3.2 EXPORT SECTION:
Foreign Exchange Regulation Act, 1947 nobody can export by post and otherwise than by post any goods either directly or indirectly to any place outside Bangladesh, unless a declaration is furnished by the exporter to the collector of customs or to such other person as the Bangladesh Bank (BB) may specify in this behalf that foreign exchange representing the full export value of the goods has been or will be disposed of in a manner and within a period specified by BB.
Bangladesh exports a large quantity of goods and services to foreign households. Readymade textile garments (both knitted and woven), Jute, Jute-made products, frozen shrimps, tea are the main goods that Bangladeshi exporters exports to foreign countries. Garments sector is the largest sector that exports the lion share of the country’s export. Bangladesh exports most of its readymade garments products to U.S.A and European Community (EC) countries. Bangladesh exports about 40% of its readymade garments products to U.S.A. Most of the exporters of BASIC Bank are readymade garment exporters. They open export L/Cs here to export their goods, which they open against the import L/Cs opened by their foreign importers.
SCRUTINY AND NEGOTIATION OF EXPORT BILL
Bank deals with documents not with goods. The bankers are to ascertain that the documents are strictly as per terms of L/C. Before negotiation of the export Bill the bankers are to scrutinize and examine each and every document’s with care. Negligence on the part of the bankers may result in non repatriation or delay in realization of export proceeds as incorrect documents may put the importers abroad into unnecessary troubles.
The scrutiny of the Bill of Exchange (Draft) and other related documents should ensure that.
- The documents are presented for negotiation before the expiry of the relative credit.
- The amount does not exceed the amount available under the credit.
- All the documents stipulated in the L/C are submitted.
- The corrections and alteration are properly authenticated in all documents.
Export documents checking:
1. General verification:
a) L/C restricted or not.
b) Exporter submitted documents before expiry date of the credit.
c) Shortage of documents etc.
2. Particular verification:
a) Each and every document should be verified with the L/C.
3. Cross verification:
a) Verified one documents to another.
While checking the export documents following things must be taken in consideration.
L/C terms:
Each and every clause in the L/C must be complied with meticulously and ensure the following:
1. That the documents are not state;
2. That the documents are negotiated within the L/C validity, It a credit expire on a recognized bank holiday its life is automatically become valid upto the next works day.
3. That the documents value does not exceeds the L/C value.
Draft/Bill of Exchange
Draft is too examined as under:
1. Draft must be dated
2. It must be made out in the name of the beneficiary’s bank or to be endorsed to the bank.
3. The negotiating bank must verify the signature of the drawer.
4. Amount must be tallied with the Invoice amount.
5. It must be marked as drawn under L/C No. dated issued by ……….. Bank.
Presentation of export documents for negotiation:
After shipment, exporter submits the following documents to BASIC Bank for negotiation.
- Bill of Exchange or Draft;
- Bill of Lading
- Invoice
- Insurance Policy/Certificate
- Certificate of origin
- Inspection Certificate
- Consular Invoice
- Packing List
- Quality Control Certificate
- G.S.P. certificate
3.3 Import:
Imports are foreign goods and services purchased by consumers, firms & Governments in Bangladesh. To import, a person should be competent to be a ‘importer’. According to Import and Export Control Act, 1950, the Office of Chief Controller of Import and Export provides the registration (IRC) to the importer.
BASIC Bank checks the documents. The usual documents are,-
i. Invoice
ii. Bill of lading
iii. Certificate of origin
iv. Packing list
v. Weight list
vi. Shipping advice
vii. Non-negotiable copy of bill of lading
viii. Bill of exchange
ix. Pre-shipment inspection report
x. Shipment certificate
Import Procedures:
1. Registration with CCI&E
- For engaging in international trade, every trader must be first registered with the Chief Controller of Import and Export.
- By paying specified registration fees and submitting necessary papers to the CCI&E. the trader will get IRC (Import Registration Certificate).After obtaining IRC, the person is eligible to import.
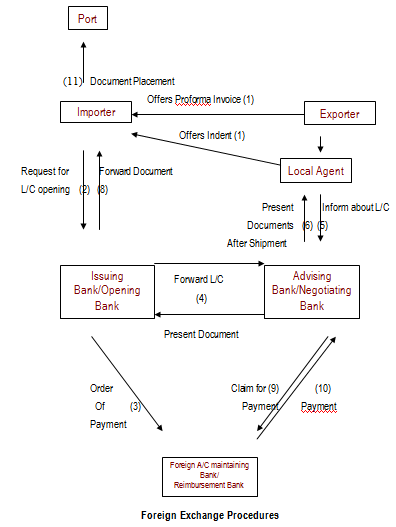
2. Purchase Contract between importers and exporter:
- Now the importer has to contact with the seller outside the country to obtain the proforma invoice / indent which describes goods.
