader.
Direct quote:
A direct quote is the number of units of the domestic currency needed to acquires on unit of the foreign currency.
An indirect quotes is the number units of the foreign currency needed to ac quire one unit of the domestic currency.
Forward market:
A discount exist when the forward rate is less than the spot rate. A premium exist when the forward rate exceeds the spot rate.
Foreign Exchange Department
Foreign Exchange department of EXIM Bank Bangladesh is one of the most important departments of all departments. This departments handles three separate sections.
- Import Section
- Export Section
- Foreign Remittance section.
1. Import section
The function of this section is mainly to deal to with various components such as:
- Import finance
Compare with convention banking and Islamic banking import finance supporting-
Conventional banking system are following-
- Letter of Credit (L/C)
- Payment against Document (PAD)
- Payment Against Trust Receipt (MTR)
- Loan against Imported Merchandise (LIM).
Islamic banking system are following-
- Letter of Credit (L/C)
- Cash payment from his own resources
- Bai-Murabaha post Import (MPI)
- Bai-Muajjal Trust receipt (MTR)
I can discuss about Islamic banking system of import finance.
Letter of Credit L/C
A letter of credit (L/C) is an instrument for payment of international trade attentive also its called of letters of guarantee (L/C). On the request of the customer (importer) a bank will issue a L/C in which it obligates itsef to pay the seller (exporter) against presentation of a draft and certain documents. Those documents are evidences of shipment and include all of the terms and conditions stipulated in the L/C.
The transaction flow of a (L/C) opening is shown below:
Transaction flows of L/C
At issuance and Advising stage
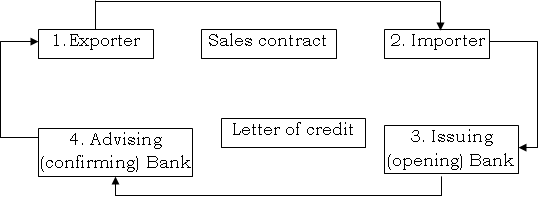
- Exporter and importer sign a sales contract, providing for payment by an L/C.
- Importer requests bank to open an L/C in favor of the exporter.
- Issuing Bank request a second Bank to adviser the credit.
- Advising Bank informs beneficiary that the L/C has been issued. Exporter examines of L/C terms and conditions. If not he must request the importer to initiate an amendment. Which can only be done with the consent of all parties: buyer seller, opening and confirming banks.
At presentation stage.
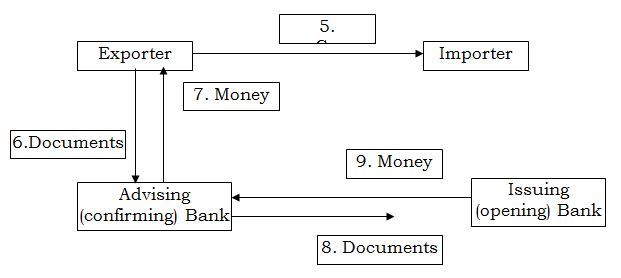
- When satisfied with the term the L/C. Then exporter is ready to ship goods.
- Exporter sends the required documents to advising / Negotiating bank.
- Bank checks documents against the requirements of the L/C. If is order, bank will pay, negotiate or accepts according to the terms of the credit.
- Advising bank will send the documents to the issuing bank.
- The issuing bank checks the document. If they meet requirements. The issuing bank will pay to advising/ Negotiated bank credit.
At repayment stage
Procedures for opening L/C
Application for opening L/C
An importer who is desirous to import goods from foreign country will apply issuing bank for opening a L/C. the importer will provide an application mentioning the following aspects:
- Full particulars of applicant’s bank account.
- Types of business.
- Historical background.
- Amount of required L/C limit.
- Amount of L/C margin.
- Name of imported goods.
- Repayment schedule and source of fund.
Documents required for opening L/C
An importer or L/C opener has to submit the following documents:
- Current deposit A/C holder
- Application form (provided by the bank)
- Valid import registration certificate (IRC)
- Proforma Invoice.
