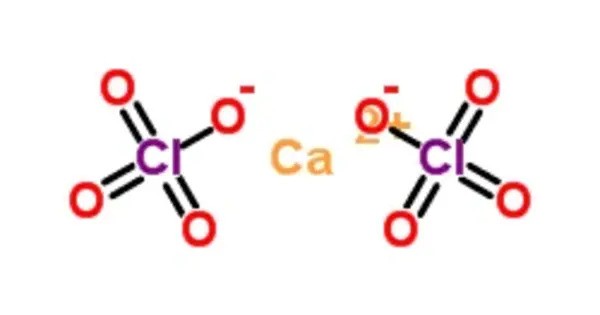
Calcium perchlorate is classified as a metal perchlorate salt with the molecular formula Ca(ClO4)2. It is the calcium salt of perchloric acid and functions as a strong oxidizing agent. It is an inorganic compound that is a yellow-white crystalline solid in appearance. Commonly used in pyrotechnics, explosives, and as a desiccant due to its hygroscopic nature, it is also studied for its role in chemical oxygen generation and rocket propellants. In aqueous solution, it dissociates into calcium and perchlorate ions.
As a strong oxidizing agent, it reacts with reducing agents when heated to generate heat and products that may be gaseous (which will cause pressurization in closed containers). Calcium perchlorate has been categorized as having explosive reactivity. Ca(ClO4)2 is a common chemical on the soil of planet Mars, counting for almost 1% of the Martian dust, by weight.
Handling requires caution, as it can react violently with organic materials or reducing agents. It is relatively stable under normal conditions but decomposes at high temperatures, releasing toxic gases. Due to environmental and health concerns associated with perchlorates, its use is regulated in some regions.
Properties
Calcium perchlorate is a strong inorganic oxidizing agent, enhancing the combustion of other substances that can potentially lead to explosion. The perchlorate ion, ClO−4, has a highly symmetrical tetrahedral structure that is strongly stabilized in solution by its low electron-donating proton-accepting power and its relatively low polarizability.
- Chemical formula: Ca(ClO4)2
- Molar mass: 238.9792 g/mol
- Appearance: White to yellow crystalline solid
- Density: 2.651 g/cm3
- Melting point: 270 °C (518 °F; 543 K)
- Solubility in water: 188.7 g/100 g
- Solubility in acetone: 61.76 g/100 g
- Solubility in ethyl acetate: 113.5 g/100 g
- Solubility in ethanol: 166.2 g/100 g
- Solubility in ethyl ether: 0.26 g/100 g
- Solubility in methanol: 237.4 g/100 g
Production
Perchlorate salts are the product of a base and perchloric acid. Calcium perchlorate can be prepared through the heating of a mixture of calcium carbonate and ammonium perchlorate. Ammonium carbonate forms in the gaseous state, leaving behind a calcium perchlorate solid.
Reactivity
- Reacts violently with reducing agents, organic materials, and combustibles.
- Strong oxidizer: may intensify fire.
Uses
- Desiccant: Because of its hygroscopic nature, it’s used as a drying agent.
- Oxidizing agent: In pyrotechnics and propellants.
- Analytical chemistry: Occasionally used in labs for specific perchlorate reactions.
- Industrial synthesis: In perchlorate-based chemical manufacturing.
Natural Occurrence
- Calcium perchlorate does not occur naturally in significant quantities. It’s a synthetic compound, typically produced via:
- Reaction of calcium salts (e.g., calcium chloride) with perchloric acid.
- Double displacement reactions involving sodium perchlorate.
Environmental Presence
Perchlorates, including calcium perchlorate, have been found in arid environments (e.g., Atacama Desert) and on Mars (detected by missions like NASA’s Phoenix lander), though the dominant perchlorates are often magnesium and sodium salts rather than calcium.
Safety and Handling
- Hazards: Strong oxidizer; contact with organic materials or heat may cause fire/explosion.
- Toxicity: Perchlorates can disrupt thyroid function by interfering with iodine uptake.
- Storage: Keep in tightly sealed containers, away from heat, moisture, and incompatible materials.