Nickel selenide is the inorganic compound with the formula NiSe. As for many metal chalcogenides, the phase diagram for nickel(II) selenide is complicated. It is a semiconductor material with significant interest in various scientific and industrial fields, including electronics, energy storage, and catalysis.
This material is a semi-conducting solid, and can be obtained as in the form of a black fine powder, or silver if obtained in the form of larger crystals. Nickel(II) selenide is insoluble in all solvents, but can be degraded by strongly oxidizing acids.
Properties
Nickel selenide typically appears as a black or dark gray solid. It is insoluble in water but soluble in acids like hydrochloric acid. It is a semiconductor, and its electrical conductivity is sensitive to factors such as temperature and the presence of dopants.
- Chemical formula: NiSe
- Molar mass: 137.65 g/mol
- Appearance: black powder
- Density: 7.2 g/cm3
- Solubility in water: Insoluble
Synthesis and structure
Typically, NiSe is prepared by high temperature reaction of the elements. Such reactions typically afford mixed phase products. Milder methods have also been described using more specialised techniques such as reactions of the elements in liquid ammonia in a pressure vessel.
It can be synthesized through various methods, including:
- Solid-State Reaction: Combining nickel salts with selenium compounds at high temperatures.
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Deposition of NiSe thin films onto substrates from gaseous precursors.
- Electrochemical Methods: Electro-deposition of nickel selenide onto electrodes.
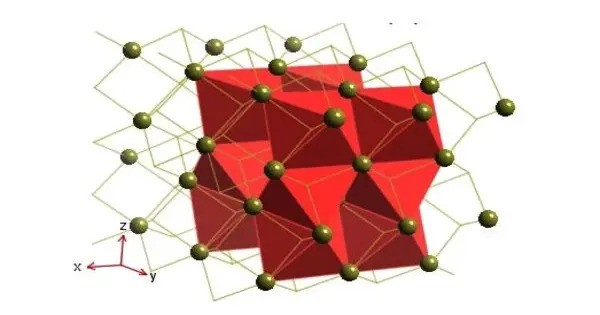
Like many related materials, nickel(II) selenide adopts the nickel arsenide motif. In this structure, nickel is octahedral and the selenides are in trigonal prismatic sites.
Industrial Applications
- Battery Technology: NiSe is being explored in battery technology, especially in lithium-ion and nickel-cadmium batteries, where its properties as a semiconductor and potential to store charge make it useful.
- Solar Cells: It is also considered for use in solar cells and other devices that require semiconductor materials with specific electrical and optical properties.
Safety Considerations
While nickel selenide is not typically considered highly toxic, both nickel and selenium compounds can be harmful in certain forms. Proper handling, including wearing gloves and protective gear, is important when working with this material, especially in its powder or vaporized form.