Introduction
In the recent years banking industry is flourishing more rapidly than any other industry. So the numbers of banks are increasing in this industry. As a result the competition is also increasing so the companies are being so much dependent on strategic management to survive in the competition. In the assignment we will see the strategic management process of Dhaka Bank.
Chapter 1
Company profile
Dhaka Bank Limited
Bangladesh economy has been experiencing a rapid growth since the ’90s. Industrial and agricultural development, international trade, inflow of expatriate Bangladeshi workers’ remittance, local and foreign investments in construction, communication, power, food processing and service enterprises ushered in an era of economic activities. Urbanization and lifestyle changes concurrent with the economic development created a demand for banking products and services to support the new initiatives as well as to channelize consumer investments in a profitable manner. A group of highly acclaimed businessmen of the country grouped together to responded to this need and established Dhaka Bank Limited in the year 1995.
The Bank was incorporated as a public limited company under the Companies Act. 1994. The Bank started its commercial operation on July 05, 1995 with an authorized capital of Tk. 1,000 million and paid up capital of Tk. 100 million. The paid up capital of the Bank stood at Tk 1,289,501,900 as on June 30, 2006. The total equity (capital and reserves) of the Bank as on June 30, 2006 stood at Tk 2,188,529,224.
The Bank has 33 branches across the country and a wide network of correspondents all over the world. The Bank has plans to open more branches in the current fiscal year to expand the network.
The Bank offers the full range of banking and investment services for personal and corporate customers, backed by the latest technology and a team of highly motivated officers and staff.
In our effort to provide Excellence in Banking services, the Bank has launched Online Banking service, joined a countrywide shared ATM network and has introduced a co-branded credit card. A process is also underway to provide e-business facility to the bank’s clientele through Online and Home banking solutions.
Dhaka Bank Ltd. is the preferred choice in banking for friendly and personalized services, cutting edge technology, tailored solutions for business needs, global reach in trade and commerce and high yield on investments.
Mission Statement As Their Own Tongue
Mission
To be the premier financial institution in the country providing high quality products and services backed by latest technology and a team of highly motivated personnel to deliver Excellence in Banking.
Priority assessment scales for Business scope

Vision
At Dhaka Bank, we draw our inspiration from the distant stars. Our team is committed to assure a standard that makes every banking transaction a pleasurable experience. Our endeavor is to offer you razor sharp sparkle through accuracy, reliability, timely delivery, cutting edge technology, and tailored solution for business needs, global reach in trade and commerce and high yield on your investments.
Goal
Our people, products and processes are aligned to meet the demand of our discerning customers. Our goal is to achieve a distinction like the luminaries in the sky. Our prime objective is to deliver a quality that demonstrates a true reflection of our vision – Excellence in Banking.
Major Functions of the Organization

Functions of Corporate Banking
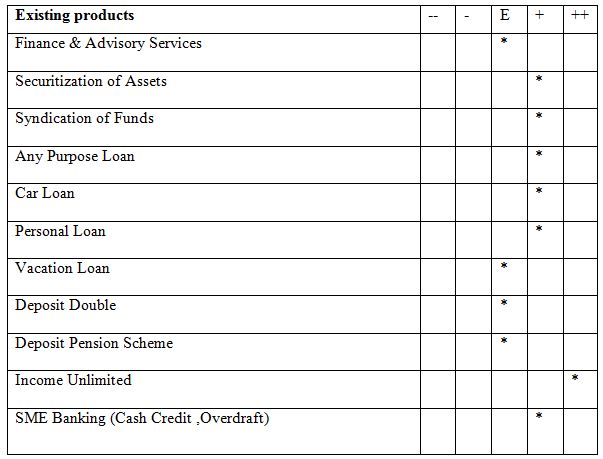
Finance & Advisory Services
Given the needs of its large and varied base of corporate clients Dhaka Bank will be positioning itself to provide investment banking advisory services. These could cover awhole spectrum of activities such as Guidance on means of raising finance from the local Stock markets, Mergers and Acquisitions, Valuations, Reconstructions of Distressed companies and other expert knowledge based advice. By this means Dhaka Bank hopes to play the role of strategic counselor to blue-chip Bangladesh companies and then move from the level of advice to possible implementation of solutions to complex financing problems that may arise from time to time. This would be an extra service that would complement the normal financing activities that Dhaka Bank already offers to corporate business houses.
