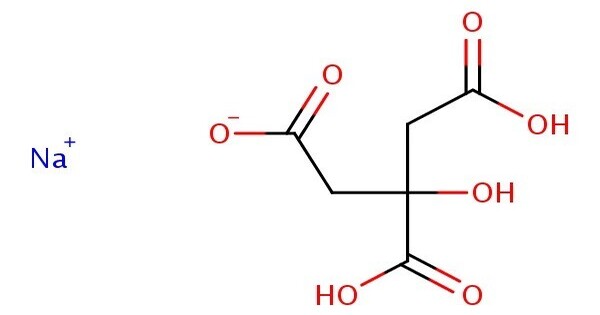
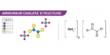
Monosodium citrate, more correctly, sodium dihydrogen citrate, is an acid salt of citric acid. It is a sodium salt of citric acid. Disodium citrate and trisodium citrate are also known. It is commonly used in food, pharmaceuticals, and biochemical applications.
It can be prepared by partial neutralisation of citric acid with an aqueous solution of sodium bicarbonate or carbonate. It has a slightly acidic taste.
NaHCO3 + C6H8O7 → NaC6H7O7 + CO2 + H2O
Na2CO3 + 2C6H8O7 → 2NaC6H7O7 + CO2 + H2O
It is highly soluble in water and practically insoluble in ethanol. Monosodium citrate is used as an anticoagulant in donated blood. It is used as an alkalinizing agent to prevent kidney stone disease. The crystals form as nearly perfect cubes.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C6H7NaO7
- Molar mass: 214.105 g·mol−1
- Appearance: white powder, hygroscopic
- Odor: odorless
- Melting point: 212 °C (414 °F; 485 K)
- Boiling point: 309.6 °C (589.3 °F; 582.8 K)
- Solubility in water: soluble
- Solubility: negligible in ethanol
Chemical Structure
Monosodium citrate is derived from citric acid (C₆H₈O₇) by replacing one of its three acidic hydrogen atoms with a sodium ion.
Occurrence
Monosodium citrate does not occur naturally in large amounts but is synthesized for industrial use. It is widely used in:
- Food Industry – As a buffering agent, preservative, or acidity regulator
- Pharmaceuticals – In antacids and urinary alkalinizers. Helps adjust pH in oral rehydration salts (ORS)
- Biochemical applications – Used in buffers for biological or chemical reactions. Chelates metal ions, helping stabilize certain formulations
Applications
- Food Industry – Food additive (E331) – as an acidity regulator, flavoring agent, and preservative. Common in processed cheese, jellies, soft drinks, and ice creams.
- Pharmaceuticals – Used as a buffering agent in medicinal syrups and effervescent tablets. Acts as an anticoagulant in blood collection tubes (prevents clotting by chelating calcium).
- Industrial Applications – Used in detergents and cleaning agents for its chelating properties. Functions as a pH regulator in various formulations.