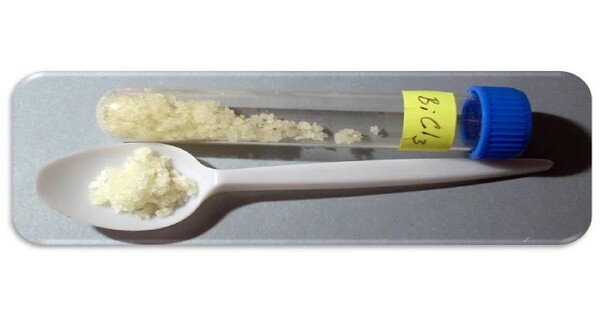
Bismuth chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula BiCl3. It typically appears as a white or colorless crystalline solid. It is a covalent compound and is the common source of the Bi3+ ion. In the gas phase and in the crystal, the species adopts a pyramidal structure, in accord with VSEPR theory. It is soluble in water and forms an acidic solution due to hydrolysis.
Structure
In the gas phase, BiCl3 is pyramidal with a Cl–Bi–Cl angle of 97.5° and a bond length of 242 pm. In the solid state, each Bi atom has three near neighbors at 250 pm, two at 324 pm, and three at a mean of 336 pm, the image above highlights the three closest neighbors. This structure is similar to that of AsCl3, AsBr3, SbCl3 and SbBr3.
Properties
- Chemical formula: BiCl3
- Molar mass: 315.34 g/mol
- Appearance: hygroscopic white to yellow crystals
- Density: 4.75 g/cm3
- Melting point: 227 °C (441 °F; 500 K)
- Boiling point: 447 °C (837 °F; 720 K)
- Solubility in water: Soluble,hydrolyses
- Solubility: soluble in methanol, diethyl ether, acetone
Preparation
Bismuth chloride can be prepared by reacting bismuth with chlorine gas or by reacting bismuth oxide with hydrochloric acid. It can be synthesized directly by passing chlorine over bismuth.
2 Bi + 3 Cl2 → 2 BiCl3
or by dissolving bismuth metal in aqua regia, evaporating the mixture to give BiCl3·2H2O, which can be distilled to form the anhydrous trichloride.
Alternatively, it may be prepared by adding hydrochloric acid to bismuth oxide and evaporating the solution.
Bi2O3 + 6 HCl → 2 BiCl3 + 3 H2O
Also, the compound can be prepared by dissolving bismuth in concentrated nitric acid and then adding solid sodium chloride into this solution.
Bi + 6 HNO3 → Bi(NO3)3 + 3 H2O + 3 NO2
Bi(NO3)3 + 3 NaCl → BiCl3 + 3 NaNO3
Uses
- Catalyst: It is used as a catalyst in certain chemical reactions.
- Chemistry: It’s used in various chemical syntheses and as a reagent in analytical chemistry.
- Medicine: In some cases, compounds of bismuth, including bismuth chloride, have been used in medicine, although they are not as common as other bismuth compounds like bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol).
Safety
While bismuth compounds are generally considered to have low toxicity compared to other heavy metals, handling bismuth chloride requires caution, particularly to avoid inhalation of dust or contact with skin, due to its acidic nature and potential irritant properties.