- Indent is got through indenters a local agent of the sellers.
- After the importer accept the preformed invoice, he makes a purchase contract with the exporter declaring the terms and conditions of the import.
- Import procedure differs with different means of payment. In most cases import payment is made by the documentary letter of credit (L/C) in our country.
- Collection of LCA form:
Then the importer collects a Letter of Credit Authorization (LCA) form from BASIC Bank UTTARA Branch.
- Opening a Letter of Credit (L/C)
In international environment, buyers and sellers are often unknown to each other. So seller always seek guarantee for the payment for his goods exported. Here is the role of bank. Bank gives export guarantee that it will pay for the goods on behalf of the buyer. This guarantee is called Letter of Credit. Thus the contract between importer and exporter is given a legal shape by the banker by its ‘Letter of Credit’.
a. Parties of L/C
i. Importer – Seller who applies for opening an L/C.
ii. Issuing Bank – It is the bank which opens/issues a L/C on behalf of the importer.
- iii. Confirming Bank – It is the bank, which adds its confirmation to the credit and it, is done at the request of issuing bank. Confirming bank may or may not be advising bank.
iv. Advising / Notifying Bank – is the bank through which the L/C is advised to the exporters. This bank is actually situated in exporter’s country. It may also assume the role of confirming and / or negotiating bank depending upon the condition of the credit.
v. Negotiating Bank – is the bank, which negotiates the bill and pays the amount of the beneficiary. The advising bank and the negotiating bank may or may not be the same. Sometimes it can also be confirming bank.
vi. Paying / Accepting Bank – is the bank on which the bill will be drawn (as per condition of the credit). Usually it is the issuing bank.
vii. Reimbursing bank – is the bank, which would reimburse the negotiating bank after getting payment – instructions from issuing bank.
b. Application For L/C limit:
Before opening L/C, importer applies for L/C limit. To have an import L/C limit, an importer submits an application to the Department of BASIC Bank Limited furnishing the following information, –
i. Full particulars of bank account maintained with BASIC Bank Ltd. Uttara branch.
ii. Nature of business
iii. Required amount of limit
iv. Payment terms and conditions
v. Goods to be imported
vi. Offered security
vii. Repayment schedule
A credit Officer scrutinizes this application and accordingly prepares a proposal (CLP) and forwards it to the Head Office Credit Committee (HOCC). The Committee, if satisfied, sanctions the limit and returns back to the branch. Thus the importer is entitled for the limit.
c. The L/C Application:
After getting the proforma invoice importer applies to the bank to open a letter of credit on behalf of him with required papers.
i. Documentary Credit Application Form: BASIC Bank provides a printed form for opening of L/C to the importer. This form is known as Credit Application form. A special adhesive stamp is affixed on the form. While opening, the stamp is cancelled. Usually the importer expresses his desire to open the L/C quoting the amount of margin in percentage.
ii. Proforma Invoice: It states description of the goods including quantity, unit price etc.
iii. The insurance cover note: The name of issuing company and the insurance number are to be mentioned on it.
iv. The Letter of credit authorization (LCA) form: LCA form should be duly attested.
v. The Form-IMP.
vi. Tax Information Certificate
vii. Forwarding for Pre-Shipment Inspection (PSI): Importer sends forwarding letter to exporter for Pre-Shipment Inspection. But all types of goods do not require PSI.
Securitization of L/C Application:
The BASIC Bank Official scrutinizes the application in the following manner, –
- The terms and conditions of the L/C must be complied with UCPDC 600 and Exchange Control & Import Trade Regulation.
- Eligibility of the goods to be imported.
- The L/C must not be opened in favor of the importer.
- Radioactivity report in case of food item.
- Survey report or certificate in case of old machinery
- Carrying vessel is not of Israel or of Serbia- Montenegro
- Certificate declaring that the item is in operation not more than 5 years in case of car.
Examination of shipping documents:
One of the basic principles of documentary credit is that all parties deal with document and not with goods (Articles 6 of UCPDC-600). That is why the documents should be scrutinized properly. If any discrepancy in the documents is found, that is to be informed to the party. A checklist may be followed for examining the documents.
3.4 Major Discrepancies:
After proper examination or checking of a described Export document we may find following discrepancies:
GENERAL
- Late shipment
- Late presentation
- L/C expired
- L/C over-drawn
- Partial shipment or transshipment beyond L/C terms.
