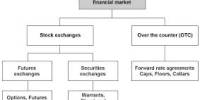
Arbitrage allows investors to profit from an imbalance in the price of a security or asset. Political arbitrage is a trading strategy that involves using knowledge or estimates of future political activity to forecast and discount security values. This arbitrage can be country- or region-specific and is considered unethical since legal trading must be based on publicly available information. It is a type of arbitrage activity that involves trading securities based on knowledge of the potential future political activity. For example, the major factor in the values of some foreign government bonds is the risk of default, which is a political decision taken by the country’s government. Before investing in one, it is crucial to understand how they work and if they make sense for your portfolio.
An arbitrage activity that includes trading securities based on knowledge of the prospective future political activity. A common instance where political arbitrage might take place is ahead of a general election. It may be country-specific or region-specific, depending on the type of political activity. The values of companies in war-sensitive sectors such as oil and arms are affected by political decisions to make war. For example, the primary factor in the values of foreign government bonds is the risk of default, which is a political decision taken by a country’s government. Although arbitrage funds are relatively low risk, the payoff can be unpredictable.
Arbitrage provides a mechanism to ensure prices do not deviate substantially from fair value for long periods of time. Political arbitrage refers to trading activity that involves trading securities based on knowledge or estimates of future political activity. Legal trading must be based on publicly available information. However, there is a grey area involving lobbyists and market rumors. In the event of impending government elections, political arbitrage is likely to be specific to that nation only, whilst the threat of war in particular regions may trigger political arbitrage to occur across a much larger region. Like insider trading, there is scope for conflicts of interest when political decision-makers themselves are in positions to profit from private investments whose values are linked to their own public political actions.