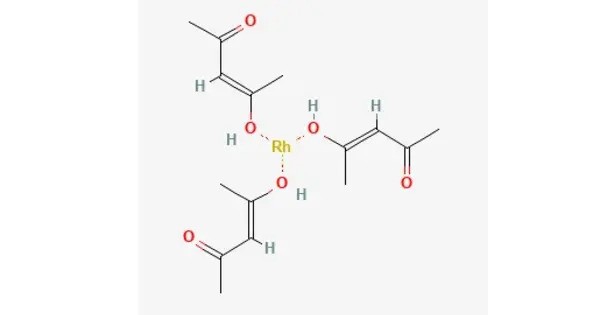
Rhodium acetylacetonate is the coordination complex with the formula Rh(C5H7O2)3, which is sometimes known as Rh(acac)3. It is soluble in organic solvents like acetone, ethanol, and dichloromethane. The molecule has D3-symmetry. It is a yellow-orange solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is generally stable under normal conditions, though it can be sensitive to moisture.
It is used in various catalytic processes, including hydrogenation and carbonylation reactions. It plays a role in producing thin films and in the synthesis of nanoparticles. It is useful in studies related to organometallic compounds due to its reactivity.
Preparation
It is prepared from RhCl3(H2O)3 and acetylacetone. The complex has been resolved into individual enantiomers by separation of its adduct with dibenzoyltartaric acid.
Properties
It usually appears as a colored crystalline solid, often exhibiting a reddish or brownish hue. It is soluble in organic solvents like dichloromethane, toluene, and ethanol but generally insoluble in water. It is relatively stable under standard conditions but can decompose at elevated temperatures or in the presence of strong acids or bases.
- Chemical formula: C15H21O6Rh
- Molar mass: 400.232 g·mol−1
- Appearance: orange solid
- Melting point: 260 °C (500 °F; 533 K) (decomposes)
Synthetic Production
Rhodium acetylacetonate is not commonly found in nature. Instead, it is synthesized in the laboratory from rhodium salts and acetylacetone.
Catalysis
It plays a significant role in catalytic processes, such as hydrogenation and hydroformylation, due to rhodium’s effectiveness as a catalyst in various chemical reactions.
Applications
It is often used as a precursor in various catalytic reactions, particularly in organic synthesis and the production of other rhodium-based compounds. In materials science and organometallic chemistry, it is studied for its unique properties and potential applications in electronics and photonics.