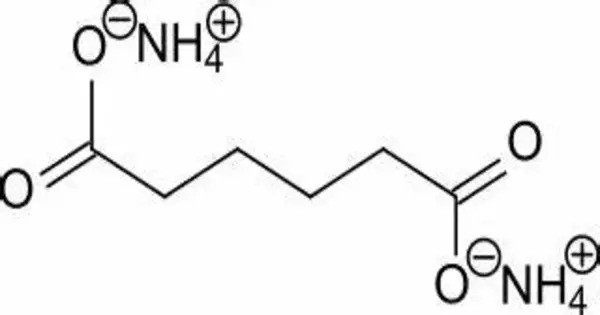
Ammonium adipate is a compound with formula (NH4)2(C4H8(COO)2). It is the ammonium salt of adipic acid. It is the ammonium salt of adipic acid, a dicarboxylic acid commonly used in the production of nylon and other polymers. It is a dicarboxylic acid commonly used in industrial and food applications. It is also used as a food additive and has the E number E359.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C6H16N2O4
- Molar mass: 180.204 g·mol−1
- Appearance: White crystalline solid (typically)
- Solubility: Soluble in water
- pH (in solution): Slightly acidic to neutral, depending on concentration
- Stability: Stable under normal temperatures and pressures
Uses
- Food industry: May be used as a food additive (e.g. acidity regulator), though more common salts of adipic acid (like sodium adipate) are typically used.
- Laboratory: Used as a buffer component or reagent.
- Chemistry: Intermediate in various syntheses, especially in the formation of polyamides or as a precursor for biodegradable polymers.
Occurrences
- Industrial Byproduct: May be formed during the neutralization of adipic acid with ammonia.
- Laboratory Synthesis: Typically synthesized for use in biochemical research or food additive applications.
- Not Naturally Occurring: Ammonium adipate is not known to occur naturally in the environment.
Safety
Generally regarded as safe (GRAS) in low concentrations.
- Handling: Like most ammonium salts, it should be handled with care—avoid inhalation or contact with skin/eyes in large quantities.
- Toxicity: Low toxicity, but may cause irritation to eyes or skin
- Storage: Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated place away from strong oxidizers