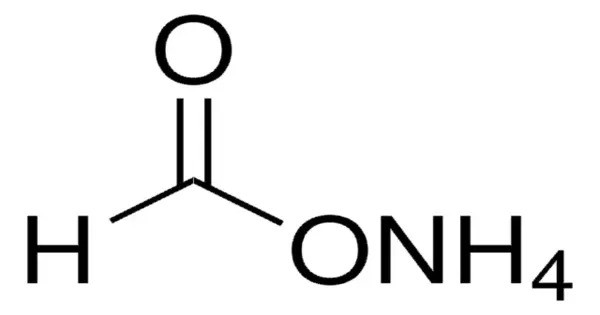
Ammonium formate, NH4HCO2, is the ammonium salt of formic acid. It is a colorless, hygroscopic, crystalline solid. It’s typically a white crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water. It is commonly used in organic synthesis and as a reagent in laboratories for various reactions, particularly in the formation of amides, and in some catalytic processes.
It’s also used in certain specialized applications like in the preparation of reducing agents or as a buffer in analytical chemistry. Because of its dual composition, it can act both as an acid and a base in various chemical reactions, depending on the conditions.
Reductive amination
Acetone can be transformed into isopropylamine as follows:
CH3C(O)CH3 + 2 HCO2− +NH4 → (CH3)2CHNHCHO + 2 H2O + NH3 + CO2
(CH3)2CHNHCHO + H2O → (CH3)2CHNH2 + HCO2H
Properties
- Chemical formula: CH5NO2
- Molar mass: 63.056 g·mol−1
- Appearance: White monoclinic crystals, deliquescent
- Odor: Slightly ammoniac
- Density: 1.26 g/cm3
- Melting point: 116 °C (241 °F; 389 K)
- Boiling point: 180 °C (356 °F; 453 K) decomposes
Occurrences
- Synthesis: Ammonium formate is primarily synthesized in the laboratory and industrial settings through neutralization of formic acid with ammonia.
- Natural Occurrence: While ammonium formate does not naturally occur in large quantities, it can be found in trace amounts in some natural processes involving the decomposition of organic matter. It is more common as a by-product of industrial processes rather than in nature.
- Biological Processes: There are some limited occurrences in biological systems, where formic acid and ammonia may combine under certain conditions, but these occurrences are not well-documented or widespread.
Uses
Pure ammonium formate decomposes into formamide and water when heated, and this is its primary use in industry. Formic acid can also be obtained by reacting ammonium formate with a dilute acid, and since ammonium formate is also produced from formic acid, it can serve as a way of storing formic acid.
- Reduction Reactions: In organic chemistry, ammonium formate is often used in hydrogenation reactions as a source of hydrogen.
- Analytical Chemistry: It is sometimes used in analytical techniques, such as mass spectrometry, as a reagent.
- Polymer Chemistry: It can also be involved in the preparation of certain polymers.