BILL OF EXCHANGE (B/E)
- Amount of B/E differ with Invoice.
- Not drawn on L/C issuing Bank.
- Not signed
- Tenor of B/E not identical with L/C.
- Full set not submitted.
COMMERCIAL INVOICE(C/I)
- Not issued by the Beneficiary.
- Not signed by the Beneficiary.
- Not made out in the name of the Applicant
- Description, Price, quantity, sales terms of the goods not corresponds to the Credit.
- Not marked one fold as Original.
- Shipping Mark differs with B/L & Packing List.
PACKING LIST
1) Gross Wt., Net Wt. & Measurement, Number of Cartoons/Packages differ with B/L.
2) Not market one fold as Original.
3) Not signed by the Beneficiary.
4) Shipping marks differ with B/L.
BILL OF LADING / AIRWAY BILL ETC (TRANSPORT DOCUMENTS)
- Full set of B/L not submitted.
- B/L is not drawn or endorsed to the Order of Prime Bank Ltd.
- “Shipped on Board”, “Freight Prepaid” or “Freight Collect” etc. notations are not marked on the B/L.
- B/L not indicate the name and the capacity of the party i.e. carrier or master, on whose behalf the agent is signing the B/L.
- Shipped on Board Notation not showing name of Pre-carriage vessel/intended vessel.
- Shipped on Board Notation not showing port of loading and vessel name ( In case B/L indicates a place of receipt or taking in charge different from the port of loading).
- Short Form B/L
- Charter party B/L
- Description of goods in B/L not agree with that of Invoice, B/E & P/L
- Alterations in B/L not authenticated.
- Loaded on Deck.
- B/L bearing clauses or notations expressly declaring defective condition of the goods and/or the packages.
OTHERS
- N.N. Documents not forwarded to buyers or forwarded beyond L/C terms.
- Inadequate number of Invoice, Packing List, B/L & Others submitted.
- Short shipment Certificate not submitted.
Invoice
It is to be scrutinized to ensure the following:
- The Invoice is addressed to the Importer
- The full description of merchandise must be given in the invoice strictly as per L/C.
- The price, quality, quantity, etc. must be as per L/C.
- The Invoice must be language in the language of L/C.
- No other charges are permissible in the Invoice beyond the stipulation on the L/C.
- The amount of draft and Invoice must be same and within the L/C value.
- If L/C calls for consular invoice, then the beneficiary’s invoice is not sufficient.
- Number of Invoice will be submitted as per L/C.
- The shipping mark and number of packing list shown in the B/L must be identical with those given in the Invoice and other documents.
- The Invoice value must not be less than the value declared in EXP Forms.
- Invoice amount must be correct on the basis of price, quantity as per L/C.
- Invoice amount, indicate sale terms/ Income terms VIZ FOB, CFR, CIF etc.
- Consular Invoice must be stamped by the local consulate/embassy of the country to which the goods are imported.
OTHER DOCUMENTS
Beneficiary statement, VISA/Export License issued by EPB, Certificate of Origin, Weight Certificate, Packing List, Inspection Certificate.
Certificate of analysis, quality certificate, MCD duly signed and any other documents required by L/C each of these certificates/documents conform to the goods invoice and are relevant to L/C.
Negotiating Bank will check the above documents whether it is as per L/C or not. If Negotiating Bank find everything in order or as per export L/C, bank will negotiate the document and will disburse the generated fund as per Banks norms.
If the Negotiating Bank will find any discrepancies in the documents. They will send the documents on collection or they can negotiate under reserve by the request of the exporter or they can seek permission/Negotiation authority from issuing Bank to allow Negotiating Bank to negotiate the documents despite the discrepancies. L/C issuing Bank will inform the matter to buyer, if the buyer accept the discrepancies mentioned by Negotiating Bank, issuing bank will authorize the Negotiating bank to negotiate the discrepant documents.
COLLECTION DOCUMENTS
Normally negotiating Bank will send the documents on collection basis mainly for the following discrepancies.
- L/C expired;
- Late shipment;
- Late presentation;
- L/C overdrawn;
- Unit price differ between L/C and Commercial Invoice;
- Consignee Name and address differ between L/C and other documents.
- Discrepancies in B/L;
- Any other Major discrepancies.
3.5 FOREIGN REMITTANCE SECTION
The basic function of this department are outward and inward remittance of foreign exchange from one country to another country. In the process of providing this remittance service, it sells and buys foreign currency. The conversion of one currency into another takes place at an agreed rate of exchange, in where the banker quotes, one for buying and another for selling. In such transactions the foreign currencies are like any other commodities offered for sales and purchase, the cost (convention value) being paid by the buyer in home currency, the legal tender.
