Objective of the study:
The major objective of the study is
To comply with the entire branch banking procedures.
To make a bridge between the theories and practical procedures of banking day to day operations.
To understand the terms that has been taught in the Human resource department
To analyze the HRM practice of Pubali Bank Limited .
To identify the problem of HRM practice in pubali bank
To recommend some suggestion to solve the identified problem
The report is a prepared as pert of practical orientation of MBA program a description of all activities done by Pubali Bank, Principal Office. The report is lively narration of various banking activities like General Banking, loans and advance management and foreign trade financing and other ancillary services.
Significance of the study:
Federal and state laws have placed many new requirements concerning hiring and employment practices on employers. Jobs have also changed. They have become more technical and require employees with greater skills. Furthermore, job boundaries are becoming blurred. In the past, a worker performed a job in a specific department; working on particular job tasks with others who did similar jobs. Today’s workers are just as likely, however, to find them working on project teams with various people from across the organization. Others may do the majority of their work at home –and rarely see any of their coworkers. And, of course, global competition has increased the importance of organizations improving the productivity of their work force. This has resulted in the need for HRM specialists trained in psychology, sociology, organization and work design, and law. Federal legislation requires organizations to hire the best-qualified candidate without regard to race, religion, color, sex, disability, or national origin—and someone has to ensure that this is done. Employees need to be trained to function effectively within the organization—and again, someone has to Oversee this. Furthermore, once hired and trained, the organization has to provide for the continuing personal development of each employee. Practices are needed to ensure that these employees maintain their productive affiliation with the organization. The work environment must be structured to induce workers to say with the organization, while simultaneously attracting new applicants. Of course, the “someone’s” we refer to, those responsible for carrying out these activities, are human resource professionals. Today, professionals in the human resources area are important elements in the success of any organization. Their jobs require a new level of sophistication that is unprecedented in
human resource management. Not surprisingly, their status in the organization has also been elevated. Even the name has changed. Although the terms personal and human resource management are frequently used interchangeably, it is important to note that the two connote quite different aspects.
Once a single individual heading the personnel function, today the human resource department head may be a vice president sitting on executive boards, and participating in the development of the overall organizational strategy.
The real Benefited teams to this Human resource practice are as below
- Bank
- Students
- Researcher
- Country as a hole
For preparing this report that was assigned to the Pubali Bank Ltd.As an internee. During the internship period the collection of information from different sources.
I have used both qualitative and quantitative method for teaming up the data and information collected through primary and secondary sources. This study followed some methodology to find out the fact and feature of the Bank which are given as follows:
To conduct the study follows methodology were used
Such as : 01. Primary source and
02. Secondary source
Primary sources:
To collect the primary data were used a structured questionnaire and interview 30 officer 15excutive
Secondary sources:
It includes annual report, general report, investment manual, general, general banking manual, selected books, journals and other publication etc
Morris (1986) reported that :
Management Strategy and Employee relations
The research is focused on the response of the Bank to changes in the financial sector which has been experiencing deregulation, increasing competition, technological innovation and an increasingly discriminating public. It examines both changing business and employee relations strategies and the links between the two. As greater diversity begins to exist amongst the retail banks the study explores the Banks attempt to find itself a niche or adopt a focus strategy. This paper is primarily concerned with Human Resource issues. Changes in the nature of banking clearly have a knock-on effect on employee relations as banks move towards being more market driven organizations with a culture consistent with that, and with staff being regarded more as a resource than a cost
Historically, it has been the case that employee relations have been regarded as a “second order” strategy, purely facilitative and not fully integrated into overall business strategy. Hence, there was little consideration of unrest was such that labor was seen as a problem, as for instance in the car industry. Although there has been a gradual rise in the number of personnel professionals at Board level, these are still a minority. Lack of serious consideration of employee relations has also been said to owe something to the dominance of financial control at this level and the lack of union influence. Certainly many would argue that while senior, management do think about human resource issues, the degree of unpredictability in this area pushes it fairly well downstream in corporate planning. However, there are dangers of looking at HR issues in this way. The importance of ensuring the active co-operations of employees in industry has been emphasized control to one of commitment and this can be even more significant for the service sector. Thus in retail banking, the banks do not yet provide significantly different products and hence consumer choice is heavily influenced by convenience and image, the latter partly created by contract with quality of service and staff quality. Yet, in banking traditionally staff have not been recruited or developed for customer contract skills but for technical and administrative ability.