- Four set of IMP form (Import form)
- Insurance cover note.
- VAT registration number.
- Letter of Credit authorization form (LCA form).
- TIN certificate (Tax identification number)
Examination for opening L/C:
The concerned officer considering the facts mentioning below must carefully check application:
- The terms and conditions of L/C applications are consistence with exchange control.
- In addition, import trade regulation Uniform Customs & Practice for Documentary Credit (UPPDC).
- Illegibility of imported goods.
- The L/C must be opened in favor of importer.
- That is signed by the importer land agreed with the terms and conditions
- Indenting registration number.
- Goods are not of Israel and vassals to be used are not of Israel.
- Insurance cover note with date of shipment.
- Whether IRC is up to date or not.
- Whether IMP form is dully filled up and signed.
- The imported goods are marketable.
After investigate all legal aspects entry is given to the margin register and charges, commission and margin is realized.
Transmitting the L/C:
The L/C is transmitted by the opening Bank to the advising bank for inform the L/C to the beneficiary. L/C is generally transmitted through tasted telex, fax or swift. Before transmission, a final examination of the L/C contents is necessary for the issuing bank. It is customary to advice a credit to the beneficiary for receiving L/C.
Add confirmation:
Very often advising bank receive request from the issuing bank to add their confirmation while advising credit to the beneficiary. The advising bank can do it if there is prior arrangement between advising and issuing bank or if it feels that the issuing bank is repute and reliable institution and good enough to discharge this obligation.
Types of L/C:
- Revocable / Irrevocable L/C
- Confirmed / unconfirmed L/C
- Transferable L/C
- Back of Back L/C
- Acceptance L/C
- Revolving L/C
- Red Clause L/C
- Green Clause L/C
The EXIM Bank deals with Irrevocable L/C, which cannot amended or cancelled by the issuing bank at any moment and without prior notice to the beneficiary. It also deals Back to Back L/C, which is the letter of Credit provided by the bank to bank exporter to the importer the raw materials from abroad in order to produce the exportable commodity for the importer.
2. Cash payment from his own resources
The issuing banks starts PAD procedure after getting all documents from the exporter as evidence of exporting goods. Documents required for PAD is mentioned below:
- Original (Non-Negotiable) bill of Leading.
- Commercial Invoice.
- Certificate of Insurance.
- Certificate of Origin.
- Bill of Exchange.
- Packing List.
- Clean Report of Findings (CRF).
Examination of PAD Documents:
Investigate documents is very important for the issuing bank. As after examining all the documents the issuing bank will make payment to the negotiating bank. So anay mistake in the examination process may cut cost issuing bank.
Examining the Bill of Exchange:
- It is drawn and duty signed by the beneficiary.
- It is drawn on the importer indicating him drawee.
- L/C number quoted on it.
- Tenors of the draft are strictly in conformity with the terms stipulated in the L/C.
- Amount is identical.
- Amount in words and in figures is same.
- Examining the commercial invoice.
- It is address to the importer .
- It is dated, signed, and submitted in required number.
- It must bear detailed description of goods that must tally with L/C and Bill of lading.
- Price, quality, quantity etc. is corresponded to L/C. It must be prepared in the language of L/C.
- Invoice must bear L/C authorization and other relevant number.
- Charges relevant to merchandise are included in the invoice and are permitted by the L/C.
Examination of Transport Document:
- It is presented in full set of negotiable and non-negotiable copies.
- Date of shipment on the Bill of lading.
- Bill of Lading must b e made out in the name of bank notify the importer.
- Description of goods in the Bill of Lading must agree with invoice and L/C.
- Port of shipment and destination is as per L/C
- The shipping company of their agent signs bill of lading.
Examination of other documents:
Weight list, inspection certificate, quality certificate, certificate of origin, packing list etc. Should agree with L/C terms and conditions and be signed by the appropriate authority. These certificates are usually dated before the date of shipment.
Common Discrepancies of the Import Document.
Following are the common discrepancies found in the documentary operation:
- Inadequate number of invoice.
