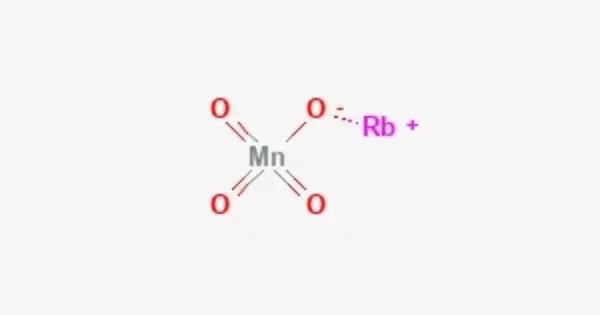
Rubidium permanganate is the permanganate salt of rubidium, with the chemical formula RbMnO4. It is an inorganic compound, belonging to the family of permanganates. It consists of rubidium cations (Rb⁺) and permanganate anions (MnO₄⁻), where manganese is in its highest oxidation state of +7. Like other permanganates, it is a strong oxidizing agent, capable of reacting vigorously with reducing agents and combustible materials.
In terms of stability, rubidium permanganate is sensitive to heat, shock, and contact with organic substances, which may trigger decomposition or even explosions. Its decomposition yields manganese dioxide (MnO₂), oxygen, and rubidium salts.
Preparation
Rubidium permanganate can be formed by the reaction of potassium permanganate and rubidium chloride:
RbCl + KMnO4 → KCl + RbMnO4 ↓
Properties
This compound typically appears as dark purple or nearly black crystalline solids, due to the intense color imparted by the permanganate ion. It is soluble in water, producing a deeply violet solution. It is chemically similar to potassium and sodium permanganates, though it is less commonly encountered because rubidium is a relatively rare and expensive alkali metal.
- Chemical formula: RbMnO4
- Molar mass: 204.404
- Appearance: purple crystals
- Density: 3.325 g·cm−3
- Melting point: 295 °C (decomposes)
- Solubility in water: 10.6 g·l−1 (19 °C)
Chemical
Similar to potassium permanganate, the two-step decomposition of rubidium permanganate leads to the formation of rubidium manganate intermediates. It breaks down into manganese dioxide, rubidium oxide and oxygen. The decomposition temperature is between 200 and 300 °C. Drift-away oxygen caused an 8% mass loss in the product.
10RbMnO4 → 3Rb2MnO4 + 7MnO2 + 2Rb2O + 6O2 ↑
2Rb2MnO4 → 2MnO2 + 2Rb2O + O2 ↑
Total reaction:
4RbMnO4 → 4MnO2 + 2Rb2O + 3O2 ↑
Occurrences
Rubidium permanganate does not occur naturally. It is synthesized in laboratories. Limited practical uses compared to potassium permanganate. It may be used in specialized chemical research, oxidation reactions, and as a reference compound in studying alkali permanganates.
Uses
In qualitative analysis, rubidium permanganate is used as a reagent to detect perchlorate ions. It is produced as an intermediate from rubidium nitrate and potassium permanganate and precipitates with existing perchlorate ions as RbClO4·RbMnO4 mixed crystal.
Practical uses are limited due to rubidium’s scarcity and cost, but in principle, it could serve in oxidation reactions, analytical chemistry, or specialized laboratory research where permanganates are needed. Naturally, it does not occur in the environment; instead, it is synthesized through chemical processes combining rubidium salts with permanganate precursors.