Securitization of Assets
A powerful and effective means of generating funds for a certain category of institutions, Securitization of Assets is still in its infancy in The need however for such a service is great and there is a lot of support from multilateral financial institutions, such as the World Bank and the Asian Development Bank, for such activities to be developed further in this country.
Dhaka Bank intends to take up this challenge and play a significant role in ensuring that Securitization of Assets becomes a normal part of the range of financial instruments available for organizations who can count on a steady, but piecemeal, flow of revenue and want to translate this stream into cash resources with which to carry out further lending activities to new customers. Some practical issues still need to be settled such as those concerning pricing, or the legal framework, but it is expected that, as Dhaka Bank and other institutions pursue more such securitization activities these will be resolved.
Syndication of Funds
There has been a surge in the number of syndication deals closed in the last few years. 2004 was an exceptionally good year for syndicated deals for the local commercial banks also for the foreign banks. The total number of syndications in 2004 exceeded 10 totaling over Tk. 10 billion. This rise in the number of syndications can be primarily attributed to the prudential lending guidelines of the Bangladesh Bank. A commercial bank may provide funded facilities up to a maximum of 25% of its equity. Due to this reason, projects with sizeable costs need to approach more than one bank for their debt requirements and therefore the demand for syndications exist. Credit risk diversification has led many international companies to introduce credit derivatives that are actively being traded. Securitzation of assets is one such credit risk derivative that allows financial institutions to diversify their portfolios.
At Dhaka Bank Limited, the Syndications and Structured Finance unit was setup on October 30, 2004. This unit successfully closed two syndicated deals in the first and second quarters of 2004. The Syndications and Structured Finance team as a business unit soon followed up by closing another deal totaling Tk 2.10 billion for a large local corporate. The year (2004) being the first full year of operation for the team ended on a high note as we were able to close three syndicated deals as the Lead Bank, two deals as the Co-Arranger and several other deals as a participant.
Personal Banking
Any Purpose Loan:Its time to do a few things you really wanted to.Introducing “Any Purpose Loan” from Dhaka Bank Limited. Now you can get loan up to Tk. 500,000* to spend it any way you choose to. Just walk into any of our branches and walk out loaded.
Car Loan:
As part of establishing a personal banking franchise of Dhaka Bank Limited, the bank has successfully launched Car Loan. The product is a term financing facility to individuals to aid them in their pursuit of have a car of their dream. The facility becomes affordable to the clients as the repayment is done through fixed installment s commonly known as EMI (equated monthly installment) across the facility period. Depending on the size and purpose of the loan, the number of installments varies from 12 to 60 months. In case of brand new cars the loan tenure will be maximum 72 months
Personal Loan:
As part of establishing a personal banking franchise of Dhaka Bank Limited, the bank has successfully launched Personal Loan. The product is a term financing facility to individuals to aid them in their purchases of consumer durables or services. The facility becomes affordable to the clients as the repayment is done through fixed installment s commonly known as EMI (equated monthly installment) across the facility period. Depending on the size and purpose of the loan, the number of installments varies from 12 to 48months.
Vacation Loan
As part of establishing a personal banking franchise of Dhaka Bank Limited, the bank has successfully launched Vacation Loan. The product is a term financing facility to individuals to aid them in their pursuit of spending a vacation in the country or abroad. The facility becomes affordable to the clients as the repayment is done through fixed installment s commonly known as EMI (equated monthly installment) across the facility period. Depending on the size and purpose of the loan, the number of installments varies from 12 to 48 months.
Deposit Double
Deposit Double is a time specified deposit scheme for individual clients where the deposited money will be doubled in 6 years. The key differentiators of the product will be:
Amount of deposit – The minimum deposit will be BDT 50,000.00 (either singly or jointly). The client will have the option of depositing any amount in multiples of BDT 10,000 subject to a maximum of Tk 20,00,000 in a single name and Tk 35,00,000 in joint name .
Tenure of the scheme – The tenure of the scheme will be 6 years.