Torrington (1994) says that:
The recent emphasis on the human resource management, Torrington suggests that not only is the management of labor being given more attention, but that the issues discussed are broader and more strategic as well as tactical define strategic human resource management as “those decisions and actions which concern the management of employees at all level in the business and which are related to the implementation of strategies directed towards creating and sustaining competitive advantage. Thus, unlike the traditional peripheral function of many personnel managers, the newer style of human resource managers attempts to:
“Relate personnel practices to beliefs, to link each and every process of the recruitment, induction, training, appraisal rewarding of individuals to an overall set of articulated beliefs of organization”
Human resource management is seen as part of the movement away from concentration on unions and collective bargaining, to an emphasis on staff as individuals. Behind all is a belief that it will release greater commitment from employees although one has to be careful to examine the extent tonew equal partnership between employers and employed, or are then really offering a convert from of employee manipulation dressed up as mutuality.
One must be wary of evaluating HRM simply by the range of activity being undertaken. HRM is about both new processes new outcomes. The existence of the former does not guarantee the latter. Many initiatives may be no more than ‘flavor of the month’ changes; other may be opportunistic rather than strategic, taking advantage of slack labor markets; in many uses the gap between the rhetoric and the reality may be wide.
Batstone (1984) reported that
The banking sector has been characterized by apparently harmonious industrial relations and has not suffered from the “British diseases” of industrial action and demarcation issues associated with parts of manufacturing industry. Banks have promoted unitary encouraging an ethos of teamwork, shared interest and loyalty, wanting commitment beyond
the cash nexus. While banks are generally seen as having a passive approach
to employee relations, paternalism did underpin the system and particularly important was the system of internal promotion supported by an unwritten
agreement between the major UK banks on no poaching. The internal labor market created two categories of employees; career and non-career which equated to a male/female divide.
Retail banking is a highly labour intensive retail banking is a highly industry labour costs forming 70% of total operting expenditure and “involment in funds transmission meant that majority of clerical staff have not been used as a means of marketing the banks’ products nor directly for increasing business but to process existing accounts. They have accordingly been regarded as an overhead rather than a resource”(Morris,1986,p.22). until the 1980s competition between banks has been limited,banks operating as an oligopoly and government’s concern with maintaining economic stability with limits to lending, to the management of staff as national wage bargaining minimized competition for labour. However ,deregulation led to the collapse of the national system and a questioning of old employment practices.
Background:
The co-operative Bank is a wholly owned subsidiary of the co-operative Whole sale Society (CWS).the bank has a network of 90 branches and some 4,000 in-store banking points in co-operative stores. it has seen itself as an alternative force in uk banking and has a reputation for innovation. In banking products. While the history of the bank shows development away from the CWS(25years ago 90%of deposit came from movement and 10 % from other sources: the reverse is now the case) it remains the banker to the co-operative movement and as it’s chief Executive stated in the 1986 Annual Report,” our co-operative philosophy dictates that we approach the bank market in a fundamentally different way”.(see Wilkinson,1991).
The development of the bank’s policy on the management of people illustrates the move from the narrower re
structure of the study:
The research divided in chapter as follow:
1st chapter includes:
Introduction
Objective of the study
Significant of the study
Methodology of the study
Literature review
Structure of the study
2nd chapter includes:
Conceptual frame work
Introduction
Human Resources management
3rd chapter includes
An overview of Pubali bank
4th chapter includes
Findings & Analysis
5th chapter includes
Recommendation and conclusion
6th chapter includes
References
7th chapter includes
Appendix
Chapter 2
Conceptual frame work
Introduction:
In formulating the Human resource management, HR managers must address three basic challenges; the need support corporate productivity and performance improvement efforts; the fact that employees play an expanded role in the employer’s performance improvement efforts; and the fact that HR must be more involved in designing not just executing the company’s strategic plan.