- Submission of documents after expiry of L/C
- Late shipment or transshipment beyond L/C terms.
- “One Board” endorsement unsigned or not dated on the Bill of Lading.
- Specifications of goods are not as per terms of L/C.
- Tenor of draft wrong.
- Inconsistent documents presented.
- Absence of some documents.
If any major discrepancies found in the documents, it is informed to the buyer for their opinion. If discrepancies are minor then these are overlooked.
Lodgment and Retirement of Import Document are usually payment is given days of documents received.
3. Bai-Murabaha Post Import (MPI)
If the importer does not come to negotiate the shipping documents from the issuing bank then it creates MPI through. The bank clears the goods from the port and holds the goods in its Godown. Beside the above as soon as the imported goods come to the port the party may fall into financial crisis and requests the bank to clear the goods from the port making payment to the exporter. In this case, the party later may take the goods partly or fully from the bank by making required payment (if he/she takes the goods time to ti me payment will be adjusted simultaneously.
4. Bai-Muajjal Trust Receipt (MTR)
Bai-Muajjal means in the opening bank will release the document from port by paid all duty and tax for a number of period times, if the importer feeling to release their document. Bai-Muajjal Trust Receipt is may be situation where storage of collateral in an independently controlled field warehouse is impractical. An improper may require the goods for further processing or for displaying the merchandise in order to make the final sale. In such cases, a financing institution that has a greate degree of trust in the importer may be willing to release the negotiable Bill of Lading and there by the goods to the importer against the signing of the trust receipt.
Interpret of Letter of Credit (L/C)
Definition:
A letter of Credit (L/C) can be defined as “an arrangement where in a bank guarantees on behalf of his customers to make payments to the beneficiary upon presentation of documents specified in the credit”
Parties involved in L/C
Opener / Buyer / Importer
The person who opens the L/C is known as Opener/Buyer/Importer of the L/C. the buyer and the seller conclude a sales contract providing for payment by documentary credit.
Opening Bank:
The bank issuing the L/C in favor of exporter is known as opening bank. The opening bank opens L/C on request importer according to the application of the importer.
Advising Bank:
The bank through L/C advised. L/C will be sent to the beneficiary through their agent (corresponded bank) abroad. The duty of the advising bank is to authenticate the message so that the seller can act on it without any fear of document.
Beneficiary:
Seller and exporter in whose favor the L/C is opened. The beneficiary is normally the seller of goods who receive payments under documentary credit if he has compiled with terms and conditions of related L/C.
Negotiating Bank:
The bank that is authorized to handle (purchase) the documents under the L/C in the exporting country are known as negotiating bank. L/C will stipulate either a notified bank to negotiate (restricted L/C) or any bank can negotiate in the seller’s country (unrestricted L/C)
Reimbursing Bank:
The bank that is (by the L/C issuing bank) to effect reimbursement is known as reimbursing bank. Reimbursing bank is authorized to honor the reimbursement claims in settlement of negotiation/ acceptance / payments lodged with it by the paying / negotiation / accepting bank.
Confirming Bank:
A confirming bank is one which adds the guarantee to the credit opened by another bank, there by undertaking the responsibility of payment / negotiating / acceptance under the credit in addition to that of the issuing bank. A confirming bank normally does so request by the issuing bank.
Export Section
This section is negotiates the export documents and collects and purchases the export bill. The two types of credit facilities allowed by the bank to the exporter in relation to export credit.
Pre-shipment Finance
Post-Shipment Finance
Export finance arises from trade between two trades trading in two different countries. A brief idea of the both categories is given below:
Pre-Shipment Finance:
An exporter intend to ship the goods to an overseas buyer he/she needs fund for purchasing goods to be exported. The supplier may also depend upon the bank for arranging credit for the supply of goods.
Post-Shipment Finance:
Post-Shipment finance is more concerned with banks than Pre-Shipment Finance. This type of finance starts after the goods have been already shipped.
Function of Export Section
Export section performs different type of tasks such as:
- Master L/C
- Function of export bill collection.