Premature encashment – If any client chooses to withdraw the deposit before the tenure, then s/he will only be entitled to prevailing interest rate on savings account in addition to the initial deposit. However, withdrawal of the deposited amount before one year will not earn any interest to the depositor(s).
OD Facility against Deposit – Clients will have the option of taking advance upto 90% of the initial deposited amount. The lending rate will be tied up with the interest rate offered on the deposit.
Deposit Pension Scheme:
Dhaka Bank is well poised to be the leading Personal Banking business amongst the local private banks. Bank’s conscious efforts in brand building, introducing and supporting new packaged products, developing PB organization along with non-traditional delivery channels have resulted in good brand awareness amongst its chosen target markets.
Installment based savings schemes are a major category of saving instruments amongst mid to upper middle-income urban population . DPS is an installment based savings scheme (Deposit Pension Scheme) of Dhaka Bank for individual clients. The key differentiators of the product will be –
Amount of monthly deposit – The scheme offers the clients the flexibility of tailoring the amount of monthly deposit based on his monthly cash flow position. The minimum monthly deposit will be BDT 500.00 The client will have the option of depositing any amount in multiples of BDT 500.00 subject to a maximum of Tk 20,000.
Income Unlimited:
The management of Dhaka Bank Limited is pleased to launch Special Deposit Scheme, a new liability product on May 04, 2005.
ProductName
Special Deposit Scheme
Product Features
| Deposit Amount | In multiples of Tk 50,000 However the minimum deposit will be Tk 1,00,000 (singly or jointly) and the maximum Tk 50,00,000 (singly/Jointly). |
| Initial Deposit Date | Any day of the month |
| Interest Due | One month after the initial deposit date the interest will be credited to the savings/current account. |
| Tenure | 3 Years |
| Monthly income on Tk 100,000 | Tk 1,000 subject to 10% Income Tax |
| Rate of Interest | 12% (simple) |
Smart Plant
Smart Plant offers you to multiply your initial cash to 10 times in 6 years. You are required to deposit at least Taka 10,000 or multiple of it to avail the opportunity. In single name you can deposit maximum Taka 50,00,000. Dhaka Bank shall contribute 4 times of your deposited amount to build up a fund for issuance of Smart Plant.
SME Banking
Since inception, the Dhaka Bank has held socio-economic development in high esteem and was among the first to recognize thepotentialsofSMEs.
Recognizing the SME segment’s value additions and employment generation capabilities quite early, the Bank has pioneered SME financing in Bangladesh in 2003, focusing on stimulating the manufacturing sector and actively promoting trading and service businesses.
Products under SME banking
Cash Credit
Overdraft
Chapter 2
Research method
Objective of the study
Strategic management is one of the important of study. For starting a new business or to survive in the market or to make improvement in the business selection of strategy is very important critical also. In the competitive age without strategy organization can not survive and run the organization successfully that is why strategy is important for all type of organization. The objective of this study is to understand, how the organization follow strategic management. The process of formulating, implementing and evaluating strategy. That means the over all practice of strategic management. Which will help us bust our knowledge on the practical practice of strategic management.
Analysis technique
In the assignment we tried to give a clear view of strategic management process. To implement this topic we have first selected a company and analyzed details about the company’s profile, mission, objective, function and then gave details of that industry. After that we took a short interview of management of that company to know details about strategic management practice of that company.
Data collection
To complete the assignment we have dependent different sources for collecting data from primary source to secondary source.
- PRIMARY SOURCE: A SHORT INTERVIEW OF DHAKA BANK MANAGEMENT
- SECONDARY SOURCES:
www.dhakabankltd.com
Chapter 3
Findings and analysis
Industry profile
After the birth of Pakistan in 1947, the State Bank of Pakistan, the central bank of the country, came into being in 1948. Later, the National Bank of Pakistan, a commercial bank was set up in 1949. In all, 36 scheduled commercial banks were in operation throughout Pakistan. Most of these banks were owned by Pakistanis. Only three of them, namely, National Bank of Pakistan, Habib Bank, and the Australasia Bank had a branch in East Pakistan in 1949. During 1950-58, three other Pakistani-owned banks, the Premier Bank, Bank of Bawalpur and Muslim Commercial Bank had opened branch offices in East Pakistan. Four Pakistani-owned banks, the United Bank, Union Bank, Standard Bank and Commerce Bank conducted business in the province during 1959 – 1965. The province had only two banks owned by local business groups and with headquarters at Dhaka, the Eastern Mercantile Bank and Eastern Banking Corporation established in 1959 and 1965 respectively.