There are six basic steps in the strategic management process ; Define the business and its mission perform an external and internal audits translate the mission into strategic goals; formulate a strategy to achieve the strategic goals; implement the strategy and evaluate the performance.
A strategy is a course of action. It shows how the enterprise will move from the business it is in now to the business it wants to be in, given its opportunities and threats and its internal strengths and weaknesses.
Strategic human resources management means formulating and executing HR systems that produce the employees competencies and behaviors the company requires to achieve its strategic aims
The high performance work system is designed to maximize the overall quality of human capital throughout the organization, and provides a set of benchmarks against which today’s HR manager can compare the structure, content, and efficiency and effectiveness of his or her HR system.
Human Resources Management:
Human Resources (HR):
Human resources (HR) are the people who are ready, willing, and able to contribute to an organizations success.
Human resources (HR): Hiring activities, including recruitment, interviewing, training, layoff planning, including out placement, and counseling.
Human resources (HR) segment contains the full set of capabilities needed to manager, schedule. Pay, and hire the people who make a company run. It includes payroll, benefits and administration, applicant data administration, personal development planning, workforce planning, schedule and shift planning, time management, and travel expense accounting.
Human Resources Management:
Human resources management is concerned with the people dimension in management. Every organization is made up of people acquiring their services developing their skills motivating them to high levels of performance and ensuring right people right time and right place.
Definition of Human Resource management:
(Randall s. schuter):
Different terms are used to describe the people who work in an organization employees, associates (Wal-Mart, for instance), personnel, human resources (HR).The term HR has gained widespread acceptance over the last decade because it expresses the belief that workers are a valuable and irreplaceable resources/asset
In simple term, Human Resource Management is about managing people in organizations.
Wright and McMahan says (1999)
“The pattern of planned human resource activities intended to enable an organization to achieve its goals”
Again, Miles and Snow says (1984)
“A human resource system that is tailored to the demands of the business strategy”
So, Human resource management is the process of acquiring, training, appraising, and compensating employees, and attending to their labor relations, health and safety, and fairness concerns.
A set of activities directed at an organization’s resources with the aim of achieving organizational goals in efficient and effective manner.
Functions of Human resource:
Human Resource Management is a process consisting of four functions, these are Staffing, Training & Development, Motivation, Maintenance .For a HR manager for maintaining an effective workforce it is necessary to know these functions.
Staffing: concerned with sourcing & hiring qualified employees.
The key areas of staffing are:
- Strategic Human Resource Planning: HRP help the organization to achieve the corporate goals by adopting and adjusting with changing situations for example rapid technological change
- Recruiting: The process of discovering potential job candidates by external & internal sources.
- Selection: Choosing the best incumbent for the organization.
Training & Development: concerned with assisting employees to develop up-to- date skills, knowledge & ability.
The major area of Training & Development is:
- Orientation: The activities involved in introducing new employees to the organization & their work units.
- Effective Training
- Employee Development: Future oriented training focusing on the personal growth of the employees.
- Carrier Development: The sequence of positions that a person has held over his/her life.
Motivation: Helping employees exert high energy level.
Some important factors of Motivation are:
- Motivational Theory & job Design.
- Performance Appraisal
- Rewards & Compensation
- Employee Benefits
- Discipline
- Maintenance: maintaining employee’s commitment & loyalty to the organization.
Maintenance consist of
- Safety & Health
- Employee/Labor Relations
- Communication
Feature of the HRM:
The activities that a company dopes to manage their human resources include—
Understanding the Environment internal environment; structure, size, business, strategy, technologies etc.
The Environment: External, Specific and General Environment
External environment-Outside institutions or forces that potentially affect an organization performance. It has two components- Specific and general
Enduring advantage will come from making better used people.
Specific environment- includes those external forces that have a direct and immediate impact on manager decisions and actions and directly relevant to the achievement of organizational goals. The main ones are customers, suppliers, competitors and pressure groups (like environmentalists, green parties, students unions etc.)
Managing Organizational and Human Resource changes: Such changes may include bending the culture of two newly merged companies, or successfully managing downsizing efforts
Staffing the organization: Staffing activities may include- analyzing the job, recruiting job candidates, selecting, selecting the most appropriate one.
