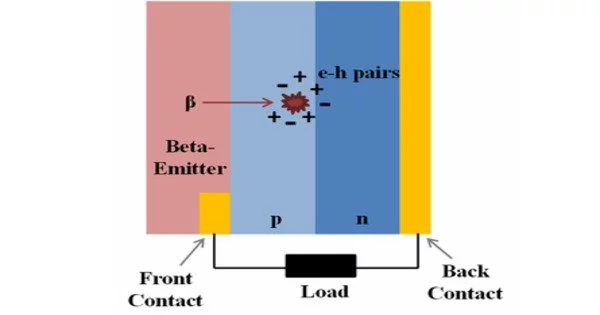
A betavoltaic device (betavoltaic cell or betavoltaic battery) is a type of nuclear battery that uses semiconductor junctions to generate electric current from beta particles (electrons) emitted by a radioactive source. It is a type of power source that converts beta radiation energy into electrical energy. The hydrogen isotope tritium is a common source. In contrast to most nuclear power plants, which use nuclear radiation to generate heat, which is then used to generate electricity, betavoltaic devices use a non-thermal conversion process to convert the electron-hole pairs produced by the ionization trail of beta particles traversing a semiconductor.
Betavoltaic power sources (and the related technology of alphavoltaic power sources) are especially well-suited to low-power electrical applications where the energy source must last a long time, such as implantable medical devices or military and space applications. Certain radioactive isotopes emit beta radiation, which is a type of ionizing radiation. This radiation is used by betavoltaic devices to generate a flow of electrons that can be harnessed and used as an electric current.
A betavoltaic device produces a relatively low voltage, typically in the range of a few hundred millivolts to a few volts. Multiple cells can be connected in series or parallel to increase the output voltage.
A betavoltaic device’s basic structure typically consists of a radioactive source and a semiconductor material. A radioactive isotope in the radioactive source emits beta particles. These beta particles have kinetic energy and can penetrate the semiconductor material, producing electron-hole pairs. The semiconductor material functions as a p-n junction, separating electrons and holes and producing a voltage potential.
The long operational life of betavoltaic devices is one of their advantages. In contrast to chemical batteries, which have a limited lifespan, betavoltaic devices have the potential to operate for many years, if not decades, depending on the half-life of the radioactive isotope used. However, when compared to other power sources, the power output of betavoltaic devices is relatively low, making them more suitable for low-power applications.
Application
Betavoltaic devices have been considered for use in a variety of applications, including low-power electronics, sensors, and medical implants. They can provide a long-lasting and compact power source, particularly in situations where replacing or recharging batteries is impractical or impractical.
It is worth noting that the use of radioactive materials in betavoltaic devices raises safety, handling, and disposal concerns. There are strict regulations and guidelines in place to ensure the safe use and management of such devices, especially to prevent any harmful effects from radiation exposure.