Epithalamus
Definition
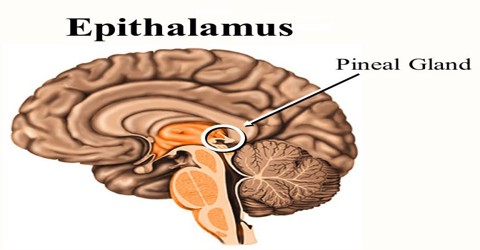
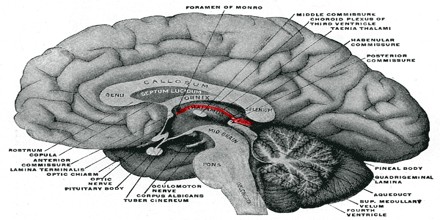
Epithalamus is a dorsal segment of the diencephalon containing the habenula and the pineal body. It is a segment of the diencephalon which is a part of the forebrain that also contains the thalamus, hypothalamus and pituitary gland. The epithalamus consists of the habenula, the habenula commissure, the stria medullaris and the pineal gland. Its purpose is to act as a connection to the limbic system to other parts of the brain. It also secretes hormones including melatonin by the pineal gland controlling circadian rhythms. It also regulates motor pathways and emotions.

It is the part of the diencephalon just superior and posterior to the thalamus, comprising the pineal body and adjacent structures; considered by some to include the stria medullaris.
Structure and Functions of Epithalamus
The epithalamus is a dorsal posterior segment of the diencephalon, which includes the habenula and their interconnecting fibers, the habenular commissure, the stria medullaris, and the pineal body. The function of the epithalamus is to connect the limbic system to other parts of the brain. Some functions of its components include the secretion of melatonin and secretion of hormones from pituitary gland by the pineal gland, involved in circadian rhythms, and regulation of motor pathways and emotions.
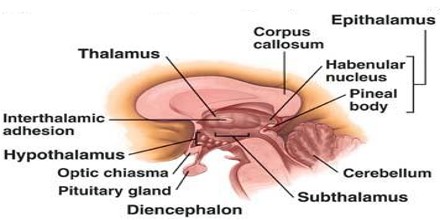
The epithalamus is located in the interior of the brain. It is a small area that is primarily covered by the pineal gland. This area of the brain is often described as the most mysterious part because it was the last gland identified within the endocrine system. It was once referred to as a person’s “third eye,” and it was thought to serve as the place where the soul exists in the body, as well as the primary place where thoughts were developed in the brain. This was mostly because of its strong relation to processing light.
The epithalamus comprises the habenular trigone, the pineal gland, and the habenular commissure. It is wired with the limbic system and basal ganglia.
Importance of Epithalamous
Epithalamus is a dorsal posterior segment of the diencephalon, which includes the habenula and their interconnecting fibers, the habenular commissure, the stria medullaris, and the pineal body. A main function of the epithalamus is the secretion of melatonin by the pineal gland.