The banking system in the territory of Bangladesh grew slowly during the British and Pakistan periods. There were only 25 bank branches in 1901 and the number grew to 668 in 1946. Creation of Pakistan was a deterrent in the sector as was evidenced by the closure of bank branches, which came down to 148 in 1950. In 1965, the number rose again to 545. Subsequent years, however, showed dramatic changes in the situation and the number of bank branches increased to 1,025 in 1970. The banking system in Bangladesh started functioning with 1,130 branches of 12 banks inherited from Pakistan. Subsequently, these banks were nationalised and renamed after being merged into six banks. The new names of the banks were the sonali bank(The National Bank of Pakistan, The Bank of Bawalpur, The Premier Bank), (Habib Bank, Commerce Bank), k(United Bank, Union Bank), i b(Muslim Commercial Bank, Standard Bank), k(Australasia Bank, Eastern Mercantile Bank) and (Eastern Banking Corporation).
b, the central bank of the country, was set up on 16 December 1971 by the Bangladesh Bank Order 1972. The government accepted the assets and liabilities of the Deputy Governor’s office of the State Bank of Pakistan in Dhaka and declared the Bangladesh Bank as a fully effective and permanent central bank.
Bangladesh Bank is empowered to regulate the issue of currency, maintain reserves, and manage the monetary and credit system with a view to stabilising domestic currency, maintaining a high level of production, reducing t, and increasing real income. It is also responsible for fostering the growth and development of the country’s productive resources. The bank has the responsibility of overseeing and regulating the country’s banking system. In addition, the head office at Dhaka, Bangladesh Bank has nine branch offices, two in Dhaka city (Motijheel and Sadarghat) and one each in Chittagong, Khulna, , Sylhet, Bogra, Rangpur and Barisal. The paid up capital of Bangladesh Bank is Tk 30 million divided into 300,000 shares of Tk 100 each. The total share capital is fully paid by the government. A nine-member board of directors headed by a Governor as the chief executive oversees the affairs of the bank.
To conduct banking in Bangladesh, all banks have to have licenses from the Bangladesh Bank under the Bank Companies Act 1991. To be able to get a license, all intending banks have to be registered with the Registrar of Joint Stock Companies under the 1994, and collect Certificate of Incorporation. Moreover, to collect capital through public offerings of shares, intending banks have to obtain permission from the country’s s commission.
Banking institutions in Bangladesh can be classified under different groups. Most banks fall under the category of branch banking ie, the banks operate through branches at home and abroad under the control of their head offices. Foreign branches of Bangladeshi banks have to abide by home country regulations. Under the ownership-based classification, banks in Bangladesh are classified as government/nationalised, private, foreign, and joint ownership banks. The country had 6 nationalised commercial banks (NCB) until 1983, when one of them, the Rupali Bank was denationalised. Another government bank, the Pubali Bank, was denationalised in 1986.
There is no independent merchant bank, investment bank or exchange bank in Bangladesh. However, some commercial banks carry out merchant banking in addition to their usual banking activities. Recently, the Securities and Exchange Commission of the country issued permission to 25 financial institutions to do merchant banking. Commercial and specialised banks invest their funds in different sectors of the economy. A total of 22 private leasing companies and financial institutions were given permission to conduct investment activities in various sectors of the economy. Some branches of both nationalised and private commercial banks have been permitted to conduct business under the Foreign Exchange Regulation Act 1947. Such banks are called authorised dealers and their club or association bears the name BAFEDA – Bangladesh Foreign Exchange Dealers Association. Apart from the authorised dealers, more than 400 Money Changers throughout the country are engaged in buying and selling of foreign exchange.
