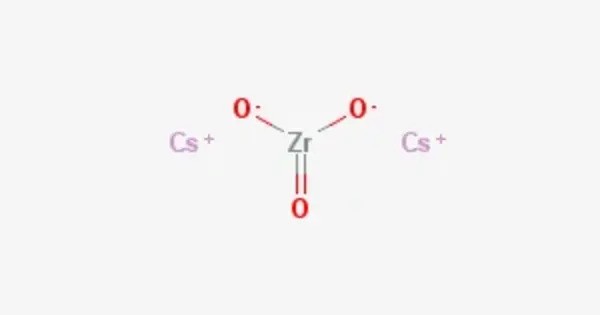
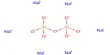
Caesium zirconate is an inorganic compound of caesium, oxygen, and zirconium with the chemical formula Cs2ZrO3. It is a highly stable compound with useful properties like high thermal stability and ion-exchange capacity. It is typically used in a variety of scientific applications, including in the field of nuclear waste management due to its ability to effectively absorb certain radioactive elements.
Properties
Caesium zirconate forms a white powder. Caesium zirconate typically appears as a white crystalline powder or solid. It is relatively stable at room temperature and has a high melting point. The melting point of caesium zirconate is relatively high, making it stable under high temperatures. It is insoluble in water and most solvents, as it is a ceramic-like material with high stability in both neutral and slightly basic environments.
- Chemical formula: Cs2O3Zr
- Molar mass: 405.032 g·mol−1
- Appearance: white powder
- Melting point: 1,010 °C (1,850 °F; 1,280 K)
Preparation
Caesium zirconate can be prepared from the reaction of CsOH with zirconia at high temperature:
2 CsOH + ZrO2 → Cs2ZrO3 + H2O
Synthesis
Caesium zirconate is typically synthesized by combining cesium carbonate (Cs₂CO₃) or cesium chloride (CsCl) with zirconium oxide (ZrO₂) in a high-temperature reaction. The reaction forms caesium zirconate as a solid precipitate, which is then isolated and purified.
Industrial and Scientific Uses:
- Nuclear Waste Management: Caesium zirconate is highly effective at removing radioactive cesium (Cs) from contaminated water. It has a high affinity for cesium ions and is used in the form of granules to absorb and isolate cesium during the cleanup of radioactive waste.
- Ion-Exchange Systems: It has a role in ion-exchange processes due to its ability to replace cesium ions with other cations.
- Radiation Shielding: Owing to its stability in radioactive environments, caesium zirconate is used in some radiation shielding applications.
- Ceramics: Its ability to withstand high temperatures and chemical stability makes it useful in ceramic products, especially those exposed to harsh conditions.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
- Environmental Impact: While caesium zirconate itself is relatively stable and non-toxic, its primary use in nuclear waste management means that it is often used to deal with highly radioactive materials. The environmental impact of caesium zirconate is mainly linked to its role in safely containing cesium during the cleanup of radioactive sites.
- Safety: Handling caesium zirconate should be done with caution due to its association with radioactive cesium. Proper safety protocols must be followed to avoid exposure to radiation, especially when used in applications involving radioactive waste.