- Packing credit (PC)
- ECC- Export credit packing.
- Accepted bills payable (ABP)
Opening Back to Back L/C
Back to Back, L/C is a secondary letter of credit opened by the advising bank in favor of a domestic or foreign supplier. On behalf of the beneficiary original foreign L/C. As the original letter of credit of bank by import letter, it is called Back to Back L/C. the second L/C is opened on the strength of the original L/C for a smaller amount maximum 80% is shipped under Lien and 10% under packing credit. There are different types of BTB L/C opened by EXIM Bank of Bangladesh Limited. There are four kind back to back L/C against master L/C.
Back to Back L/C (Local)
When Back to Back L/C is opened for local purchase of materials it is called Back to back L/C (Local). It is generally payable within 90 days at sight.
Back to Back L/C (Foreign)
When the BTB L/C is opened in a foreign country supplier, it is called BTB L/C (Foreign). It is generally payable within 120 days at site.
Back to Back L/C (EPZ)
EPZ menas is Export Processing Zone. When the back to back L/C is opened for EPZ in the Bangladesh its called EPZ BTB L/C. There are six EPZs in Bangladesh of which four are operating now, Here the L/C issued for EPS (Export processing zone) though there is foreign investors. The maximum beneficiary party is EPZ by foreign investors
Back to Back L/C (EDF)
EDF is Export Development Fund that is provided by the ADB. ADB given financial support for export promotion of Third-world-country like as Bangladesh. When the Bank is not in a position to support the amount of back to back L/C then they apply for loans to the Bangladesh Bank for Back to Back (EDF).
L/C Margin
L/C margin varies bank to bank and customer to customer. Generally, L/C margin depends on the following factors:
- Relationship between the banker and customer.
- Seasonal factor.
- Feature of the goods.
- Government restriction.
EXP Form
The exporter will first fill an EXP from declaring the amount to be export, item, and quantity, country etc. The EXP-form has a specific number given to the party. This number is very important. Suppose the number is 1949-0135- 03. This number will be treated as the reference number on invoice (Where the price and quantity is mentioned by the importer). A copy of (duplicate) is send to Bangladesh Bank. Original EXP form is retained with the party. Triplicate is required for customer purpose. A quadruplet is kept for office purpose. I Exp. form, banks authorized officer will sign in two places mentioning the date of Exp. The supplier must declare all export from Bangladesh on EXP forms to the Bank enabling them to submit the duplicate within 14 days from the date of shipment.
The shipper is required to repatriate the export proceeds within 4 months from the date of shipment otherwise, penalty is imposed upon them. The following things are in EXP form
- Quantity of goods to be exported (pieces or dozens)
- Item of the goods (Suppose men’s shirt etc)
- Amount in dollar or Euro (Amount will match the L/C value or may slight vary for sampling and other purpose.)
- Bill of Lading number
- Carrying vessel no.
- Date of departure
- Last date of shipment
- Mood of advising L/C
- Whether transshipment is allowed
- Export L/C number and date.
The application form along with other 3 papers (1) promissory note (2) Exchange form with a forwarding that the party wants to open back to back L/C is submitted to the bank. Before the procedure of Back to Back L/C, the party must submit the original master L/C to the bank. The form is to be stamped under stamp act, enforce in Bangladesh.
LCA form
L/C authorization form consists of six copies. First, copy the original one for exchange control purpose, second copy is for custom purposes for delivery goods. Third and fourth copy for the concerned licensing office. Fifth copy is for registration unit of the Bangladesh bank. Sixth copy is retained in the Bank.
About the Master L/C
The original master L/C is a beneficiary not mentioning that the importer will pay the money as soon as he receives the goods at his disposal. It may take three months or more.
The L/C or letter of credit is a document or paper mentioning L/C no, terms and condition from the importers parts, form of L/C revocable or irrevocable etc.
- Latest date of shipment
- Transshipment allowed or not
- Issuing bank
- Beneficiary name
- Description of goods
- Trade terms
Back to Back L/C opening Procedures:
The party will propose to open that back to back L/C with in the limit of original master L/C. as discussed earlier the party will apply for opening BTB L/C. The following procedure is followed.
