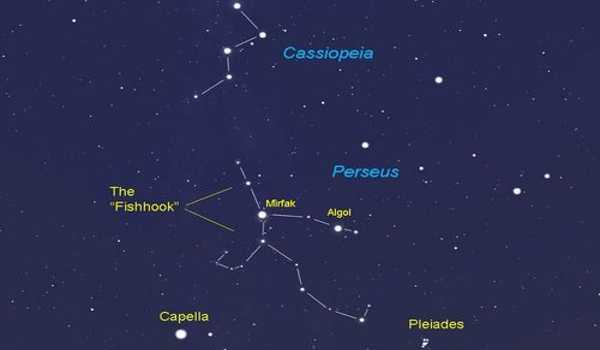
RS Persei is a red supergiant variable star in Perseus’ Double Cluster. It is a Supergiant Star with a high luminosity. The apparent magnitude of the star ranges from 7.82 to 10.0, indicating that it is never visible to the naked eye. It is not part of the Perseus constellation outline, but it is within its boundaries.
Because of our ever-changing atmosphere, all stars appear to twinkle. However, some people’s brightness does fluctuate. Variable stars appear to pulsate, either because they are in a binary system and their companion frequently eclipses them, or because the star itself periodically swells and shrinks, pulsating in brightness. Polaris, the north star known for being so constant, is itself a variable star.
RS Persei is a red supergiant variable star located in the Double Cluster in Perseus. It is a Supergiant Star with a high luminosity.
Location
RS Persei is a member of the NGC 884 cluster Persei, which is one-half of the famous Double Cluster.
Variability
RS Persei is classified as a semiregular variable star, with its brightness varying from magnitude 7.82 to 10.0 over 245 days. Extensive research has revealed that it also pulsates with a long secondary period of 4,200 ±1,500 days.
SRC variables are evolved stars (mostly M supergiants) whose brightness varies with semi-regular periods ranging from months to years. The variation in their light is caused by a combination of pulsation, convection, and other processes such as dust ejections. There is a wealth of data for the stars, but it is underutilized.
Properties
The temperature of RS Persei is 3,500 K, making it a large cool star. This makes it luminous, though the majority of its radiation is infrared. In 2005, it was calculated that RS Per has a bolometric luminosity of 145,000 L☉ and a radius of around 1,000 R☉. Based on the measured angular diameter and luminosity, 2014 calculations across all wavelengths give the star a lower luminosity of 77,600+9,5008,400 L☉ and a radius of 770±30 R☉.
Even more recent measurements based on its Gaia Data Release 2 parallax yield a luminosity of less than 40,000 L☉ and a radius of 491 R☉. It is surrounded by dust that has condensed from the star’s material loss.
Although RS Persei has been thought to be a highly evolved low mass Asymptotic Giant Branch (AGB) star, calculations of its current mass indicate that it is a low mass supergiant. NGC 244 is also too young to be home to AGB stars.