Workforce Diversity: (varied backgrounds of employees) : managing people was considerably simpler fifty-years before because workforce was more or less homogenous (within as well as outside the national boundary). After 1960s minority and female workers started to rise in USA and accommodating their demands and needs have become vital responsibilities for managers. Until very recently, organizations took a melting-pot approach to differences in organizations. It was assumed that people who were different would somehow automatically want to assimilate. But today’s manager have found that employees do not set aside their cultural values and lifestyle preferences when they come to work. The challenge for the managers therefore, is to make concerted efforts to attract and maintain a diversified workforce, not only in USA but all over the world.
Evidence involves four factors:
- The person belong to a protected class
- The person applied for, and was qualified for, a job the employer was trying to fill
- The person was rejected despite being qualified
- The position remained open and the employer continued to seek applicants as qualified as the person rejected
More clearly, disparate impact occurs when the standard is applied to all applicants or employees, but that standard affects a protected class more negatively.
CHAPTER 3
An overview of Pubali bank
Bank Profile
History of Pubali Bank Limited
After liberation the Eastern mercantile bank was converted into Pubali Bank and was taken under the government management because the government policy was nationalized of all financial institutions. The objective was strengthening the rural economy. The result of the policy was a mixed one. In late 70s when the government wanted to establish a market oriented economy with less public sector role. As pert of the privatization and liberalization process this bank was denationalized in the year 1983. it started function as a public limited company Limited and registered as Pubali Bank Limited. All liabilities and asset of the bank is transferred to the limited company.
The bank was incorporated under the Companies Act (Act VII) of 1913 as a limited company having its Head Office in Dhaka. The Bank started functioning with the approval of Bangladesh Bank under the guidelines, rules and regulations given for scheduled commercial banks in Bangladesh.
Organization Structure of PBL
Pubali Bank Ltd expanded as a largest commercial bank in the country. Its operational networks cover almost every part of the country including the major cities, rural townships, which are prospective business centers in Bangladesh.
The bank was established primarily as private bank. After liberation it was nationalized and it remained so for quite a long period. Though it has been denationalized again and has gone back to its private norm it could not get rid of all the rules and norms of nationalized bank. The bank is run by an excellent management team under the direct supervision of a competent board of directors. The board of directors comprises total fourteen members headed by the chairman. Mr.E.A.Chaudhury is the present chairman of the board. The Managing Director (MD) heads management team. Under him a General Manager (GM) heads each department of the bank. Mr. Khondkar Ibrahim Khaled is the present MD of PBL. There are total twelve divisions in the Head Office of PBL. List of various divisions of PBL is given below:
- Boards of Directors
- Mr. E. A. Chaudhury
- Mr. Moniruddin Ahmed
- Mr. Sk. Wahidur Rahman
- Mr. Monzurur Rahman
- Mr. Giashuddin Ahamed
- Mr. M. A. Raquib
- Mr. Syed Moazzem Hussain
- Mr. Ahmed Shafi Chowdhury
- Mr. Fahim Ahmed Faruk Chowdhury
- Mr. Habibur Rahman
- Mr. Manir Ahmed
- Mr. Mohammed Yaqub
- Mr. Muhammad Faizur Rahman
Divisions of Head Office:
| Sl# | Division | Functions |
| 1. | Board & MD’s Secretariat Division | Deals with Shares |
| 2. | Human Resource Division | Recruitment, promotion, training, Disciplinary action, dismiss, discharge, retirement, pay and allowances, career plan, trade union etc. |
| 3. | Establishment division | Engineering, transport, telephone, telex, fax, security system, real estate etc. |
| 4. | Credit Division | All sorts of credit, its allocation, estimation, sanction, etc. |
| 5. | Credit Monitor and recovery Division | Monitoring of credit, classification, evaluation and recovery of credit etc. |
| 6. | International Division | All types of works with foreign banks or organizations. |
| 7. | Central Accounts Division | Correct accounts, financial evaluation and forecast of future financial events of the bank. |
| 8. | Branch Operation Division | Management of branches, control, monitoring and evaluation of performance of branches of the bank. |
| 9. | General Services & Develop Division | Looks for improvement services, sets strategy for business promotion and development of the bank. |
| 10. | Audit Division | Conduct internal audits of the branches. |
| 11. | Information Technology Division | Mainly looks after the computer system, provides necessary support to the branches in regards to computer and electronic equipments. |
| 12. | Lease Financing & Law Division | Deal with the lease financing and help the bank to move with its legal aspects. |
Divisions Of Head Office ( Organizational Structure ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Registered Head Office:
Pubali Bank Bhaban
26, Dilkusha Commercial Area
Dhaka – 1000, Bangladesh
Post Box No. 853
Cable: pubalipeak, Dhaka.