In the L/C opening register, the following things will be recorded:
- L/C No.
- Beneficiary name
- Importers name
- Shipment date
- Shipment expiry date
- Goods of items
- Master L/C No. and issuing bank, date of issuing
- EXP No.
- Commission charged
A certain amount will be paid as the commission for opening BTB L/C. This is 0.5% of the total amount of L/C converted into Taka. For data transmission or courier charge or postage charge, some fees will be deducted from party account.
Consideration for back to Back L/C
- Whether client can manufacture within the time period.
- The unit of the finished pro-forma invoice should be considering while allowing margin.
- Consider the expiry date and shipment date.
- On-side inspection whether manufacturing is carried out.
Payment under Back to Back L/C
Deferred payment is made in case of Back to Back L/C as 60, 90, 120, 180 days date of maturity period. Payment will be given after realizing export proceed from the L/C issuing bank from the abroad.
Reporting of Bangladesh Bank
At the end of every month reporting of Bangladesh Bank is mandatory regarding the whole month’s export operation. The procedures in this respect are as follows:
- To fill-up the E-2/P-2 schedule of S-1 category. The whole month import amount, quantity, goods category, country, currency etc. all are mentioned. Respective IMP forms are also attached with the schedule to fill the E-3/ P-3 for all invisible payment.
- Original IMP is forwarded to Bangladesh Bank with mentioning invoice value.
- Duplicate IMP is skipped with the bank along with bill of entry.
Amendment of L/C
In case of revocable L/C, amendment can be brought without prior notice of the beneficiary or issuing bank. However, in case of irrevocable L/C prior notice of the beneficiary is essential. Issuing bank will accept amendment of the L/C after getting consent of both important exporter.
How amendment for BTB L/C is made
Amendment can be made through Telex, swift, fax or courier, Swift copy is retained in the L/C file. Message given by the swift is very easy. Just send message through swift that how much the amount would be or the new shipment date or the quantity changed.
The party will make an application to the manager of the branch for the necessary amount to done. The followings thing are amended:
- Value of the L/C
- Quantity of the goods
- Shipment date
Value of the L/C
If the value of the Back to Back L/C increases it will be treated as a new L/C. L/C commission will be taken from the party in addition to the old L/C. In L/C opening register, the value will be included. Other charges like L/C opening amendment commission, Datamax charge or the courier charge will be taken from the party. In the Back to Back liability, register liability is created and the liability voucher is passed. While amending, the following accounting treatment is done:
Export procedures
When person desire to export should apply to obtain ERC. Then the person should take step for exporter purpose into the bank for obtaining EXP form. The exporter must submit the following documents:
- Trade License.
- Export registrations certificate (ERC)
- Certificate from concerned Government Organization.
After satisfaction on the documents, the banker will issue EXP form to the exporter. Now exporter will be getting shipping and other documents form the shipment procedure. Exporter should submit all these documents along with letter of indemnity to bank for negotiation.
Documents of Export
Requirement of document for export purpose
- Commercial Invoice.
- Bill of Lading.
- EXP form.
- Bill of Exchange.
- Export master L/C copy.
- Packing List.
- Certificate of Origin.
- Quality Control Certificate.
- Weight list.
- Clean report of finding (CRF).
Function of Export Bill Collection
There are two types of procedures regarding collection of Export Bill.
- Foreign Documentary Bill for Collection (FDBC).
- Foreign Documentary Bill for Purchase (FDBP).
Foreign Documentary Bill for Collection (FDBC)
Exporter can collect the bill through negotiating bank on the basic collection Exporter in this case will submit all the documents to the negotiating bank for collection of bill from inspector. The exporter will get money when the issuing bank gives payment. In this case, the opening bank will investigate all the documents as per terms and conditions mentioned in L/C.
Foreign Documentary Bill for Purchase (FDBP)
When exporter sale all the export documents to the negotiating bank then it is called FDBP. In this case, the exporter will submit all the documents to the bank. The bank give 80%-90% amount to the exporter against total L/C value. If, the exporter need financial assist then the advising Bank will give FDBP facilities to opening bank.
