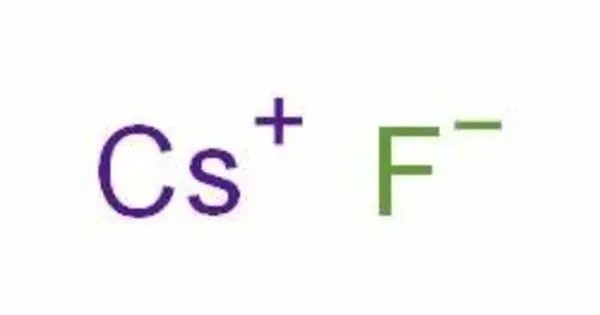Caesium fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula CsF. A hygroscopic white salt, caesium fluoride is used in the synthesis of organic compounds as a source of the fluoride anion. The compound is noteworthy from the pedagogical perspective as caesium also has the highest electropositivity of all commonly available elements and fluorine has the highest electronegativity.
It is a synthetic compound used for a variety of industrial purposes. It is highly soluble in water, and while it has useful properties, it requires careful handling due to its reactivity, especially its ability to release hazardous hydrofluoric acid upon exposure to moisture.
Properties
- Chemical formula: CsF
- Molar mass: 151.903 g/mol
- Appearance: white crystalline solid
- Density: 4.64 g/cm3
- Melting point: 703 °C (1,297 °F; 976 K)
- Boiling point: 1,251 °C (2,284 °F; 1,524 K) (2,284 °F; 1,524 K)
- Solubility in water: 573.0 g/100 mL (25 °C)
- Solubility: Insoluble in acetone, diethyl ether, pyridine and ethanol, 191 g/100 mL in methanol.
- Basicity (pKb): −744 kJ/mol
Synthesis
Caesium fluoride can be prepared by the reaction of caesium hydroxide (CsOH) with hydrofluoric acid (HF) and the resulting salt can then be purified by recrystallization. The reaction is shown below:
CsOH + HF → CsF + H2O
Using the same reaction, another way to create caesium fluoride is to treat caesium carbonate (Cs2CO3) with hydrofluoric acid and again, the resulting salt can then be purified by recrystallization. The reaction is shown below:
Cs2CO3 + 2 HF → 2 CsF + H2O + CO2
CsF is more soluble than sodium fluoride or potassium fluoride in organic solvents. It is available in its anhydrous form, and if water has been absorbed, it is easy to dry by heating at 100 °C for two hours in vacuo. CsF reaches a vapor pressure of 1 kilopascal at 825 °C, 10 kPa at 999 °C, and 100 kPa at 1249 °C.
Uses
- Industrial Applications: CsF is used in the manufacture of optical glasses, where it helps improve the transmission of light in certain wavelengths.
- Catalysis: It is sometimes used in catalytic reactions, particularly in organic chemistry for processes like dehydrofluorination.
- Nuclear Industry: CsF is used in the purification and extraction processes in the nuclear industry, especially in areas involving radioactive isotopes of caesium.
- Fluoride Treatment: CsF can be used as a source of fluoride ions for various chemical processes, including in the production of certain polymers.