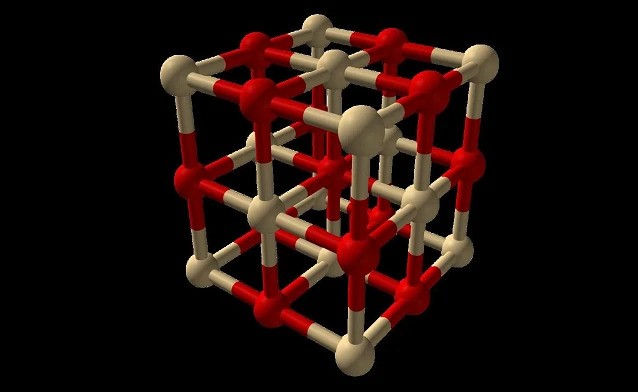
Cadmium oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula CdO. It is a chemical compound of cadmium and oxygen. It is one of the main precursors to other cadmium compounds. It appears as a yellowish or reddish powder. It crystallizes in a cubic rocksalt lattice like sodium chloride, with octahedral cation and anion centers.
It occurs naturally as the rare mineral monteponite. Cadmium oxide can be found as a colorless amorphous powder or as brown or red crystals. Cadmium oxide is an n-type semiconductor with a band gap of 2.18 eV (2.31 eV) at room temperature (298 K).
Properties
It is a semiconductor, which means it can conduct electricity under certain conditions. It is insoluble in water but can dissolve in strong acids or bases. It can react with acids to form cadmium salts and can also react with strong bases to form cadmium hydroxide.
- Chemical formula: CdO
- Molar mass: 128.413 g·mol−1
- Appearance: colorless powder (alpha form), red-brown crystal (beta form)
- Odor: odorless
- Density: 8.15 g/cm3(crystalline), 6.95 g/cm3 (amorphous) solid.
- Melting point: 900–1,000 °C (1,650–1,830 °F; 1,170–1,270 K), decomposition of amorphous form
- Boiling point: 1,559 °C (2,838 °F; 1,832 K) sublimation
- Solubility in water: 4.8 mg/L (18 °C)
Production and structure
Since cadmium compounds are often found in association with zinc ores, cadmium oxide is a common by-product of zinc refining. It is produced by burning elemental cadmium in air. Pyrolysis of other cadmium compounds, such as the nitrate or the carbonate, also affords this oxide. When pure, it is red, but CdO is unusual in being available in many differing colours due to its tendency to form defect structures resulting from anion vacancies. Cadmium oxide is prepared commercially by oxidizing cadmium vapor in air.
Natural Sources
Cadmium oxide can be found in trace amounts in certain ores, primarily in association with zinc ores such as sphalerite.
Industrial Production
It is produced as a byproduct during the smelting and refining of zinc and can also be synthesized for various applications.
Uses
Cadmium oxide is used in cadmium plating baths, electrodes for storage batteries, cadmium salts, catalysts, ceramic glazes, phosphors, and nematocide. Major uses for cadmium oxide are as an ingredient for electroplating baths, optoelectronic devices, and in pigments.
- Used in the production of pigments (such as cadmium yellow).
- Employed in electronics, particularly in the manufacture of solar cells and other semiconductor devices.
- Utilized in the production of ceramics and glass.
Health and Environmental Concerns
Cadmium compounds are toxic, and exposure can lead to serious health issues, including kidney damage and lung disease. Thus, handling CdO requires caution and appropriate safety measures.