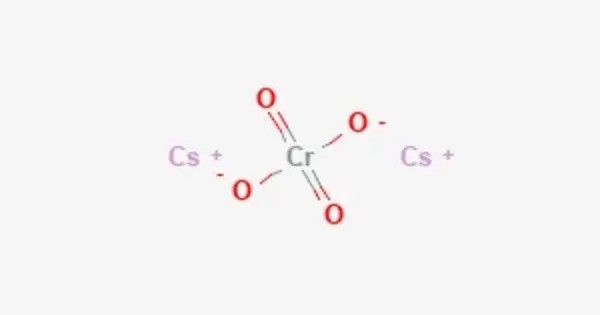
Caesium chromate or cesium chromate is an inorganic compound with the formula Cs2CrO4. It’s typically a yellow solid and is used in various chemical processes. It is a yellow crystalline solid that is the caesium salt of chromic acid, and it crystallises in the orthorhombic system. It is used as a precursor in the production of other chromium compounds, and sometimes in the manufacturing of pigments. However, it is not as commonly used today due to its toxicity.
Its major application in the past was for the production of caesium vapour during vacuum tube manufacture. Currently it is only used as the precursor for other compounds of academic interest.
Properties
Caesium chromate is typically a yellow solid, similar in appearance to other chromate salts. It is soluble in water, although it dissolves less readily compared to some other chromate salts. It is stable under normal conditions but can decompose or react under certain circumstances, particularly with reducing agents, releasing toxic chromium(VI) compounds.
- Chemical formula: Cs2CrO4
- Appearance: Yellow crystalline solid
- Density: 4.237 g/cm3
- Melting point: 954 to 961 °C (1,749 to 1,762 °F; 1,227 to 1,234 K)
- Solubility in water: 45.50 g/100 g (25 °C)
- Crystal structure: orthorhombic
Preparation
Caesium chromate is mainly obtained from the reaction of chromium(VI) oxide with caesium carbonate, wherein carbon dioxide gas is evolved:
CrO3(aq) + Cs2CO3(aq) → Cs2CrO4(aq) + CO2(g)
Alternatively, salt metathesis between potassium chromate and caesium chloride can be performed:
K2CrO4(aq) + 2 CsCl(aq) → Cs2CrO4(aq) + 2 KCl(aq)
Finally, caesium dichromate (itself derived via salt metathesis from ammonium dichromate) yields the chromate following alkalinisation with caesium hydroxide:
Cs2Cr2O7(aq) + 2 CsOH(aq) → 2 Cs2CrO4(aq) + H2O(ℓ)
Occurrences
- Laboratory Synthesis: Caesium chromate is typically synthesized in the laboratory rather than occurring naturally. It can be produced by reacting caesium carbonate (Cs₂CO₃) with sodium chromate (Na₂CrO₄) in aqueous solution.
- Chromium-containing deposits: While caesium chromate itself isn’t commonly found in nature, chromate compounds (such as sodium chromate or potassium chromate) do occur naturally in some mineral deposits.
Applications
Caesium chromate was formerly used in the final stages of creating vacuum tubes. Therein, caesium vapour was produced by reaction of caesium chromate with silicon, boron, or titanium as reducing agents. The vapour was then added to the tube to react with and remove remaining gases, including nitrogen and oxygen.
- Industrial Applications: Caesium chromate is used in the production of pigments (due to its yellow color), and as a reagent in analytical chemistry, particularly in the determination of certain metal ions.
- Specialized Chemicals: It may also be used in the synthesis of other caesium compounds, or as a source of the chromate ion in various chemical processes.