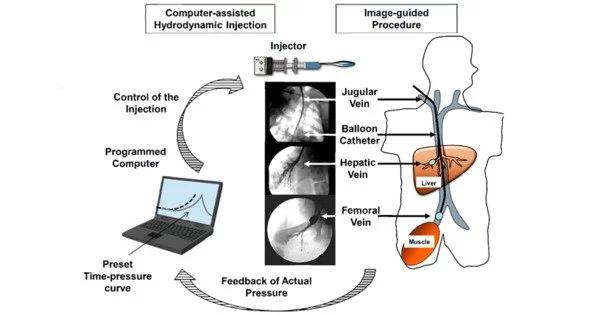
Hydrodynamic delivery (HD) is a method of delivering substances or agents, such as drugs or therapeutic molecules, that uses fluid dynamics principles. It is a method for inserting DNA into rodent models. This method typically involves the use of a fluid, usually a liquid, to transport and deliver the desired substance to a specific location within the body.
Genes are introduced into the animal’s bloodstream and expressed in the liver. The fluid dynamics involved in hydrodynamic delivery play an important role in facilitating the movement of substances through biological systems. This protocol can be used to determine gene function, regulate gene expression, and develop pharmaceuticals in vivo.
Application
Hydrodynamic delivery can be used for a variety of medical purposes, including chemotherapy drug delivery, pain management, and the treatment of certain medical conditions. The goal is to achieve more efficient and targeted therapeutic agent delivery to specific tissues or organs while minimizing side effects in non-targeted areas.
Hydrodynamic delivery is commonly used in gene therapy, where it is used to introduce genetic material into cells. This is especially important in the treatment of genetic disorders or other conditions that can be addressed by modifying the genetic makeup of cells.
The injection or infusion of a solution containing the therapeutic substance into the bloodstream is a common method of hydrodynamic delivery. The fluid dynamics created by the solution’s flow through blood vessels aid in the distribution of the substance to the intended target tissues or cells. This method can be useful for reaching specific organs or areas that are difficult to reach using traditional delivery methods.
Hydrodynamic delivery has been investigated in a variety of research and medical applications, and it is still an area of active research and development. Researchers are looking into ways to improve delivery systems, improve targeting, and increase the efficiency and safety of hydrodynamic delivery methods for various therapeutic purposes.