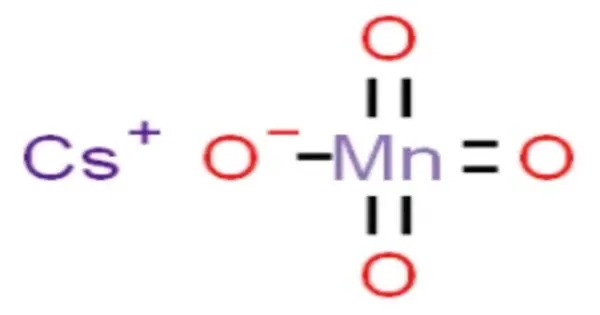
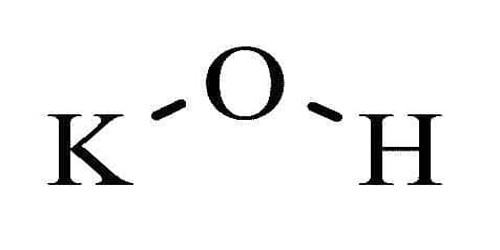Caesium permanganate is the permanganate salt of caesium, with the chemical formula CsMnO4. It is a strong oxidizing agent, used in oxidation reactions and as a specialty chemical in electronic and metallic compounds. It decomposes between 200–300°C into manganese dioxide, caesium oxide, and oxygen, with an 8% mass loss due to oxygen release. Safety precautions are critical due to its oxidizing properties, requiring protection against inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact.
It must be stored away from heat, sparks, and combustible materials to prevent fire or explosion risks. Available in high-purity forms, it is supplied by companies like American Elements for research and industrial applications.
Preparation
Caesium permanganate can be formed by the reaction of potassium permanganate and caesium nitrate:
CsNO3 + KMnO4 → KNO3 + CsMnO4 ↓
Properties
It is a chemical compound, a permanganate salt of caesium, with a molecular weight of 251.84 g/mol. It consists of caesium (52.77%), manganese (21.81%), and oxygen (25.41%). Formed by reacting potassium permanganate with caesium nitrate, it appears as a crystalline solid with an orthorhombic crystal structure, similar to rubidium, ammonium, and potassium permanganates. It is soluble in water, with solubility increasing with temperature: 0.97 g/L at 1°C, 2.3 g/L at 19°C, and 12.5 g/L at 59°C.
- Chemical formula: CsMnO4
- Molar mass: 251.8406
- Appearance: purple crystals
- Density: 3.6
- Melting point: 200-300 °C (decomposes)
- Solubility in water: 2.3 g·l−1 (19 °C)
Chemical
Similar to potassium permanganate, the two-step decomposition of caesium permanganate leads to the formation of caesium manganate intermediates. It breaks down into manganese dioxide, caesium oxide and oxygen. The decomposition temperature is between 200 and 300 °C. Drift-away oxygen caused an 8% mass loss in the product.
10CsMnO4 → 3Cs2MnO4 + 7MnO2 + 2Cs2O + 6O2 ↑
2Cs2MnO4 → 2MnO2 + 2Cs2O + O2 ↑
Total reaction:
4CsMnO4 → 4MnO2 + 2Cs2O + 3O2 ↑
Occurrences
- Natural Occurrence: Caesium permanganate is not commonly found in nature due to its reactivity and is typically synthesized in laboratory or industrial settings.
- Synthesis: Formed by the reaction of potassium permanganate (KMnO₄) with caesium nitrate (CsNO₃). It can also be prepared for specific applications, such as metallic compounds and electronic chemicals.
Uses
- Organic Synthesis: Used as an oxidizing agent to convert alkenes to glycols, oxidize alcohols to aldehydes or ketones, and cleave alkenes to form carboxylic acids.
- Disinfection: Employed as a disinfectant due to its ability to destroy microorganisms by oxidizing their cell walls and membranes, applicable in water treatment, medical equipment cleaning, and surface disinfection.
- Laboratory and Industrial Applications: Utilized in research for the analysis and synthesis of organic compounds, leveraging its strong oxidizing properties.
- Specialized Applications: Used in the preparation of non-stoichiometric, microcrystalline mixtures of transition metal oxides and as a reagent in specific chemical reactions.