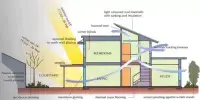
Prefabricated homes, also known as prefab homes or simply prefabs, are types of prefabricated buildings that are manufactured off-site in advance, usually in standard sections that can be easily shipped and assembled. Architectural details inspired by postmodernism or futurist architecture can be found in some modern prefab home designs.
Prefabricated homes, also known as prefab homes or modular homes, are houses that are constructed off-site in sections or modules in a factory or manufacturing facility. These sections are then transported to the final location and assembled to form a complete house. Because of their numerous advantages, prefabricated homes have grown in popularity in recent years.
The term “prefabricated” can refer to buildings built in components (e.g., panels), modules (modular homes), or transportable sections (manufactured homes), as well as mobile homes, or houses on wheels. Although the methods and designs of the three are similar, they differ significantly. There are two-story house plans available, as well as custom house plans. The various construction types differ significantly. Mobile and mobile homes in the United States are built in accordance with HUD building codes, whereas modular homes are built in accordance with the IRC (International Residential Code).
Here are some key features and benefits of prefabricated homes:
- Construction Efficiency: Prefabricated homes are constructed in a controlled environment using efficient construction techniques. When compared to traditional on-site building methods, this allows for more precise measurements, quality control, and faster construction. In a factory setting, the use of specialized machinery and skilled labor helps to streamline the construction process.
- Design Flexibility: Prefabricated homes come in a variety of designs to suit a variety of architectural styles and personal preferences. These houses can be tailored to specific size requirements, layout preferences, and aesthetic preferences. Many manufacturers offer a catalog of pre-designed models to choose from, while others allow for the creation of a custom design.
- Cost Savings: Prefabricated homes can often be more cost-effective compared to traditional site-built homes. The controlled factory environment reduces material waste, and bulk purchasing of materials by manufacturers can lead to lower costs. Additionally, the faster construction time can help reduce labor costs. However, it’s important to consider factors such as location, customization, and additional site work that may impact the overall cost.
- Quality Control: Prefabricated home manufacturing allows for strict quality control measures. Factory inspections and standardized building techniques ensure that the home’s components are of high quality. In addition, the controlled environment reduces the risk of weather-related damage during construction.
- Sustainability: Prefabricated homes can be designed to be environmentally friendly. When compared to traditional building methods, the off-site construction process produces less waste and causes less disruption to the environment. Furthermore, the ability to incorporate energy-efficient features like insulation, solar panels, and efficient HVAC systems can make prefab homes more environmentally friendly.