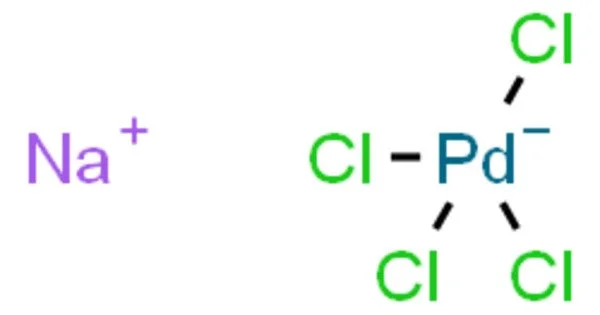Sodium tetrachloropalladate(II), also known as Na2PdCl4, is a chemical compound that consists of sodium cations (Na+) and tetrachloropalladate anions (PdCl4 2-). It is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Na2PdCl4. This salt, and the analogous alkali metal salts of the form M2PdCl4, may be prepared simply by reacting palladium(II) chloride with the appropriate alkali metal chloride in aqueous solution. It is a yellow to orange crystalline powder that is soluble in water and ethanol.
It is worth noting that Sodium Tetrachloropalladate is toxic and should be handled with care. Proper safety precautions should be taken when working with this compound.
Properties:
Sodium Tetrachloropalladate is a salt of palladium in its +2 oxidation state. It is hygroscopic, meaning it can absorb moisture from the air. It is a strong oxidizing agent and can oxidize certain organic compounds. It can be reduced to metallic palladium using reducing agents such as hydrazine or sodium borohydride. It is stable under normal conditions but can decompose at high temperatures or under strong acidic or basic conditions.
- Appearance: Yellow-orange crystalline powder
- Odor: Odorless
- Density: 2.32 g/cm³
- Melting point: Decomposes before melting
- Solubility: Soluble in water and ethanol
- pH: pH of a 0.1 M aqueous solution is around 7.5

Palladium(II) chloride is insoluble in water, whereas the product dissolves:
PdCl2 + 2 MCl → M2PdCl4
The compound crystallizes from water as trihydrate (Na2PdCl4·3H2O, reddish-brown powder with molar mass 348.22), which is the commercially available form. This compound may further react with phosphines to give phosphine complexes of palladium.
An alternative method of preparing such phosphine complexes is to break up the coordination polymer of palladium(II) chloride into reactive, monomeric acetonitrile or benzonitrile complexes, followed by reaction with phosphines.
Application
Sodium tetrachloropalladate is commonly used as a source of palladium in chemical reactions, particularly in organic synthesis. It can be used as a catalyst for a variety of reactions, including hydrogenation, oxidation, and coupling reactions.
However, it should be handled with care as it is toxic and can cause skin and eye irritation, respiratory problems, and other health hazards. It is also a hazardous waste and must be disposed of properly.