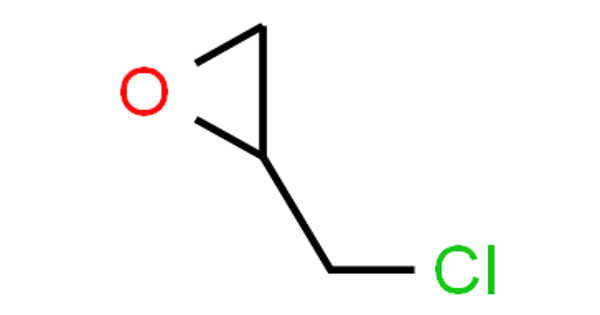
Epichlorohydrin is an epoxide and an organochlorine compound. It is not a halohydrin, despite its name. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent, garlic-like odor that is moderately soluble in water but miscible with the majority of polar organic solvents. It is a chiral molecule that exists as a racemic mixture of right- and left-handed enantiomers. Epichlorohydrin is a highly reactive electrophilic compound used to make glycerol, plastics, epoxy glues and resins, epoxy diluents, and elastomers.
Epichlorohydrin (ECH) is a liquid epoxide most frequently manufactured by the chlorohydrination of allyl chloride. It is one of the more commercially important aliphatic epoxides used extensively as an insecticide, an industrial intermediate, and as a laboratory reagent.
Epichlorohydrin is a volatile and flammable clear, colorless liquid chlorinated cyclic ether with an irritating, chloroform-like odor that, when heated to decomposition, emits toxic fumes of hydrochloric acid and other chlorinated compounds. Epichlorohydrin is a chemical that is used in the production of epoxy resins, synthetic glycerin, and elastomers. Epichlorohydrin causes eye, skin, and respiratory tract irritation, as well as chemical pneumonitis, pulmonary edema, and renal lesions. This substance also has an effect on the blood. Epichlorohydrin is likely to be a human carcinogen and may be linked to an increased risk of developing respiratory cancer.
Applications
- Glycerol and epoxy resins synthesis
The majority of epichlorohydrin is converted to bisphenol. A diglycidyl ether is a building block used in the production of epoxy resins. It is also a monomer precursor for other resins and polymers. Another application is the production of synthetic glycerol. However, because glycerol is a waste product in biodiesel production, there is a glut of glycerol on the market, making this process uneconomical. Synthetic glycerol is now only used in sensitive pharmaceutical and biotech applications with extremely high-quality standards.
- Minor and niche applications
Epichlorohydrin is a versatile precursor that can be used in the synthesis of a wide range of organic compounds. It is converted, for example, to glycidyl nitrate, an energetic binder used in explosive and propellant formulations. When epichlorohydrin reacts with an alkali nitrate, such as sodium nitrate, glycidyl nitrate, and alkali chloride are formed. It is used as a solvent for cellulose, resins, and paints, as well as an insect fumigant.
Epichlorohydrin-derived polymers, such as polyamide-epichlorohydrin resins, are used in paper reinforcement and the food industry to make tea bags, coffee filters, and sausage/salami casings, as well as in water purification.
An important biochemical application of epichlorohydrin is its use as a crosslinking agent for the production of Sephadex size-exclusion chromatographic resins from dextrans.
Safety
Several international health research agencies and groups have classified epichlorohydrin as a probable or likely carcinogen in humans. Prolonged oral consumption of high levels of epichlorohydrin may cause stomach problems as well as an increased risk of cancer. Inhaling epichlorohydrin at work may cause lung irritation as well as an increased risk of lung cancer.
Information Source: