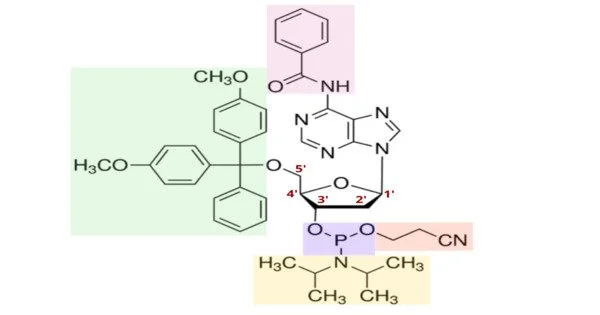
A phosphoramidite (RO)2PNR2 is a phosphite diester monoamide. It’s a chemical substance that’s commonly employed in the production of DNA and RNA. The main property of phosphoramidites is their extremely high reactivity to nucleophiles catalyzed by weak acids such as triethylammonium chloride or 1H-tetrazole. The entering nucleophile replaces the NR2 moiety in these reactions. It is a critical component of the solid-phase DNA synthesis process, which is used to generate synthetic DNA sequences for a variety of purposes such as molecular biology research, genetic engineering, and diagnostic testing.
A phosphoramidite molecule’s general structure consists of a nucleoside base (adenine, cytosine, guanine, or thymine/uracil) coupled to a deoxyribose or ribose sugar via a phosphate group. This phosphate group is changed to incorporate an amidite moiety, allowing the phosphoramidite to be added to the developing DNA chain in a controlled manner.
Applications
Phosphoramidites are generally utilized in automated DNA synthesizers, where they are introduced to a developing DNA chain one at a time. To guarantee that the right sequence of nucleotides is constructed, particular chemical groups on the nucleotide bases are protected and deprotected. Phosphoramidite chemistry allows for the precise insertion of individual nucleotides, making it an indispensable tool in biotechnology and molecular biology.
- Nucleoside phosphoramidites
Phosphoramidites derived from protected nucleosides are referred to as nucleoside phosphoramidites and are widely used in chemical synthesis of DNA, RNA, and other nucleic acids and their analogs.
- As ligands
In asymmetric synthesis, certain phosphoramidites are also utilized as monodentate chiral ligands. A substantial number of these ligands are obtained from the chiral diol BINOL and can be synthesized by reacting BINOL with phosphorus trichloride to form chlorophosphite and then reacting it with simple secondary amines. This ligand was originally employed in an asymmetric copper-catalyzed addition of dialkylzincs to enones in 1996.
In conclusion, phosphoramidites are essential components in the chemical synthesis of DNA and RNA, allowing researchers to generate custom-designed genetic sequences for a variety of applications in biology and biotechnology.