Local Documentary Bill for Purchase (LDBP)
- Incoming of L/C customer with the L/C to negotiate.
- Documents given with L/C
- Investigate documents as per L/C terms and conditions.
- Forward the documents to L/C opening bank.
- L/C issuing bank give acceptance and for ward acceptance letter
- Payment given to the party by collection basis or by purchasing.
Packing Credit (PC)
It is one kind of credit sanctioned by the department to meet the exported goods shipment timely. The bank will give the facility after deduction of back to back L/C value. The bank take 7% profit from PC.
ECC (Export cash credit)
It is also one kind of credit section by the negotiation (Advisory Bank before section of (PC) packing credit. The bank take 13% on ECC.
Accepted bill for payment (ABP)
The party after receiving the goods will pay for the importers. This will obviously done by the party’s bank. With ABP the party can make the payment at a latter time after receiving his payment against the original L/C. he may take 90 days or 120 days for this purpose. This arrangement is called accepted bill for payment (ABP). This means that the bank has accepted the bill from the importer for payment. The importer must have sent the documents to the branch bank. The document includes bill of lading, commercial invoice, certificate of origin, packing list, DHL receipt etc.
ABP Process
Upon receive the documents an ABP no will be given on the documents and on the L/C file. In the ABP register, the number is given first with the date of maturity and due date.
In the ABP liability register, a liability will be created debiting banker’s liability on ABP and crediting customer’s liability on ABP.
The document received from the exporter from whom BTB L/C opener imports goods handed over to the party. Then the question of payment comes. At the maturity/due date, the bank will pay to the negotiating bank of the importer, Maturity date should be convened to the negotiating bank.
Foreign Remittance Section
Different funds are mobilized from foreign country to our country through the foreign remittance section. Purchase of currencies institutes inward foreign remittance and sale of foreign currencies constitutes outward foreign remittance. EXIM Bank has a rich environment where funds flow from different countries. The transaction of the authorized dealer in foreign exchange involves either inward or outward remittances of foreign exchange between the two countries.
Remittance procedure of Foreign Currency by the Exim bank.
There are two types of remittance:
- Inward Remittance.
- Outward Remittance.
Inward remittance: Inward remittance can be divided into different types. These remittance procedures are describe in the following:
Foreign Demand Draft (FDD)
If any draft is send to the name of any organization from abroad then the draft is fill-up from “C” where the draft holder is to fill-up who has send this draft, from where this draft has been sent etc. Whether family purpose or not, if the draft has been family purpose then no VAT is required against the draft. For payment of draft concerned officer maintains a register, which is called Register for foreign Currency paid.
Foreign telegraphic Transfer (FTT)
TT is one of the important tools of foreign currency from one country to another. The person who wants to send TT to the abroad at first he / she has to deposit amount mentioned in voucher to the cash department. The bank branch through their respective NOSTRO account that is maintaining any foreign bank account outside the country generally performs it. The original bank send a message to the paying foreign bank for making payment against the mentioned TT accounts number. The foreign make payments to the party and make debit ‘account’ against respective bank. At the same time foreign bank send advice to Head Office ID division for acknowledgement the payment.
Outward Remittance: Out ward remittance includes sales of TC and FC notes etc.
Sales of TC and FC Notes
To get TC and FC notes at least the customer has to submit an application form filling up the required column, which is formatted by the bank, is called T/M form, After checking the form, the desk officer passes voucher and issues a TC and gives cash dollar to the customer. In both the cases, the banker endorses total amount in customer’s passport. The bankers require photocopy of customer’s passport (page one to seven) and endorsement paper. The charge of endorsement taken by the branch is Tk. 300 only. Sale of TC and FC and Notes amount varies from different countries.***
FOREIGN REMITTANCE
- ISSUANCE OF TC, CASH DOLLAR/POUND.
- ISSUANCE OF FDD, FTT & PURCHASING, PAYMENT OF THE SAME.
