Adipic Acid
Definition
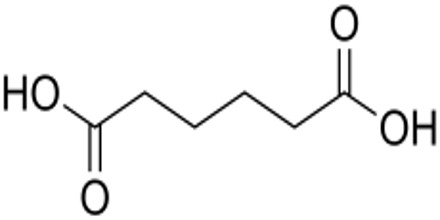
Adipic Acid is a colourless crystalline solid used in the preparation of nylon. It is insoluble in water. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. It is used to make plastics and foams and for other uses. The C6 straight-chain dicarboxylic acid is slightly soluble in water and soluble in alcohol and acetone. Nearly all commercial adipic acid is produced from cyclohexane.

It is produced from a mixture of cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone called “KA oil”, the abbreviation of ketone-alcohol oil. The KA oil is oxidized with nitric acid to give adipic acid, via a multistep pathway. Early in the reaction the cyclohexanol is converted to the ketone, releasing nitrous acid: HOC6H11 + HNO3 → OC (CH2)5 + HNO2 + H2O
Almost 90 percent of adipic acid produced is used in the production of nylon 66. The nylon, which has a protein-like structure, is further processed into fibers for applications in carpeting, automobile tire cord, and clothing. Adipic acid is also used to manufacture plasticizers and lubricant components. Food grade adipic acid is used as a gelling aid, an acidulant, and as a leavening and buffering agent.
Applications of Adipic Acid
The majority of the 2.5 billion kg of adipic acid produced annually is used as a monomer for the production of nylon by a polycondensation reaction with hexamethylene diamine forming 6,6-nylon. Other applications include some Polyurethane. Esters of Adipic Acid, such as DOA (Di-2-Ethylhexyl Adipate) are used as plasticizers for PolyVinyl Chloride (PVC) resins.
Adipic Acid has been incorporated into controlled-release tablets to obtain a pH-independent release for both weakly basic and weakly acidic drugs.
In foods, small but significant amounts of adipic acid are used as a food ingredient as a flavorant and gelling aid. It is used in some calcium carbonate antacids to make them tart.

Uses of Adipic Acid
Adipic Acid is used mainly in the production of nylon. It is also used in some calcium carbonate antacids to make them tart. Adipic acid has also been incorporated into controlled-release formulation matrix tablets to obtain pH-independent release for both weakly basic and weakly acidic drugs. Adipic acid in the urine and in the blood is typically exogenous in origin and is a good biomarker of jello consumption. Adipic acid, rare in nature, does occur naturally in beets, but this is not an economical source for commerce compared to industrial synthesis.
Reference: pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, thechemco.com, dictionary.com, wikipedia.