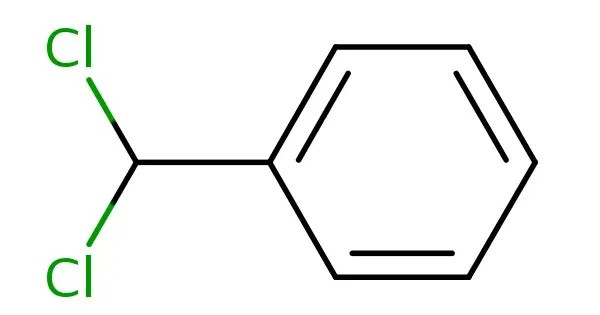
Benzal chloride is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CHCl2. This colourless liquid is a lachrymator and is used as a building block in organic synthesis. It is also known as Benzylidene dichloride and is a chlorinated derivative of benzyl chloride. It is an industrially important compound primarily used as an intermediate in the production of benzaldehyde and other chemicals.
Benzal chloride is toxic by inhalation and ingestion, and it can irritate the skin and eyes. It should be handled with care in well-ventilated areas. It is a reactive liquid with specific physical and chemical properties, including low solubility in water, a sharp odor, and toxicity. It is not found in significant quantities in nature, being synthesized mostly in chemical processes.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C7H6Cl2
- Molar mass: 161.03 g/mol
- Appearance: Colorless liquid
- Density: 1.254 g/cm3, liquid
- Melting point: −17 to −15 °C (1 to 5 °F; 256 to 258 K)
- Boiling point: 205 °C (401 °F; 478 K) (82 °C at 10 mmHg)
- Solubility in water: 0.25 g/L at 39 °C
- Vapor pressure: 0.6 kPa (45 °C)
Preparation
Benzal chloride is produced by the free radical chlorination of toluene, being preceded in the process by benzyl chloride (C6H5CH2Cl) and followed by benzotrichloride (C6H5CCl3):
C6H5CH3 + Cl2 → C6H5CH2Cl + HCl
C6H5CH2Cl + Cl2 → C6H5CHCl2 + HCl
C6H5CHCl2 + Cl2 → C6H5CCl3 + HCl
Benzylic halides are typically strong alkylating agents, and for this reason benzal chloride is treated as a hazardous compound.
Treatment of benzal chloride with sodium gives stilbene.
Most benzal chloride main industrial use is as a precursor to benzaldehyde. This conversion involves hydrolysis in the presence of base:
C6H5CHCl2 + H2O → C6H5CHO + 2 HCl
Uses
- Intermediate in organic synthesis: Benzal chloride is used in the production of various chemicals, including benzaldehyde (a valuable fragrance compound and precursor to pharmaceuticals).
- Plasticizers: It is sometimes used in the manufacture of plastics and resins.
- As a reagent: In laboratory settings, it is used as a reagent for various chemical reactions, such as the formation of benzylidene derivatives.