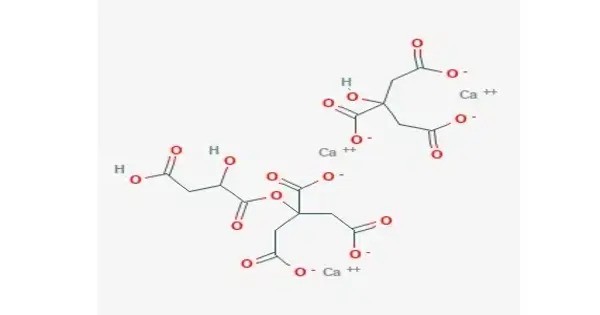
Calcium citrate malate is a water-soluble calcium supplement. It is the calcium salt of citric acid and malic acid with variable composition. It is a water-soluble form of calcium that’s commonly used in supplements. It’s a compound of calcium with citric acid and malic acid, and it offers high bioavailability, meaning your body can absorb it efficiently.
Calcium citrate malate’s bioavailability stems from its water-solubility and its method of dissolution. When dissolved, it releases calcium ions and a calcium citrate complex. It is used primarily as a dietary calcium supplement and is known for its high bioavailability.
Properties
- Chemical formula: (C6H7O7)x·(C4H5O5)y·(Ca2+)z
- Molar mass: Variable
- Appearance: White solid
- Solubility: Moderately soluble in water (more than calcium carbonate)
- pH (1% solution): Slightly acidic
- Bioavailability: High (better absorbed than calcium carbonate, especially on an empty stomach)
- Stability: Stable under normal storage conditions
- Odor/Taste: Odorless, slightly tart taste due to citrate content
Health and Functional Benefits
- Highly bioavailable: CCM is one of the most absorbable forms of calcium due to the presence of citric and malic acids which enhance solubility.
- Effective without food: Unlike calcium carbonate, CCM does not require stomach acid for absorption, making it effective for older adults or individuals with low stomach acid.
- Bone health: Commonly used in supplements to help maintain bone density and prevent osteoporosis.
Occurrences and Sources
Natural Occurrence:
- Does not occur naturally in pure form.
- Derived synthetically by reacting calcium carbonate or calcium hydroxide with citric acid and malic acid.
Dietary Supplements:
- Commonly found in fortified foods (e.g., orange juice, cereals) and calcium supplements.
- Used in functional beverages and pharmaceutical formulations.
Use in Clinical Nutrition
Recommended in cases of calcium deficiency, osteoporosis prevention, and postmenopausal bone health support.