Depending upon the relationship with and the degree of control of the Bangladesh Bank banks in Bangladesh are divided into scheduled and non-scheduled banks. Scheduled banks are enlisted by the Bangladesh Bank under the provisions of section 37 of the Bangladesh Bank Order 1972. They are promise bound to obey central bank instructions, rules and regulations especially, those relating to required capital and provisions, statutory liquidity reserves, audited returns etc. Through scheduling, banks gain special status and enjoy some special facilities from the central bank such as re-discounting, participation in the money market, membership of the clearing house and deposit insurance scheme. Non-scheduled banks do not enjoy such privilege. The list of non-scheduled banks in Bangladesh includes the Eden Bank, Saidpur Commercial Bank, Comilla Co-operative Bank, Dinajpur Industrial Bank, Rajshahi Bank, Shankar Bank, Faridpur Banking Corporation and Madaripur Commercial Bank.
Banks in Bangladesh have correspondent relationship with other banks in foreign countries in order to sell their services or to purchase services from them. A summary picture of the country’s commercial banks is presented in the table on Banks of Bangladesh.
Although only three in number, nationalised commercial banks dominate banking activities in the country, especially the mobilisation of deposits and making advances. Their share in total bank deposits on 31 March 2000 was 57.28%, while that of domestic private banks, foreign private banks, and the specialised banks was 29.01%, 8.42% and 5.29% respectively. The share of NCBs, domestic private banks, foreign private banks and specialised banks in advances on the same date was 51.66%, 29.25%, 6.03% and 13.06% respectively.
Laws that directly regulate the banking system of Bangladesh are: Bangladesh Bank Order 1972; Bank Company Act, 1991; Bangladesh Bank (Nationalisation) Order 1972; Companies Act 1913 and 1994; Deposit Insurance Order 1984; Bankruptcy Act 1997; Insolvency Act 1920; Financial Court Act 1990; Foreign Exchange (Regulation) Act 1986; Financial Institutions Act 1993; Financial Institutions Rules 1994; and Co-operative Societies Ordinance 1984.
Laws that indirectly influence the banking system and for which references are made in the Banking Company Act 1991 are: Code of Civil Procedure 1898; Code of Criminal Procedure 1898; Evidence Act 1872; General Clauses Act 1897; Limitations Act 1908; Negotiable Instruments Act 1881;
Table Statement of Banks in the year 2004
| Name of Bank | Branches | Correspondent Banks |
| Sonali Bank | 1307 (1)* | 369 |
| Janata Bank | 898 (4) | 1160 |
| Agrani Bank | 903 | 980 |
| Rupali Bank | 514 (1) | 160 |
| Pubali Bank | 350 | 433 |
| Uttara Bank | 198 | 300 |
| National Bank | 66 | 143 |
| The City Bank | 76 | 252 |
| United Commercial Bank | 79 | 110 |
| Arab – Bangladesh Bank | 62 (1) | 310 |
| IFIC Bank | 54 (2) | 200 |
| Islami Bnak Bangladesh | 109 | 650 |
| Al-Baraka Bank Bangladesh | 34 | 117 |
| Eastern Bank | 21 | 37 |
| National Credit & Commerce Bank | 27 | 232 |
| Prime Bank | 20 | 198 |
| South-East Bank | 12 | 190 |
| Dhaka Bank | 12 | 271 |
| Al-Arafa Islami Bank | 34 | 127 |
| Social Investment Bank | 12 | 52 |
| Dutch-Bangla Bank | 6 | 9 |
| Mercantile Bank | 8 | 9 |
| Standard Bank | 9 | 13 |
| One Bank | 1 | 55 |
| Exim Bank | 3 | 7 |
| Premier Bank | 4 | 11 |
| First Security Bank | 1 | 3 |
| Mutual Trust Bank | 2 | 14 |
| Bank Asia | 5 | 5 |
| Trust Bank | 5 | 25 |
| Bangladesh Commerce Bank | 24 | 13 |
Strategic Management Process in The Organization
Company’s strategy is an important and secret subject. All the time the company doesn’t want to disclose the information. So it is very difficult to know about the strategy of the company.
But when we talked to the management of the company they said us usually there is not any fixed strategy, the market condition and the competition rapidly change so the strategies are also changes, though there does not happen any massive change in the corporate level strategy.
Management also said that at the corporate strategy there had used formal strategic management process. Such as defining the organization’s guiding philosophy, purpose, mission; establishing long range objectives to achieve the mission; selecting the strategy to achieve the long range objectives; development of organizational structure, selecting leadership and providing motivational system; establishing short range objectives, developing budgets and developing functional strategy and establishing standards to evaluating the performance, monitoring progress in the execution; initiating corrective actions etc.
