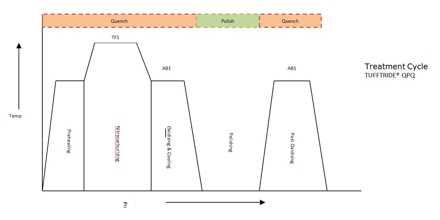
Ferritic nitrocarburizing or less commonly known as Ferritic nitrocarburising, in British English, is an array of case hardening operations that diffuse nitrogen and also carbon into ferrous metals at sub-critical conditions. The processing heat range ranges from 525°C to help 625°C, but usually occurs from 565 °C (1,049 °F). The process is used to improve three main surface integrity aspects: scuffing resistance, fatigue properties and corrosion resistance.
Ferritic Nitrocarburizing