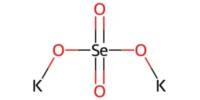
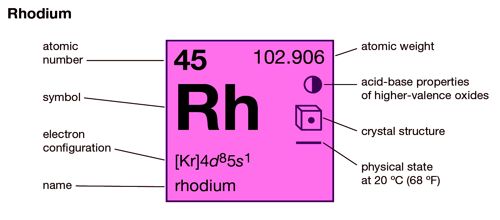
Rhodium is considered to be a precious metal. It is a chemical element with the symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is a precious, silver-white metal, with high reflectivity for light. It is an ultra-rare, silvery-white, hard, corrosion-resistant, and chemically inert transition metal. It is a rare element comprising up to 4.6 percent of native platinum alloys. It is a noble metal and a member of the platinum group.
Rhodium is generally obtained commercially as a by-product of the extraction of nickel and copper from their ores. It is a rare element comprising up to 4.6 percent of native platinum alloys.
The name rhodium comes from the Greek word “rhodon,” meaning rose, named for the rose-red color of its salts. It is found in platinum or nickel ores together with the other members of the platinum group metals. It was discovered in 1803 by William Hyde Wollaston in one such ore, and named for the rose color of one of its chlorine compounds. He discovered the metal in an ore that apparently came from South America.
Properties
Rhodium is a silver-white metal. It has a melting point of 1,966°C (3,571°F) and a boiling point of about 4,500°C (8,100°F). Its density is 12.41 grams per cubic centimeter. It is a relatively inactive metal. It is not attacked by strong acids. When heated in air, it combines slowly with oxygen.
- atomic number: 45
- atomic weight: 102.905
- melting point: 1,966° C (3,571°F)
- boiling point: 3,727° C (6,741°F)
- specific gravity: 12.4 (20°C)
- oxidation states: +1, +2, +3, +4, +5, +6
Occurrence
Rhodium is one of the rarest elements in the Earth’s crust, comprising an estimated 0.0002 parts per million (2 × 10-10). It occurs in nature in association with the other platinum metals, and its separation and refinement form part of the overall metallurgical processing of the group. Naturally-occurring rhodium is usually found as a free metal, as an alloy with similar metals, and rarely as a chemical compound in minerals such as bowieite and rhodplumsite. It is one of the rarest and most valuable precious metals.
Its rarity affects its price and its use in commercial applications. The concentration of rhodium in nickel meteorites is typically 1 part per billion. Rhodium has been measured in some potatoes with concentrations between 0.8 and 30 ppt.
Uses
Rhodium is generally obtained commercially as a by-product of the extraction of nickel and copper from their ores. It is used primarily to make alloys with other metals. These alloys are used for specialized industrial purposes and in jewelry. The metal is also used to produce reflecting surfaces for optical instruments.