When we wanted to know about the strategy process model, the management said any strategy is not formulated based on model but when any strategy is goon to formulate the model is automatically followed.
Management also said when they go to formulate any strategy for business unit and function unit, first they identify the reason which indicates the guiding philosophy, purpose and the mission. Then they analysis all the factors relevance to the strategy which may be inside of the organization and outside of the organization. After that they find out the best way to do the job and then they set factors to implement or to get done the job. This over all process actually indicates the model.
One thing more, In case of formulating business unit and functional unit strategy the company give priorities on competitors so the competitive position of the company is analyzed bellow
Competitive Analysis
Total Operating Expenses:
| Name of the Bank | Total Operating Expenses(Taka in million) |
| Dhaka Bank | 3.80 |
| Dutch Bangla Bank | 3.09 |
| HSBC Bank | 2.60 |
| Southeast Bank | 3.10 |
| Prime Bank | 2.90 |
Total Assets:
| Name of the Bank | Total Assets ( Taka In million) |
| Southeast Bank | 231.35 |
| Dutch Bangla Bank | 260.55 |
| Dhaka Bank | 405.40 |
| HSBC Bank | 360.34 |
| Prime Bank | 326.62 |
Total Liability:
| Name of the Bank | Total Liability( Taka In million) |
| Social Investment Bank | 203.68 |
| Mercantile Bank | 232.69 |
| HSBC Bank | 112.00 |
| Dutch Bangla Bank | 235.15 |
| Dhaka Bank | 383.50 |
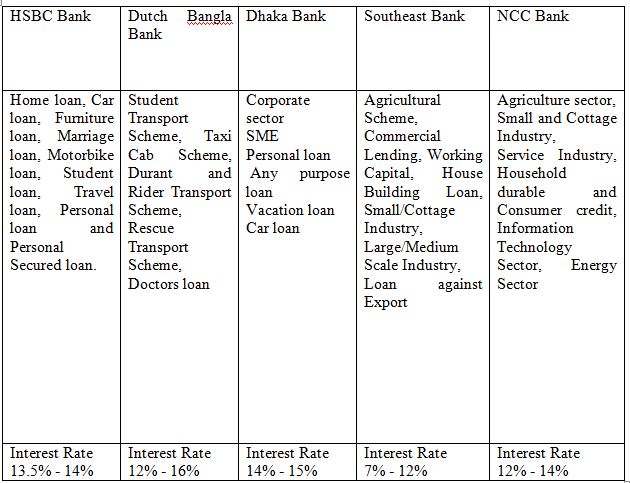
Bank Loans and Interest Rate:
Number of Branches:
| Types of Bank | Number of branches |
| Standard Chartered | 16 |
| Southeast Bank | 27 |
| HSBC Bank | 5 |
| Dhaka Bank | 33 |
| Social Investment Bank | 24 |
| Dutch Bangla Bank | 21 |
Some Competitors of Dhaka Bank:
- Brac Bank Limited.
- Southeast Bank Limited.
- Standard Chatered Bank Limited.
- The One Bank Limited.
- HSBC Bank Limited.
- AB Bank Limited.
- EXIM Bank Limited.
- The Oriental Bank Limited.
- National Bank Limited.
- Dutch Bangla Bank Limited.
- Marchentile Bank Limited.
- IFIC Bank Limited.
- Basic Bank Limited.
- Standard Bank Limited.
- Mutual Trust Bank Limited.
- Shahjala Bank Limited.
- Jamunna Bank Limited.
- Social investment Bank Limited.
- Bank Asia Limited.
Conclusions & Recommendation
The over all attempts in the assignment were to find out and to give a clear idea about the practical practice of strategic management in a company. In the assignment we tried out best to do so. For doing this job we have given details of the company and speech of the management about the strategic management. And presented a competitive scenery of the company.
By analysis the data we find that strategic management is not usually practiced formally in the organization but it is true elements or steps of strategic management are followed automatically and unconsciously in the company. We also find that only in the corporate level the strategic management process remain fixed. It is not usually changed but in the business and functional level strategy changed frequently. And it is so complex and important job for the company to survive in the competition.