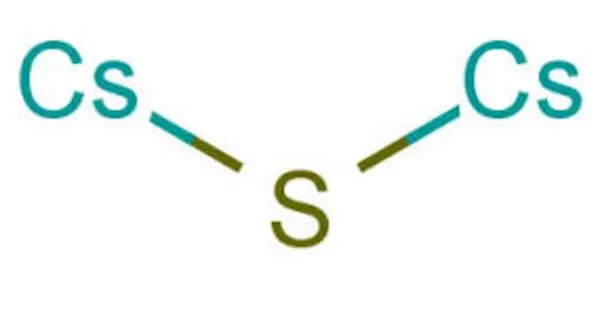
Cesium sulfide is an inorganic salt with a chemical formula Cs2S. It is a strong alkali in aqueous solution. In the air, cesium sulfide emits rotten egg smelling hydrogen sulfide. It appears as a white or colorless crystalline solid and is commonly used in various applications, including in the production of cesium-containing compounds or as a potential material for certain types of battery technologies.
Production
Similar to sodium sulfide, anhydrous cesium sulfide can be produced by reacting cesium and sulfur in THF. It needs ammonia or naphthalene to react.
2 Cs + S → Cs2S
By dissolving hydrogen sulfide into cesium hydroxide solution, it will produce cesium bisulfide, then it will produce cesium sulfide too.
CsOH + H2S → CsHS + H2O
CsHS + CsOH → Cs2S + H2O
Properties
- Chemical formula: Cs2S
- Molar mass: 297.876 g/mol
- Appearance: White crystal
- Density: 4.19 g·cm−3
- Melting point: 480 °C
- Solubility in water: Hydrolyzes to form caesium bisulfide[3]
- Solubility in ethanol and glycerol: Soluble
Occurrences
- Natural Occurrence: Cesium sulfide is quite rare in nature in its pure form, but its elements are found in certain minerals. The most notable natural source of cesium is the mineral pollucite, which contains cesium in the form of cesium-aluminum silicate, though not typically as sulfide.
- Synthesis: It can be synthesized in the laboratory by reacting cesium metal with sulfur at elevated temperatures.
Applications
Cesium sulfide has limited direct industrial uses, but its related compounds (like cesium salts) are valuable in applications such as in atomic clocks, radiation detectors, and medical imaging.