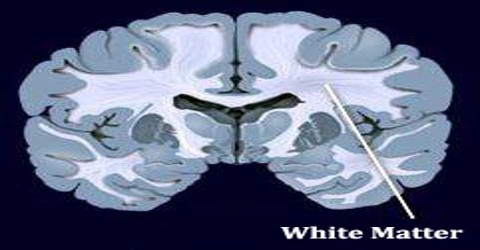
White Matter
Definition
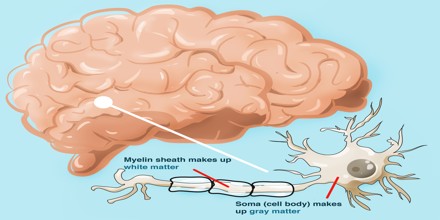
White matter is the whitish tissue of the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, made up chiefly of nerve fibers (axons) covered in myelin sheaths. White matter is named for its relatively light appearance resulting from the lipid content of myelin. However, the tissue of the freshly cut brain appears pinkish white to the naked eye because myelin is composed largely of lipid tissue veined with capillaries. Its white color in prepared specimens is due to its usual preservation in formaldehyde.
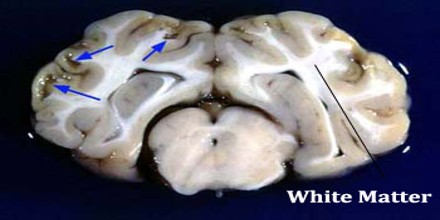
Structure and Functins of White Matter
The internal capsules are white matter tracts which connect with the corona radiata and white matter of the cerebral hemispheres superiorly, and with the brain stem inferiorly.The corpus callosum is a white matter tract located in the midline. It arches over the lateral ventricles and connects white matter of the left and right cerebral hemispheres.
White matter forms the bulk of the deep parts of the brain and the superficial parts of the spinal cord. Aggregates of gray matter such as the basal ganglia (caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, substantia nigra, subthalamic nucleus, nucleus accumbens) and brainstem nuclei (red nucleus, cranial nerve nuclei) are spread within the cerebral white matter.
It is the tissue through which messages pass between different areas of gray matter within the central nervous system. The white matter is white because of the fatty substance (myelin) that surrounds the nerve fibers (axons). This myelin is found in almost all long nerve fibers, and acts as an electrical insulation. This is important because it allows the messages to pass quickly from place to place.
Disease and Prevent of White Matter
Many different diseases, injuries, and toxins can cause changes in your white matter. Doctor’s point to the same blood vessel problems that lead to heart trouble or strokes: Long-term high blood pressure, Ongoing blood vessel inflammation, Smoking, Diabetes, High cholesterol, Parkinson’s disease and Stroke. Alcohol use disorders are associated with decrease in white matter volume. Animal studies suggest that alcohol may cause loss of white matter by damaging oligodendrocytes, the glial cell responsible for maintaining myelin.
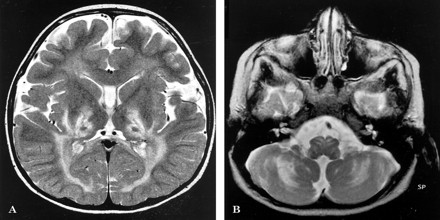
White matter disease is different from Alzheimer’s, which affects the brain’s gray matter. A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) test, which takes pictures of the inside of your brain, can show any damage. Changes to white matter will show up super-bright white on an MRI scan.
There isn’t a specific treatment. The goal is to treat the cause of the damage and stop the disease from getting worse.