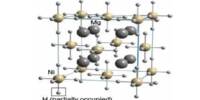
Sodium hydride is the chemical compound with the empirical formula NaH. It is an inorganic compound consisting of sodium and hydrogen. It’s a white, solid, ionic compound that is highly reactive, particularly with water, producing hydrogen gas and sodium hydroxide
This alkali metal hydride is primarily used as a strong yet combustible base in organic synthesis. NaH is a saline (salt-like) hydride, composed of Na+ and H− ions, in contrast to molecular hydrides such as borane, silane, germane, ammonia, and methane. It is an ionic material that is insoluble in all solvents (other than molten sodium metal), consistent with the fact that H− ions do not exist in solution.
Preparation
Industrially, NaH is prepared by introducing molten sodium into mineral oil with hydrogen at atmospheric pressure and mixed vigorously at ~8000 rpm. The reaction is especially rapid at 250−300 °C.
2 Na + H2 → 2 NaH
The resultant suspension of NaH in mineral oil is often directly used, such as in the production of diborane. It is a strong reducing agent and can react with acids, alcohols, and moisture. Its reactions with water and acids can be quite exothermic.
Properties
Sodium hydride is a white or yellowish crystalline solid at room temperature. It has a melting point of about 800 °C (1472 °F) and does not have a well-defined boiling point as it decomposes before boiling. It is insoluble in water and reacts vigorously with water to produce sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and hydrogen gas (H₂).
- Chemical formula: NaH
- Molar mass: 23.998 g/mol
- Appearance: white or grey solid
- Density: 1.39 g/cm3
- Melting point: 638 °C (1,180 °F; 911 K)(decomposes)
- Solubility in water: Reacts with water
- Solubility: insoluble in all solvents
Uses
- Strong Base: Often used as a strong base in organic chemistry, particularly for deprotonating weak acids.
- Reducing Agent: Used in the preparation of various organometallic compounds.
- Hydride Source: It can be a source of hydrogen in certain reactions.
Safety
Sodium hydride is highly flammable and can react violently with water. Proper safety precautions, including handling under inert atmospheres and wearing protective gear, are essential when working with it.