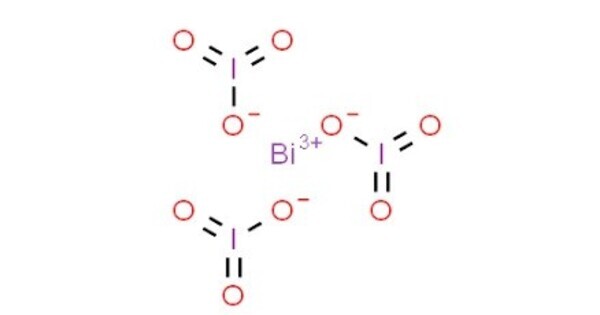
Bismuth iodate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Bi(IO3)3. It is an iodate salt of bismuth. In its typical form, it features bismuth in a +3 oxidation state. It often appears as a crystalline solid. The color can vary, but it’s generally a light yellow to white. It is relatively insoluble in water. Its solubility characteristics can influence how it is used or handled in various chemical processes.
Its anhydrate can be obtained by reacting bismuth nitrate and iodic acid, dissolving the resulting precipitate in 7.8 mol/L nitric acid, and heating to volatilize and crystallize at 70 °C; The dihydrate can be obtained by reacting bismuth nitrate and potassium iodate or sodium iodate. It is obtained by evaporation and crystallization in 7 mol/L nitric acid at 50 °C. Its basic salt BiOIO3 is known.
Properties
- Chemical formula: Bi(IO3)3
- Molar mass: 733.69
- Appearance: colourless crystals (dihydrate)
- Density: 6.096 g (anhydrous)
- Stability: It is generally stable under standard conditions but should be stored away from strong acids and bases, which could potentially decompose the iodate.
Reactivity
Like other iodates, it can be oxidized and might react with reducing agents. Its reactivity profile is influenced by the iodate ion’s ability to participate in redox reactions.
Occurrences
- Natural Occurrence: Bismuth iodate is not commonly found in nature in significant amounts. It is typically synthesized in a laboratory setting rather than being mined or extracted from natural sources.
- Synthesis: It can be prepared in a laboratory through the reaction of bismuth salts with iodic acid. The precise synthesis conditions can affect the properties and purity of the resulting compound.
Applications
Although it is not widely used in industry, bismuth iodate might find application in specialized areas such as catalysis or analytical chemistry. Its specific properties can make it useful in certain niche chemical processes or experiments.