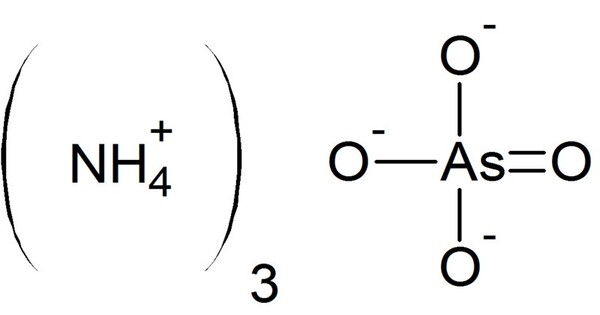Ammonium arsenate is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)3AsO4. It is the ammonium salt of arsenic acid. It is prepared by treating a concentrated solution of arsenic acid with ammonia, resulting in precipitation of colorless crystals of the trihydrate. Upon heating, it releases ammonia. This compound is used in various applications, including as a herbicide and in the preparation of certain types of glass.
Like other compounds of arsenic, it is classified as an IARC Group 1 carcinogen, i.e. carcinogenic to humans. Acid salts are also known, including diammonium arsenate and ammonium dihydrogen arsenate. However, due to the toxic nature of arsenic, its use is limited and regulated. Proper safety measures should be taken when handling or working with ammonium arsenate.
Properties
Ammonium arsenate typically appears as a white, crystalline solid. It is soluble in water, which makes it possible for it to dissolve and be transported in aqueous environments. It is relatively stable under standard conditions, but it can decompose upon heating or exposure to strong acids or bases.
- Chemical formula: (NH4)3AsO4. 3 H2O
- Molar mass: 247.1 (trihydrate)
- Solubility in water: Soluble
Industrial and Laboratory Uses
- Pesticides: Historically, ammonium arsenate was used as a pesticide and herbicide. However, due to its toxicity, its use has been largely restricted or banned in many countries.
- Wood Preservation: It has been used in wood preservation treatments, but again, its use is limited due to environmental and health concerns.
- Laboratory Reagent: It may be used in laboratories for certain chemical reactions or as a reagent in analyses involving arsenic.
Natural Occurrence
Ammonium arsenate does not occur naturally in significant quantities. It is usually found in nature as part of mineral deposits that contain arsenic, but it is more commonly synthesized for specific uses.
Toxicity
Due to the presence of arsenic, ammonium arsenate is highly toxic. Arsenic compounds are well known for their harmful effects on health, potentially causing poisoning or cancer with prolonged exposure.