- PASSPORT ENDORSEMENT.
- ENCASHMENT CERTIFICATE.
- F/C ACCOUNT OPENING & FILING.
- OPENING OF EXPORT FC RETENTION QUOTA A/C & MAINTAIN.
- MAINTANCE OF LEDGER OF CASH DOLLR, FC DEPOSIT A/C & TC.
- MAINTANCE FBC RESISTER & FOLLOW UP FBC.
- OPENING OF STUDENT FILE & MAINTAIN.
- PREPARATION OF ALL RELATED STATEMENT, VOUCHER & POSTING.
- ATTENDING ALL RELATED CORRESPONDENCE TO OTHER BANK OR INSTITUTIONS.
- KEEP THE SECURITY DOCUMENT UNDER LOCK & KEY.
Islamic Banking System of Investment
Introduction:
Islamic is not a only religion. It is complete code of life. Islam is described as a system of financial inter mediation that avoids receipt and payment of interest in its transactions and conducts its operations is accordance with objectives of an Islamic economy. Islamic banking is based on the Islamic legal concepts of
- Sherkah (partnership)
- Mudarabah (profit-sharing)
They have several distinguishing factors as listed below-
- Islamic banking financing arrangement are interest free.
- The public good is always taken into consideration for any request for financing.
- Islamic banks are multi purpose banks.
- Islamic banks scrutinize their investments more closely on the are liable for any losses incurred.
- Due to the profit sharing feature of Islamic banking. Banks and entrepreneurs have a shared interest in the out come of an investment which fosters economic development.
What is Islamic Banking?
The definition of Islamic bank, as approved by the OIC. is elated in the following manner “An Islamic bank is a financial investigation whose status, rules and procedures expressly state its commitment to the principle of Islamic shariah and to the banking of the receipt and payment of interest on any of its operations.
Dr. Ziauddin Ahmed says, “Islamic banking is essentially a nonnative concept and could be closed as conduct of banking in consonance with the ethos of the value system of Islam.
Alternatively this is a banking system whose operation is based on Islamic principles of transaction of which profit and loss sharing (PLS) is a major feature, ensuring justice and equity in the economy.
Distinguishing features of Islamic Banking:
An Islamic bank has several distinctive features as compound to its conventional banking / other part six essential difference as bellow:
- Abolition of interest (Riba) = Since riba is prohibited in the Holy Quran and interest is a all its form is akin to riba, the first distinguishing features of and Islamic bank must that it is interest free.
- Adherence to public Interest: Activity of commercial banks being primarily based on the use of public funds, public interest rather than individuals or group interest will be served by Islamic commercial Banks.
- Multi-purpose bank: Islamic banks will universal or multi-purpose banks and not purely commercial bank.
- More care Evaluation of Investment Demand: Another very important features of an Islamic bank is its very carefully attitude towards toward evaluation of applications for equity oriented financing. Their main concern does not go beyond ensuring the security of their principal and interest receipts.
- Work as catalyst of Development: Project loss sharing being a distinctive characteristic of an Islamic bank fosters closer relation between banks and entrepreneurs. It helps develop financial expertise in Non-financial firms and also enable the bank to assume the role of technical consultant and financial adviser. Which acts a catalyst in the process industrialization and development.
Object
- To offer contemporary financial services in conformity with Islamic shariah.
- To contribute towards economic development and prosperity within the principles of Islamic justices.
- Optimum allocation of scarce financial resources.
- To help ensure equitable distribution of income.
Investment Decision under Islamic banking:
Under the profit loss sharing systems of investment financing, the bank receives a variable rate of return or it share a percentage of profits earned by borrower.
Though there is a consumer as to sharing losses in proportion to capital participation, some of the Muslim economist think that the ratio may vary with the application of different types of modes of financing. Thus, the profit loss sharing systems of investment financing may be termed a variable returns system.
Sin the Islamic banking system does not change interest on any financing agreements, the client neither receives nor a pay fixed rate of returns while financing investment.
















