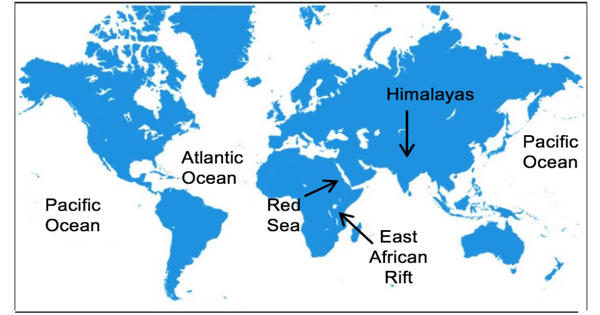
SLM refers to strategies and technologies that strive to integrate the management of land, water, and other natural resources in order to meet human needs while also guaranteeing long-term sustainability, ecosystem services, biodiversity, and livelihoods. This strategy considers a variety of ecological, economic, and social aspects to guarantee that land resources are neither depleted or degraded over time.
The phrase is used in a variety of contexts, including regional planning, soil or environmental conservation, and property and estate management. It is essential for dealing with concerns such as land degradation, habitat loss, food security, and climate change.
Key principles and practices of sustainable land management include:
- Soil Conservation: Protecting and improving soil quality is critical for long-term agricultural and land usage. Crop rotation, organic farming, and no-till farming are all practices that assist avoid soil erosion and increase soil health.
- Biodiversity Conservation: The preservation of biodiversity and natural habitats is critical for preserving an area’s ecological equilibrium. Protecting ecosystems such as wetlands and forests helps to ensure the land’s long-term health.
- Water Management: Water efficiency and management are crucial for long-term land usage. This covers methods such as rainwater harvesting, irrigation efficiency, and water pollution reduction.
- Afforestation and Reforestation: Planting trees and restoring forests can aid in carbon sequestration, battle desertification, and give wildlife habitat. Forestry practices that are sustainable are also significant.
- Land Use Planning: Responsible urban and rural land use planning can help minimize urban sprawl, protect natural areas, and promote efficient land use in both residential and agricultural areas.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Promoting practices like organic farming, integrated pest management, and agroforestry can help reduce the environmental impact of agriculture while maintaining or improving productivity.
- Land Degradation Control: Implementing measures to combat land degradation, such as erosion control, desertification prevention, and the restoration of degraded land, is a key component of sustainable land management.
Local communities should benefit from sustainable land management, and it should be socially equitable. It should take into account the needs and aspirations of individuals who rely on the land for a living. It can help to mitigate climate change by storing carbon in soils and vegetation. It can also assist communities in adapting to climate change by making land and water resources more resilient.
Sustainable land management strategies are critical in combating a variety of global concerns such as land degradation, biodiversity loss, food security, and climate change. Individuals, communities, and governments can help ensure that the land remains productive and environmentally healthy for future generations by embracing these concepts and practices.