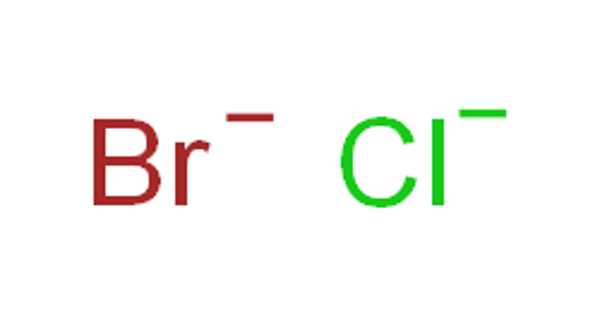Bromine monochloride is an interhalogen inorganic compound with the chemical formula BrCl. It is also known as bromine(I) chloride, bromochloride, and bromine chloride. It’s a reddish-yellow liquid with an obnoxious odor. It is a highly reactive golden yellow gas with a boiling point of 5 degrees Celsius and a melting point of 66 degrees Celsius. It has the CAS number 13863-41-7 and the EINECS number 237-601-4. It is a powerful oxidizing agent.
Properties
It appears as a reddish-yellow mobile liquid with an unpleasant odor. It’s a reddish-brown gas. It acts as an oxidizer. It is used in analytical chemistry to determine the amount of mercury in a substance. It can be used in industrial settings to kill bacteria and mold. It is extremely dangerous.
Toxic when ingested or inhaled, and an irritant to the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Prolonged exposure of the containers to high temperatures may cause violent rupturing and rocketing.
Reaction
The hydroxylamine oxidation by bromine monochloride, elementary chlorine in hydrochloric acid medium, and bromate and bromic acid has been studied. For the analytical determination of hydroxylamine, bromine monochloride oxidation is used.
Uses
Bromine monochloride is used in analytical chemistry to quantitatively oxidize mercury in the sample to Hg(II) state in order to determine low levels of mercury.
In industrial recirculating cooling water systems, bromine monochloride is used as a biocide, specifically as an algaecide, fungicide, and disinfectant. It is used in industry as a disinfectant, particularly for wastewater treatment.
In some types of Li-SO2 batteries, bromine monochloride is added to increase voltage and energy density.
Hazards
- Bromine Chloride can affect you when breathed in.
- Contact can severely irritate and burn the skin and eyes.
- Breathing Bromine Chloride can irritate the nose and throat.
Fire Hazard
Although the substance does not burn, it will aid in the combustion process. Liquefied gas vapors are initially heavier than air and spread along the ground. These are powerful oxidizers that will react violently or explosively with a wide range of materials, including fuels. It has the potential to ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Some will erupt violently when exposed to air, moist air, and/or water. Through pressure relief devices, cylinders exposed to fire may vent and release toxic and/or corrosive gas. When heated, containers may explode. Cylinders that have ruptured may take off in a rocket.