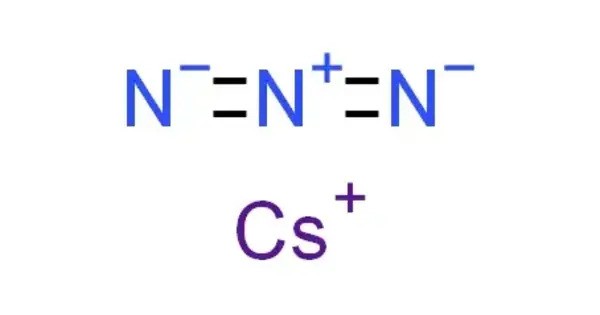Caesium azide or cesium azide is an inorganic compound of caesium and nitrogen. It is a salt of azide with the formula CsN3. Azides are salts containing the azide ion, which is a linear anion made up of three nitrogen atoms (N₃) connected by alternating single and triple bonds. Caesium azide is a white, crystalline solid and is highly reactive, especially because of the instability of the azide ion, which can decompose explosively under certain conditions.
Properties
aesium azide typically appears as a white crystalline solid. It is soluble in water, forming a colorless solution. It is highly reactive, especially under certain conditions. Caesium azide is known to be sensitive to heat, shock, and friction, making it potentially dangerous. Its decomposition releases nitrogen gas (N₂), which is highly exothermic.
- Chemical formula: CsN3
- Molar mass: 174.926 g/mol
- Appearance: colorless needles
- Density: 3.5 g/cm3
- Melting point: 310 °C (590 °F; 583 K)
- Solubility in water: 224.2 g/100 mL (0 °C)
Structure
CsN3 adopts the same structure as KN3, RbN3, and TlN3, crystallizing in a tetragonal distorted caesium chloride structure where each azide ion coordinates to eight metal cations, and each metal cation coordinates to eight terminal N centers. When heated to 151 °C, it transitions to a cubic structure.
Preparation and reactions
Caesium azide can be prepared from the neutralization reaction between hydrazoic acid and caesium hydroxide:
CsOH + HN3 → CsN3 + H2O
Caesium carbonate can also be used as the base:
Cs2CO3 + HN3 → CsN3 + CO2 + H2O
Caesium sulfate reacts with barium azide to form insoluble barium sulfate and caesium azide:
Cs2SO4 + Ba(N3)2 → 2CsN3 + BaSO4↓
The thermal decomposition of CsN3 in vacuo can be used as a method of generating high purity caesium metal:
2 CsN3 → 2 Cs + 3 N2
Occurrence
Caesium azide does not occur naturally in the environment, but it can be synthesized in a laboratory setting. It’s typically made by reacting caesium salts with sodium azide (NaN₃) or other azide compounds. Caesium azide is often used in chemical research and has applications in industries that require high-energy materials or specialized chemical reactions.
Applications
- Explosives: Due to its high reactivity, caesium azide has been studied for potential use in explosives or as a propellant material, although its instability limits its practical use.
- Chemical Synthesis: It may be used as a reagent in chemical reactions where the azide ion is needed for nucleophilic substitution or in other specialized synthesis processes.