Plutonium silicide is a binary inorganic compound of plutonium and silicon with the chemical formula PuSi. The compound forms gray crystals. It is a compound of plutonium and silicon. The compound has good thermal stability and conductivity, which are important for maintaining the integrity of the fuel under the extreme conditions present in a reactor. Its ability to absorb neutrons makes it suitable for radiation shielding applications in nuclear facilities.
Properties
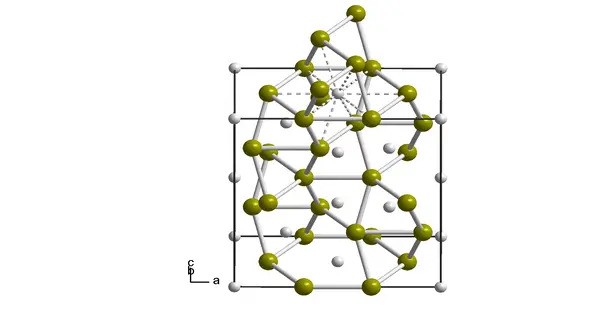
Plutonium silicide forms gray crystals of orthorhombic crystal system, space group Pnma, cell parameters: a = 0.7933 nm, b = 0.3847 nm, c = 0.5727 nm, Z = 4, TiSi type structure.
At a temperature of 72 K, plutonium silicide undergoes a ferromagnetic transition.
- Chemical formula: PuSi
- Molar mass: 272.09 g/mol
- Appearance: Grey crystals
- Density: 10.15
- Melting point: 1,576 °C (2,869 °F; 1,849 K)
- Solubility in water: insoluble
Nuclear Fuel
Plutonium silicide is considered for use as a nuclear fuel. It has favorable properties such as high thermal conductivity and a high melting point, which make it an attractive material for advanced nuclear reactors.
Applications
Plutonium, being a fissile material, is a critical component in nuclear reactors. The use of silicides can potentially improve the neutron economy of the reactor, making it more efficient.
Studies on plutonium silicide involve understanding its phase behavior, compatibility with other materials, and performance under irradiation. This research is crucial for developing safer and more efficient nuclear fuel systems.
Safety and Handling
Working with plutonium compounds requires stringent safety protocols due to the radioactive nature of plutonium. Specialized facilities and equipment are needed to handle and study these materials safely.
Due to the hazardous nature of plutonium and the complex challenges associated with its use, research and development in this area are typically conducted in highly specialized laboratories with appropriate safety measures in place.