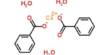
Admixtures that slow down water penetration into cement and the formation of hydration products are known as water-reducing and set-retarding agents. They work by delaying the initial reaction between cement and water.
Concrete remains usable for a longer period of time as a result. The temperature, consistency class, water-to-cement ratio, and quantity of retarder employed all affect how long concrete will be workable.
Retarded concrete requires precise proportioning to reduce bleeding because it is fresh for a longer period of time. It reduces the requirement for shaping, putting, and assembling discrete components by allowing the installation of enormous quantities of concrete over long periods of time.
Effects on Fresh Concrete:
- Decrease water required by at least 5% for the same slump concrete.
- Reduce rate of slump loss.
- Extend working time
- Improve finishing characteristics of concrete. This is especially helpful when poor material qualities or gradation pose challenges for concrete finishing.
- Delay in setting time of concrete. The delay in setting time increases with the increase of dosages and lower temperatures.
- It has been reported to contribute to premature stiffening.
Effects on Hardened Concrete:
- Strength increase due to reduction of w/cm ratio.
- The increase in flexural strength is not the same as compressive strength.
- Long-term shrinkage may be less than that of concrete without admixture.
- Creep is reduced in proportion to the increase in the strength of the concrete.
Dosage:
- According to ACI 212.3R, the dosage of the admixture should be determined from information provided by one or more of the following sources:
- Results of construction projects in which the admixture was used under sound field control, preferably with the same materials and in anticipated conditions.
- Laboratory tests carried out to evaluate the admixture.
- Information and technical literature from the manufacturer.
Applications:
- It is primarily used to counteract the hastening effect of hot weather and to maintain the workability of concrete throughout the full laying period. This is essential to avoid form deflection-induced cracking in concrete beams, bridge decks, or composite construction.
- Used to maintain concrete usable until further lifts can be installed without causing the structural unit’s cold joints to form.
- When the complexity of slip-forming necessitates a sluggish rate of increase, this kind of admixture is used.