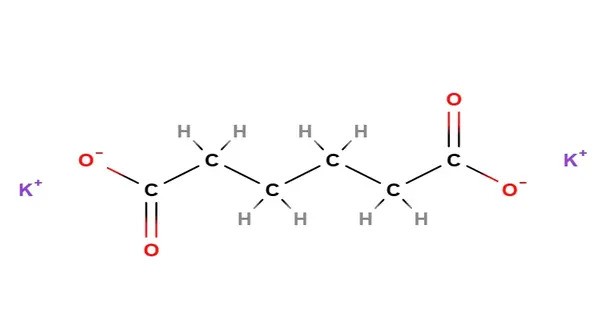
Potassium adipate is a compound with formula K2C6H8O4. It is the dipotassium salt of adipic acid, a naturally occurring acid found in beets and sugar cane. It is a potassium salt and common source ingredient of adipic acid. It functions as an acidity regulator, firming agent, and flavor enhancer in baked goods, beer, and jams. It has E number E357.
Potassium adipate is metabolized or excreted by the body, with no known side effects in moderation. However, concerns exist about its synthetic production using petroleum hexanes, potentially linked to teratogenic effects, though evidence is limited. It is considered safe for all dietary groups, including vegans and religious diets, provided it’s not derived from pork fat (Haram). Industrially, it’s used in plastics, antacids, and fertilizers.
Properties
With a molecular weight of 222.32 g/mol, it appears as white, odorless crystals or powder, soluble in water (60 g/100 ml at 20°C). It is primarily used as a food additive (E357) to regulate acidity in products like herbal salts, desserts, and beverages, with an acceptable daily intake of 0-5 mg/kg body weight.
- Chemical formula: K2C6H8O4
- Molar mass: 222.322 g/mol
- CAS Number: 19147-16-1wikidata.org
- Appearance: White, odorless crystals or crystalline powderatamanchemicals.com
- Melting Point: 151–152 °Catamanchemicals.com
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water, approximately 60 g/100 ml at 20 °C
- Stability: Stable under normal conditions but may be combustible at high temperatures. It is reactive with oxidizing agents and sensitive to excess heat, dust, and moisture
- E Number: E357
Safety and Toxicity
Generally considered safe with no known side effects within the ADI. It is suitable for all religious groups, vegans, and vegetarians. However, some sources suggest adipic acid (its parent compound) may have teratogenic properties (potential to cause congenital deformities), though evidence is limited and not specific to potassium adipate. One source claims carcinogenic potential for adipates, but this lacks corroboration from authoritative bodies like JECFA.atamanchemicals.comfood-detektiv.deatamanchemicals.com
Natural Occurrence
The adipic acid component is naturally present in beets and sugarcane juice, but potassium adipate itself is synthetically produced for commercial use.atamanchemicals.comatamanchemicals.com
Food Industry
Used as an acidity regulator (E357) in low-sodium herbal salts, beverage powders, pudding mixes, fruit-flavored or jelly-like desserts (up to 6 g/kg), baking powder, beer, jams, ice blocks, and margarine. It also functions as a firming and raising agent in some applications.atamanchemicals.cominfocons.orgwotzinurfood.com
Medical Applications
Employed as an electrolyte replenisher for treating hypokalemia (low potassium levels), particularly in cases related to diuretic therapy, digitalis intoxication, or hypokalemic familial periodic paralysis.atamanchemicals.comwotzinurfood.com
Other Uses
Utilized in buffer solutions, fertilizers, and explosives due to its chemical stability and solubility. It is also used in the production of plastics, including PVC, and in antacids (despite its acidic nature).atamanchemicals.comatamanchemicals.comwotzinurfood.com
Safety
- Side Effects: No significant side effects are reported within the ADI. Excessive potassium intake (e.g., >18 g at once) can lead to hyperkalemia, causing tissue damage, blood cell rupture, kidney issues, or heart arrhythmia, but this is unlikely with normal dietary use of potassium adipate.wotzinurfood.com
- Environmental Impact: Adipates may contribute to water, air, and soil contamination when derived from industrial waste or incineration, and they are difficult to decompose. However, this is not specific to potassium adipate and requires further validation.