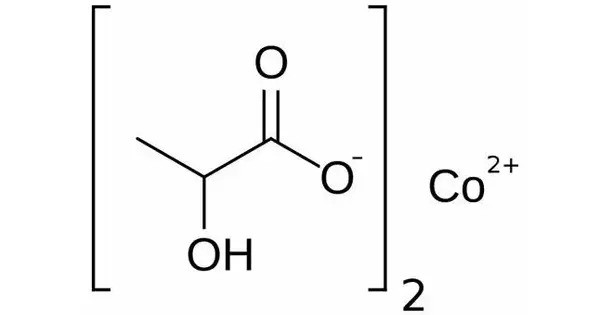
Cobalt lactate is a chemical compound, a salt of cobalt and lactic acid with the formula Co(C3H5O3)2. It is a coordination compound formed from cobalt and lactic acid, often appearing as a blue or greenish powder. It typically appears as a pinkish or reddish crystalline powder and is used in various applications, including as a dietary supplement in some animal feeds, particularly for livestock.
In addition to its use in agriculture, cobalt lactate can also be found in some biochemical applications and research settings. However, its use should be carefully monitored due to potential toxicity associated with cobalt in high concentrations.
Synthesis
Cobalt lactate can be formed by boiling hydrated oxide of cobalt with lactic acid.
Properties
Cobalt lactate forms a peach-blossom red salt. It is soluble in water. When heated, the compound becomes black, takes fire, and leaves cobalt oxide. It is soluble in water, which makes it useful in various applications. The compound generally appears as a blue or violet crystalline solid. It is relatively stable under normal conditions but can decompose under extreme conditions. It has a moderate melting point, usually in the range of 100-200 °C depending on purity and form.
- Chemical formula: C6H10CoO6
- Molar mass: 239.09
- Appearance: Peach-blossom pink salt
- Solubility in water: Soluble
Use
Cobalt lactate is used as a ruminal source of cobalt in a high-forage total mixed ration fed to late-lactation dairy cows. It is used in biochemical research and catalysis due to its unique properties and behavior in biochemical reactions.
Cobalt is an essential trace element in the human diet, particularly as part of vitamin B12. Cobalt lactate is sometimes used in nutritional supplements. It is employed in various industries, including food additives, where it serves as a source of cobalt.