Telex: 675844 Pub BJ/632240 UCBL- H- O- BJ
Fax: 880-2-9564009
PABX: 9551614
Email: pubali@bdmail.net
Website: www.pubalibangla.com
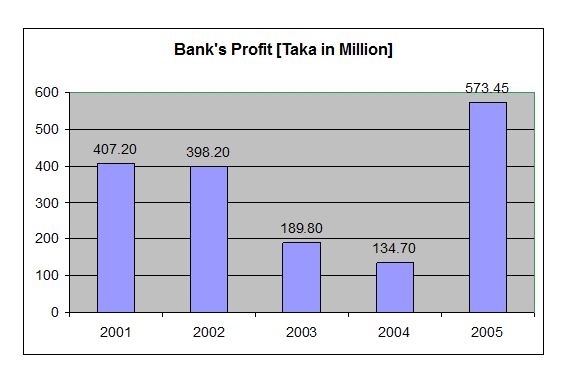
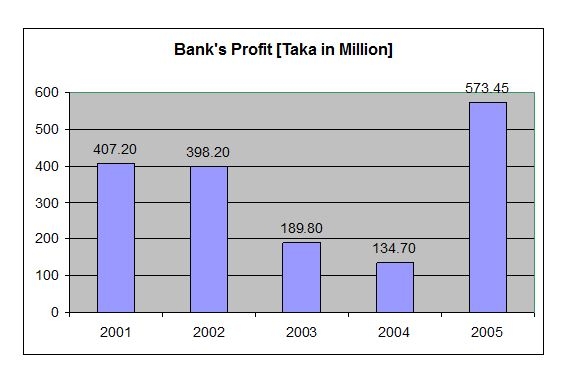
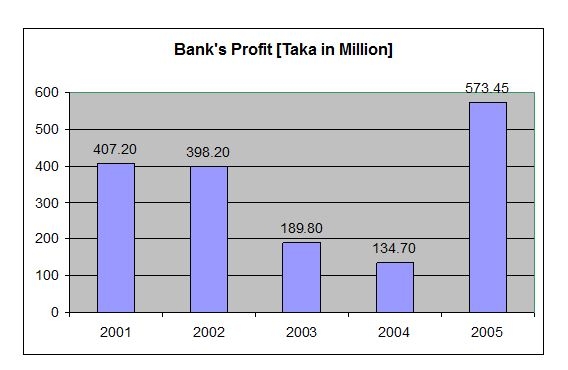
Financial Analysis of Information
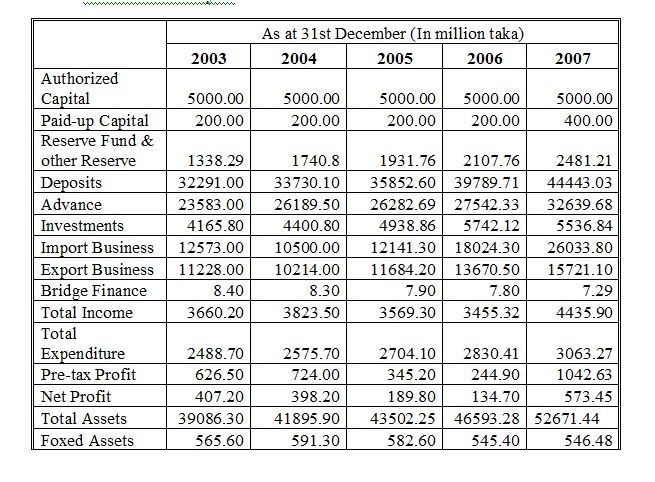
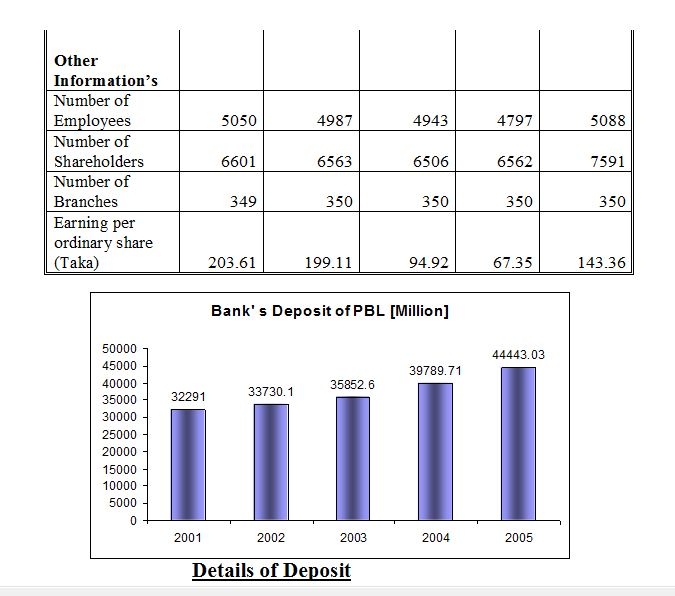
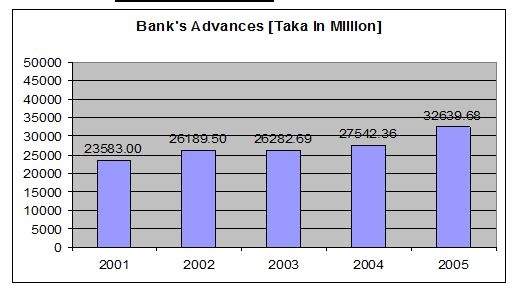
Details of advance
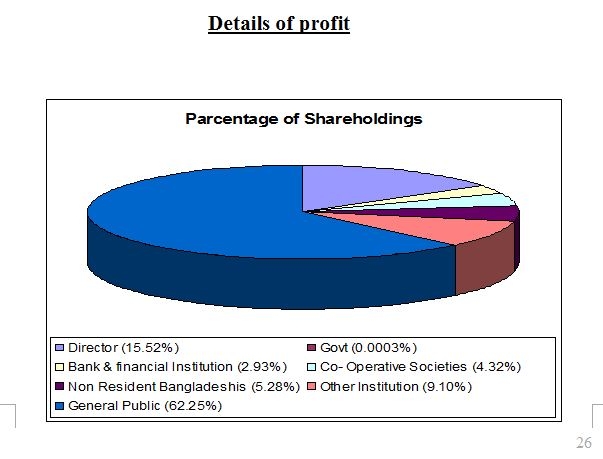
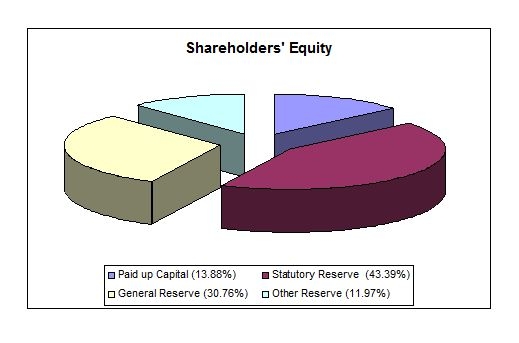
Details of shareholders:
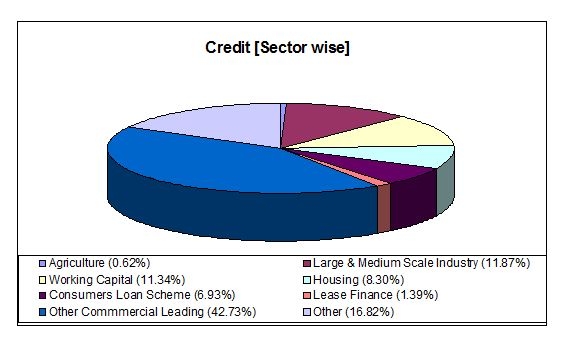
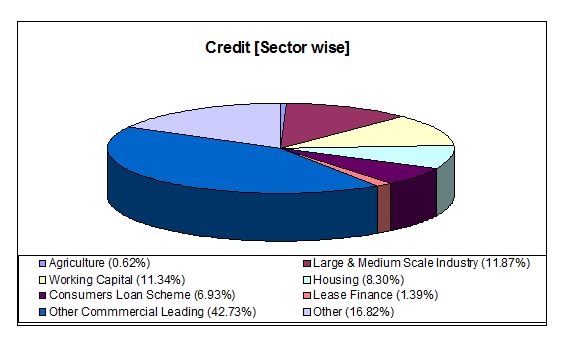
