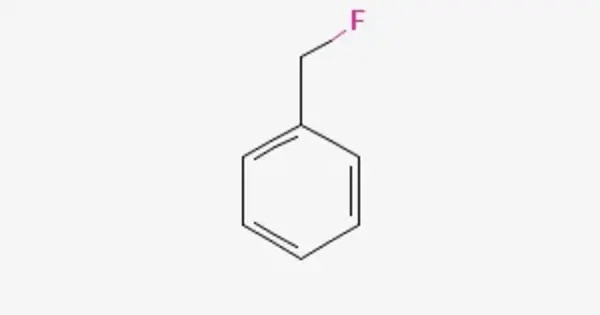
Benzyl fluoride is an organic compound consisting of a benzene ring substituted with a fluoromethyl group. It is a colorless liquid that is primarily used as an intermediate in organic synthesis. It is soluble in organic solvents like alcohol, acetone, and ether but has low solubility in water. It can undergo electrophilic substitution reactions, common for aromatic compounds, as well as nucleophilic substitution due to the presence of the fluorine atom.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C7H7F
- Molar mass: 110.129 g/mol
- Appearance: Colorless liquid
- Density: 1.0228 g/cm3
- Melting point: −35 °C (−31 °F; 238 K)
- Boiling point: 140 °C (284 °F; 413 K)
Synthesis
Benzyl fluoride can be synthesized through several methods, with the most common being the fluorination of toluene or benzyl chloride using various fluorinating agents (e.g., hydrogen fluoride, fluorine gas, or other fluoride compounds).
Occurrences
Synthetic Production: Benzyl Fluoride is mainly produced synthetically and is not commonly found in nature. It can be prepared through the halogenation of toluene (methylbenzene) with elemental fluorine or other fluorine sources under controlled conditions. This process often requires careful management, as fluorine is highly reactive.
Applications
- Organic Synthesis: Used as an intermediate in the synthesis of other compounds, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemicals.
- Fluorinated Compounds: Benzyl fluoride serves as a precursor to various fluorinated aromatic compounds used in industry and research.
- Polymer Industry: It is sometimes used in the preparation of specialty polymers and materials that require a fluorine atom attached to an aromatic ring.
Safety Considerations
- Toxicity: It may be harmful if ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin. Adequate safety precautions, such as using gloves and protective eyewear, are advised when handling benzyl fluoride.
- Reactivity: It can react with strong oxidizing agents and may be hazardous under certain conditions.