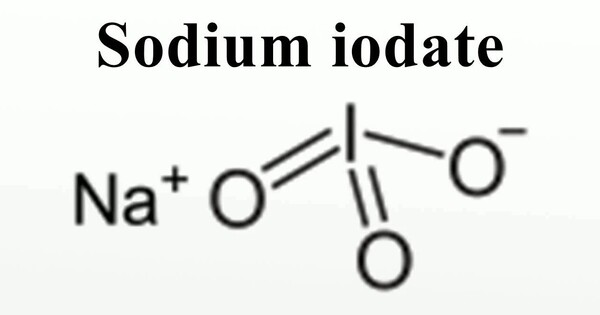
Sodium iodate (NaIO3) is the sodium salt of iodic acid. Sodium iodate is an oxidizing agent. It is a white, crystalline solid that is soluble in water. It has several uses. It is a versatile compound with important properties and various applications, particularly in chemistry and medicine. Its natural occurrence is limited, making synthetic production the primary source for its use.
It can be harmful if ingested or inhaled, and appropriate safety precautions should be taken when handling it, as it can cause irritation to the skin and eyes.
Preparation
It can be prepared by reacting a sodium-containing base such as sodium hydroxide with iodic acid, for example:
HIO3 + NaOH → NaIO3 + H2O
It can also be prepared by adding iodine to a hot, concentrated solution of sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate:
3 I2 + 6 NaOH → NaIO3 + 5 NaI + 3 H2O
Properties
- Chemical formula: INaO3
- Molar mass: 197.891 g·mol−1
- Appearance: White orthorhombic crystals
- Odor: Odorless
- Density: 4.28 g/cm3
- Melting point: 425 °C (797 °F; 698 K) (anhydrous)
- Solubility in water: 2.5 g/100 mL (0 °C), 32.59 g/100 mL (100 °C)
- Solubility: Soluble in acetic acid, Insoluble in alcohol
Reactions
Sodium iodate can be oxidized to sodium periodate in water solutions by hypochlorites or other strong oxidizing agents:
NaIO3 + NaOCl → NaIO4 + NaCl
Occurrences
- Natural Sources: Sodium iodate can be found in some natural mineral deposits, primarily in regions with volcanic activity. It may also occur in certain seawater concentrations.
- Manufacturing: It is primarily produced through the reaction of iodine with sodium hydroxide or by oxidizing iodine with chlorate salts.
Uses
The main use of sodium iodate in everyday life is in iodised salt. The other compounds which are used in iodised table salt are potassium iodate, potassium iodide, and sodium iodide. Sodium iodate comprises 15 to 50 mg per kilogram of applicable salt. It is also used as a dough conditioner to strengthen the dough.
- Analytical Chemistry: It is used as an analytical reagent and in iodometric titrations.
- Food Industry: Sodium iodate can be used as a source of iodine in animal feed and as a supplement in food.
- Medicinal Applications: It has been studied for its potential in treating iodine deficiency and other medical applications.
Safety
Iodates combined with organic compounds form an explosive mixture. It can be harmful if ingested or if it comes into contact with skin or eyes. It can cause irritation and should be handled with appropriate safety measures.