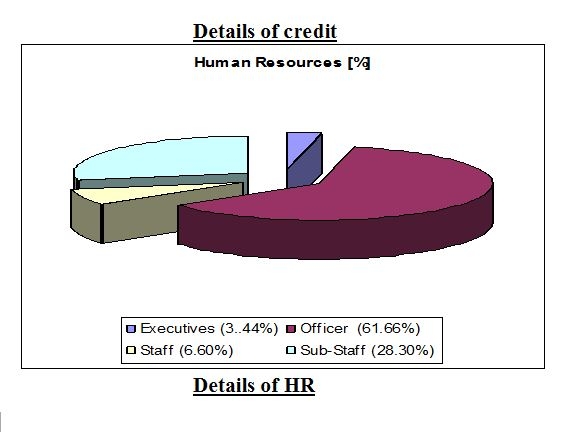

Branch Profile:
Location of Principal Branch
Principal Branch of Pubali Bank is situated in the ground floor of Pubali Bank Bhaban, 26 , Dilkusha C/A , Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh.. The office is highly decorated and it is the most important and busy branch maintaining all types of banking transactions. There 96 employees are working in this branch.
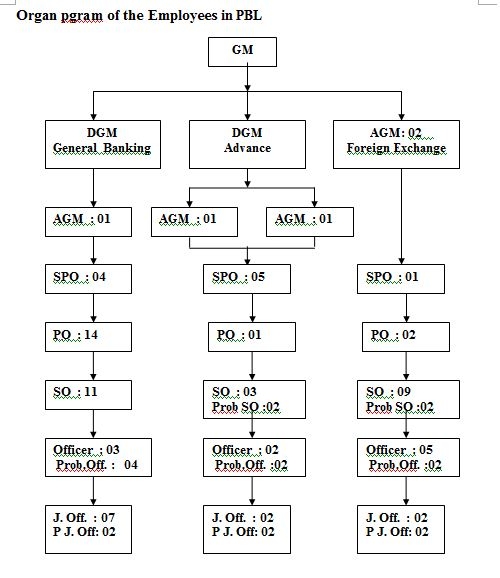
Distribution of Employees:
| DESIGNATION | NO |
| General Manager | 01 |
| Deputy General Manager (DGM) | 02 |
| Assistant General Manger (AGM) | 05 |
| Senior Principal Officer (SPO) | 10 |
| Principal Officer (PO) | 17 |
| Senior Officer (SO) | 23 |
| Officer | 10 |
| Junior Officer | 11 |
| Prob. Senior Officer | 04 |
| Prob. Officer | 08 |
| Prob. Junior Officer | 06 |
Branch Financial Position as on Date 27th October, 2008
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT IN TK. |
| Cash & Bank Balance | 337,30,85,825.99 |
| Loans and Advances | 850,51,24,720.18 |
| Deposit | 254,59,07,560.17 |
| Bills Payable | 4,59,40,870.48 |
| Bills Discounted & Purchase | 5,78,44,600.50 |
| Fixed Asset | 2,19,30,264.90 |
| Other Asset | 14,12,02,956.30 |
| Income | 82,89,01,879.59 |