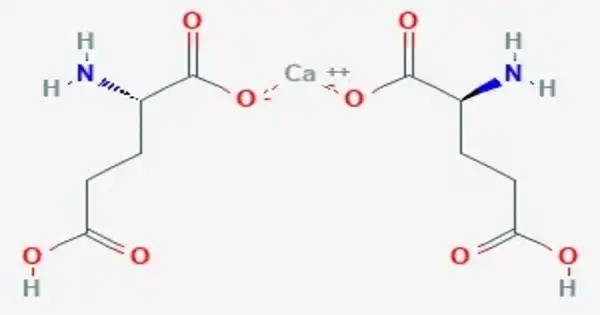
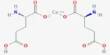
Calcium diglutamate, sometimes abbreviated CDG and also called calcium biglutamate, is a compound with formula Ca(C5H8NO4)2. It is a calcium acid salt of glutamic acid, specifically the calcium salt of two glutamate anions. It is known for its use as a flavor enhancer, much like monosodium glutamate (MSG), but with a different cation (calcium instead of sodium). It appears as a white, odorless crystalline powder and is known by the E number E623.
CDG is a flavor enhancer (E number E623)—it is the calcium analog of monosodium glutamate (MSG). Because the glutamate is the actual flavor-enhancer, CDG has the same flavor-enhancing properties as MSG but without the increased sodium content. Notably, only the L isomer is used in flavouring as D-glutamate does not have an umami/savoury flavour. It is typically used in processed foods, soups, and snack products to enhance savory flavors.
As a soluble source of calcium ions, this chemical is also used as a first-aid treatment for exposure to hydrofluoric acid. This compound provides an umami taste and is commonly used in low-sodium food products as a sodium-free alternative to MSG. It is considered safe by food safety authorities when consumed in typical amounts.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C10H16CaN2O8
- Molar mass: 332.322 g·mol−1
- Molecular Weight: ~324.31 g/mol
- Appearance: White crystalline powder
- Solubility: Soluble in water
- Taste: Umami (savory), similar to MSG
- State: Solid (crystalline)
- pH (in solution): Slightly acidic to neutral
- Stability: Stable under normal conditions
- Odor: Odorless
- Melting Point: Decomposes before melting
Production
Typically synthesized by neutralizing glutamic acid (or its salts) with calcium compounds (e.g., calcium carbonate or calcium hydroxide).
Occurrences
1. Food Industry
- E Number: E623 (as a food additive in the EU)
- Used as a flavor enhancer, especially in low-sodium food formulations.
- Preferred in products aimed at reducing sodium intake (as it replaces sodium in MSG).
2. Nutritional Supplements – Source of calcium and glutamate, sometimes used in mineral supplementation.
3. Biotechnology & Research – Occasionally used in studies involving calcium or glutamate signaling in cells.
Safety and Regulation
- Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) by FDA when used appropriately.
- Less controversial than MSG due to reduced sodium content.
- Excessive intake may still lead to glutamate sensitivity in some individuals (though evidence of “Chinese Restaurant Syndrome” remains largely anecdotal).