About Erythropoietin (EPO)
Definition
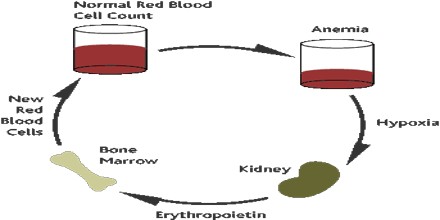
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a hormone produced by the kidney that promotes the formation of red blood cells by the bone marrow. The kidney cells that produce erythropoietin are sensitive to low level of oxygen in blood that travels through kidney. These cells make and produce erythropoietin when oxygen level is too low.
A low oxygen level may indicate a diminished number of red blood cells (anemia), or hemoglobin molecules that carry oxygen through the body. It is also produced in perisinusoidal cells in the liver. While liver production predominates in the fetal and perinatal period, renal production is predominant during adulthood. Recombinant human erythropoietin (rhEPO) is produced by recombinant DNA technology in cell culture. Several different pharmaceutical agents are available with a variety of glycosylation patterns and are collectively called erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESA).
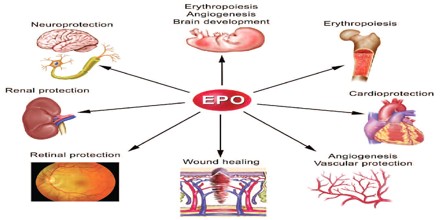
As the prime regulator of red cell production, erythropoietin’s major functions are to:
- Promote the development of red blood cells.
- Initiate the synthesis of hemoglobin, the molecule within red blood cells that transports oxygen.
In chemically EPO is a protein with an attached sugar (a glycoprotein). It is one of a number of similar glycoproteins that serve as stimulants for the growth of specific types of blood cells in the bone marrow. It stimulates the bone marrow to produce more red blood cells. The resulting rise in red cells increases the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
Work and Uses of EPO
Erythropoietin is a type of protein called a growth factor. There are different types; epoetin alfa, beta, zeta, theta (Eprex®, NeoRecormon®) and darbepoetin alfa (Aranesp®). People often call them EPO for short. It stimulates the bone marrow to make red blood cells. The bone marrow is a spongy material inside the bones where all of our blood cells are made.
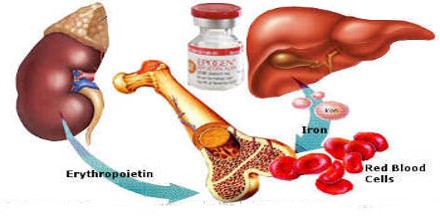
Erythropoietin is made naturally in the body. But it can be made outside the body and used as a treatment for anaemia. Anaemia means having too few red blood cells. Many people with cancer will develop anaemia at some time during their illness. Anaemia can also be caused by treatment with chemotherapy. Doctors sometimes use erythropoietin to treat anaemia instead of giving them a blood transfusion or if they cannot have a blood transfusion.
There are certain cancers that erythropoietin may not be safe to use in, for example, head and neck or breast cancer.
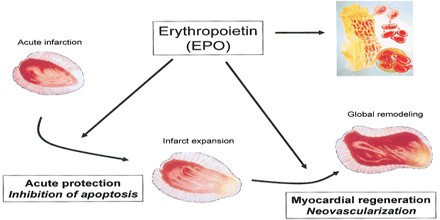
Facts of Erythropoietin (EPO)
- Erythropoietin (EPO) is a hormone produced by the kidney.
- Erythropoietin promotes the formation of red blood cells by the bone marrow.
- The erythropoietin hormone level can be detected and measured in the blood (the EPO test).
- Measurement of the blood erythropoietin level can be used to detect certain medical conditions.
- Erythropoietin can be synthesized and used as a treatment of some forms of anemia.
- Erythropoietin has been misused as a performance-enhancing drug by some athletes.
Side Effects of Erythropoietin (EPO)
Even though erythropoietin is a naturally-occurring substance, we may have side effects. When anyone given erythropoietin injections, the amount of it in their body becomes much higher than normal. However, these side effects aren’t usually severe and they do reduce after erythropoietin treatment ends.
Sometimes cancer drugs can result in very serious side effects, which rarely may be life-threatening. Rarely some people have an allergic reaction to erythropoietin, like as:
- red, warm and itchy bumps on the skin (like nettle rash)
- swelling of the lips, tongue or throat
- breathlessness, wheezing, a cough or sudden difficulty breathing
- tight chest or chest pain.
Some people have flu-like symptoms, such as feeling sick, joint pains, weakness, dizziness and tiredness. Cancer can increase the risk of developing a blood clot (thrombosis), and erythropoietin may increase this risk further. A clot can cause symptoms such as pain, redness and swelling in a leg, breathlessness and chest pain.
Erythropoietin can increase the risk of having a stroke. Signs of a stroke include weakness or numbness in one side of someone body, slurred speech or drooping of their face, mouth or eye.
Benefits of EPO
A number of trials have looked at the benefits of using erythropoietin to treat people with different types of cancer. The results from some of these trials have raised questions about its safety. Some have suggested that sometimes erythropoietin may cause the cancer to grow in size. These results are being reviewed by the drug safety authorities.
Although some people with cancer will benefit from having erythropoietin, their doctor will carefully consider the benefits and risks in their situation.