Workings of this department:
- Overall supervision of Foreign Remit. Dept.
- Foreign TT payment & Purchase of F. Drafts, preparations of F.B.P. (Foreign Bill Purchased).
- Issuance of outward TT & FDD.
- Issuance of proceed responding certificate (PRC).
- Foreign Collection, Bangladesh Bank Clearing Check Collection, which comes from all branch of BASIC Bank Limited.
- Withdrawal from F.C. A/C.
- Encashment of T.C. & Cash Dollar and Sterling Pound.
- Deduction of Tax and VAT. On behalf of Bangladesh Bank.
- Preparation of related statements including convertible Taka Accounts.
- Preparation of IBCA & IBDA and Balancing of Collection and other special assignment as desired by Department in charge.
- Balancing of Account Statements.
- Compliance of audit & inspection.
- Statement of all related works submitted to Bangladesh Bank.
Inward Foreign Remittance:
Inward remittance covers purchase of foreign currency in the form of foreign T.T., D.D, T.C. and bills etc. sent from abroad favoring a beneficiary in Bangladesh. Purchase of foreign exchange is to be reported to Exchange control Department of Bangladesh bank on Form-C.
Outward Foreign Remittance:
Outward remittance covers sales of foreign currency through issuing foreign T.T. Drafts, Travelers Check etc. as well as sell of foreign exchange under L/C and against import bills retired. Sale of foreign exchange is reported to Exchange control Department of Bangladesh Bank on form T/M.
Foreign exchange means foreign currency and includes all deposits, credits and balances payable in foreign currency as well as foreign currency instruments such as Drafts, T.C.s, bill of exchange, and Letters of Credit Payable in any Foreign Currency. All foreign exchange transactions in Bangladesh are subject to exchange control regulation of Bangladesh Bank.
Foreign Remittance Department deals with the following instruments:
| Cash Remittance (Dollar/ Pound) | Sell | Bank sells Dollar/Pound for using in abroad by the purchaser. The maximum amount of such sell is mentioned in the Bangladesh Bank publication of ‘Convertibility of Taka for Currency Transactions in Bangladesh. |
| Purchase | Bank can purchase dollar from resident and non – resident Bangladeshi and Foreigner. Most dollars purchased comes from realization of Export Bill of Exchange. | |
| Telex Transfer | Outward TT | It remits fund by tested TT via its foreign correspondence bank in which it is maintaining its NOSTRO Account. |
| Incoming TT | It also makes payment according to telegraphic message of its foreign correspondence bank from the corresponding VOSTRO Account. | |
|
Foreign Demand Draft
Foreign Demand Draft | Bank issue Demand Draft in favor of purchaser or any other according to instruction of purchaser. The payee can collect it for the drawee bank in which the Issuing bank of Demand Draft holds its NOSTRO Account. Bank also makes payment on DD drawn on this bank by its foreign correspondence bank through the VOSTRO Account. The procedure concerning issue of FDD is same as issue of Travelers check except that the customer is not required to submit his passport.
Following steps to be followed in payment of FDD:
| |
Figure : 3 Foreign Exchange Procedures as following:
Cash Remittance
(Dollar/ Pound)SellBank sells Dollar/Pound for using in abroad by the purchaser. The maximum amount of such sell is mentioned in the Bangladesh Bank publication of ‘Convertibility of Taka for Currency Transactions in Bangladesh.PurchaseBank can purchase dollar from resident and non – resident Bangladeshi and Foreigner. Most dollars purchased comes from realization of Export Bill of Exchange.
Telex TransferOutward TTIt remits fund by tested TT via its foreign correspondence bank in which it is maintaining its NOSTRO Account.Incoming TTIt also makes payment according to telegraphic message of its foreign correspondence bank from the corresponding VOSTRO Account.
Foreign Demand Draft
Bank issue Demand Draft in favor of purchaser or any other according to instruction of purchaser. The payee can collect it for the drawee bank in which the Issuing bank of Demand Draft holds its NOSTRO Account. Bank also makes payment on DD drawn on this bank by its foreign correspondence bank through the VOSTRO Account. The procedure concerning issue of FDD is same as issue of Travelers check except that the customer is not required to submit his passport.
Following steps to be followed in payment of FDD:
- At first the FDD is to be crossed.
- Serial number is given.
- Forwarding letter to the bank with which the bank has agreement.
- Party is given the cash or his account is credited.
Some More Parts-
Report on Basic Bank Limited (Part-1)