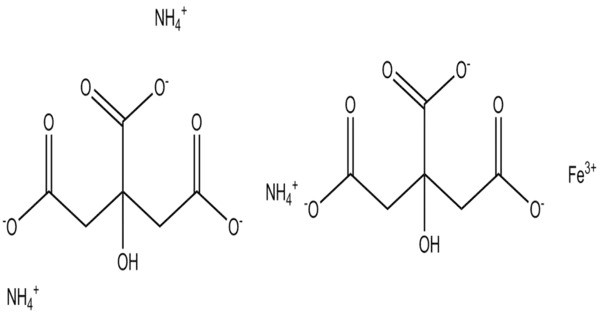
Ferric Ammonium Citrate also known as or ammoniacal ferrous citrate, has the formula [NH4]y[Fex(C6H4O7)]. The iron in this compound is trivalent. All three carboxyl groups and the central hydroxyl group of citric acid are deprotonated. It is often used in various applications, including as a source of iron in nutritional supplements and in the manufacturing of photographic chemicals, particularly in the cyanotype process.
A distinguishing feature of this compound is that it is very soluble in water, in contrast to ferric citrate which is not very soluble. In its crystal structure each moiety of citric acid has lost four protons. The deprotonated hydroxyl group and two of the carboxylate groups ligate to the ferric center, while the third carboxylate group coordinates with the ammonium.
Properties
- Appearance: It typically appears as a dark green or dark brown powder.
- Solubility: It is soluble in water, which makes it useful in various solutions for different applications, including medical formulations and laboratory solutions.
- Stability: The compound is relatively stable under normal conditions. Its stability can be affected by the pH of the solution in which it is dissolved.
- pH: In solution, it typically results in a mildly acidic pH due to the presence of ammonium ions and the acidic nature of citric acid.
Natural Sources
Ammonium ferric citrate is not typically found in nature in its pure form. However, iron and citric acid are naturally occurring substances. Iron is abundant in the Earth’s crust, and citric acid is found in citrus fruits and many other plants.
Synthetic Production
It is usually synthesized in a laboratory or industrial setting by reacting ferric salts (such as ferric chloride) with citric acid in the presence of ammonium compounds (like ammonium hydroxide). This results in the formation of the ammonium ferric citrate complex.
Common Uses
- Iron Supplement: It is sometimes used in dietary supplements as a source of iron, particularly for treating or preventing iron deficiency anemia.
- Photography: In traditional photographic processes like cyanotype, ammonium ferric citrate is used in the preparation of solutions for the sensitization of paper, which results in blueprints when exposed to light.
- Water Treatment: It can be used in some water treatment processes as a coagulant.
- Biological Research: In laboratory settings, ammonium ferric citrate may be used in various experiments that require iron as a nutrient or catalyst.
In summary, ammonium ferric citrate is a useful compound with a variety of applications, from medical and nutritional uses to its role in food and analytical chemistry. Its stability and solubility in water make it convenient for these purposes.